This is a continuation of a nerdy technical series with Predicting Conditions from PubMed Studies earlier. I continue using depression as my canary. We use two data sets from two different retail providers: Ombre Labs (USA) and Biomesight (UK).
Means, T-Scores – Walking Two Paths
There are two paths available, with no clear best choice:
- Compare averages from samples that reported some amount (thus excluding zero values)
- Lower degree of freedom and thus T-Scores
- Compare averages from samples with a zero being used when an item is not reported.
- Higher degrees of freedom and higher T-Scores
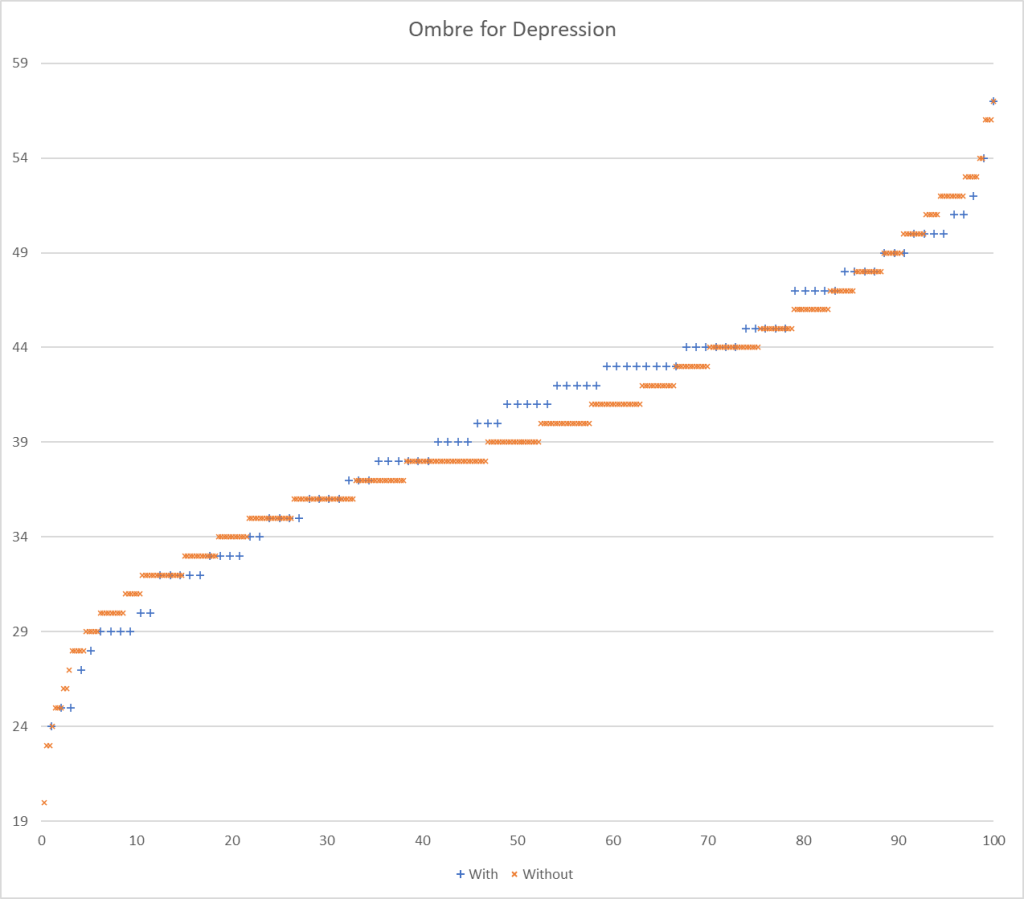
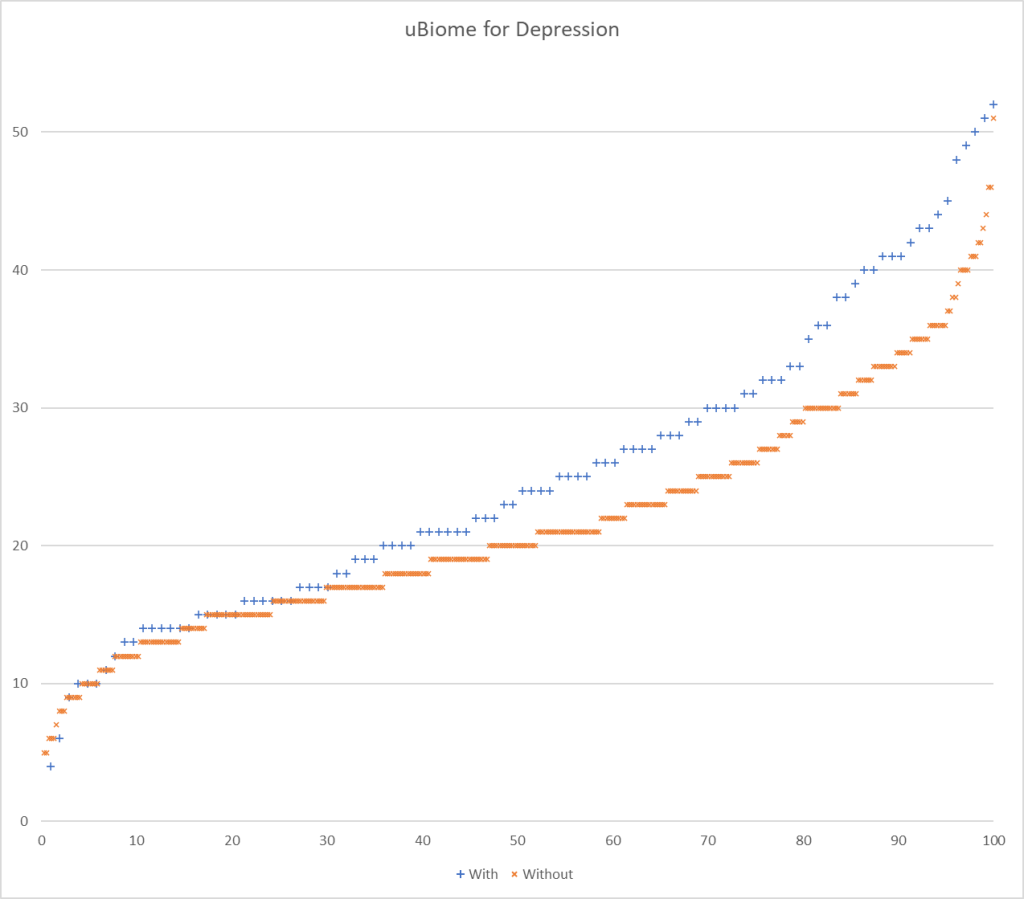
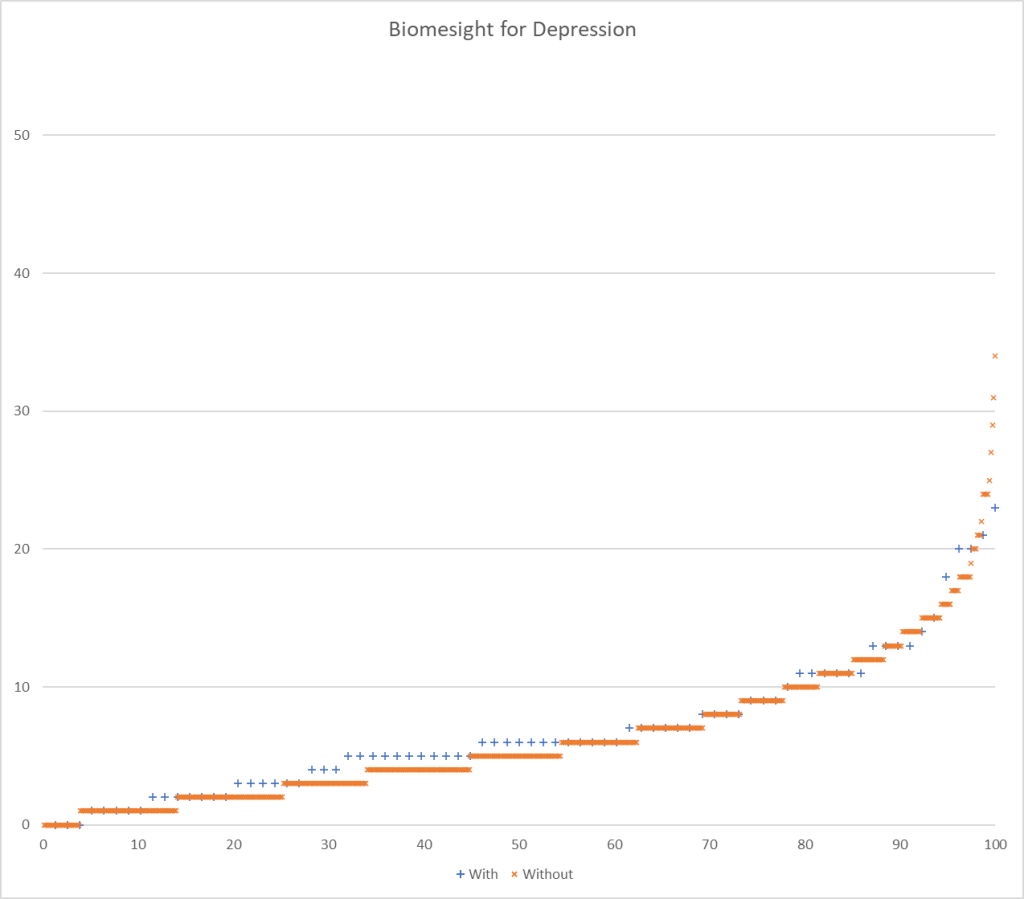
Picking one or the other of these paths seems to be done a priori by most researchers. To get a feel for the differences, I processed data from Ombre Labs and Biome Sight by both methods. Ombre Labs is almost solely from American Samples. BiomeSight is from around the world. The data suggests that Americans are more prone to depression.
| Measure | Biomesight | Ombre Labs |
| Bacteria Taxon Seen | 1,878 | 2,586 |
| With Depression | 87 | 101 |
| Without Depression | 639 | 343 |
| Percentage with Depression Reported | 12% | 23% |
| Highest T-Score with reported only (No Zero values) | 95 | 60 |
| ABs(T-Score) over 3.2 (No Zero values) | 1135 | 1185 |
| Highest T-Score with Zero if missing | 282 | 176 |
| Abs(T-Score) over 3.2 (with Zero if missing) | 1391 | 1492 |
| Highest Composite T-Score (Sqrt of the above t-score multiple by each other) | 158 | 92 |
| Composite T-Score over 3.2 ( < 0.001) | 1193 | 1306 |
| Percentage of Bacteria with T-Score over 3.2 | 63% | 50% |
We then did a composite T-Score between the two labs by bacteria to see the best indicators (in decreasing order of significance). We then compared to results from studies on the US National Library of Medicine
| Bacteria | Depression | PubMed |
| Blautia wexlerae | Increased | Genus has 50% high and 50% low |
| Catonella | Increased | |
| Catonella morbi | Increased | |
| Pseudobutyrivibrio | Increased | |
| Clostridiaceae | Decreased | |
| Sutterella wadsworthensis | Decreased | Match (genus) |
| Slackia | Increased | Match |
| Anaerobranca | Decreased | |
| Actinobacillus | Decreased | |
| Haemophilus parainfluenzae | Decreased | Match (genus) |
| Proteinivoraceae | Decreased | |
| Bacteroides ovatus | Decreased | |
| Thermoclostridium | Decreased | |
| Eggerthellales | Increased | Match |
| Eggerthellaceae | Increased | |
| Thermoanaerobacterales | Increased | |
| Prevotella | Decreased | General Match at genus |
| Veillonella dispar | Decreased | Match (genus) |
| Blautia glucerasea | Increased | Genus has 50% high and 50% low |
| Blautia hansenii | Increased | Genus has 50% high and 50% low |
| Lachnospira | Decreased | General Match at genus |
| Alphaproteobacteria | Increased | |
| [Ruminococcus] torques | Increased | Disagree |
| Desulfallaceae Watanabe et al. 2020 | Increased | |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | Decreased | Disagrees, but the genus was a match |
Where there was a study available, we had our results in good agreement. Note that our sample sizes far exceed those of any of the studies we found.
We had about 20% less significant bacteria by eliminating those samples with no/zero counts. By requiring both methods to be significant reduces the risk of false positives. In this case, we have an abundance of significant bacteria and such a criteria is viable.
Many of the items deemed very significant were of low frequency of being seen in samples
- Erwinia tasmaniensis: seen in 7.2% of Biomesight samples, not reported in Ombre.
- With Condition: Seen in 3% of samples with count of 353 /million
- Without Condition: Seen in 7.7% of samples with count of 128 / million
- Significant with excluding (11.2), significant with deeming zero (23)
This takes us to the phrase of the analysis: Given a random sample, what is the probability of correctly predicting depression. The end goal is to determine the most influential bacteria responsible for depression. One approach is using random forest on the data trimmed to those bacteria deemed significant or very significant. Another approach is use splines mixed with logistic regression. We must be careful not to shove this problem into an existing square or round hole, instead we need to allow the data to speak to us.
Remember, bacteria do not operate independent of each other. They are highly dependent on the metabolites of each other. Some of my earlier explorations found the KEGG Enzymes estimators were better predictors than bacteria. To be continued.




Recent Comments