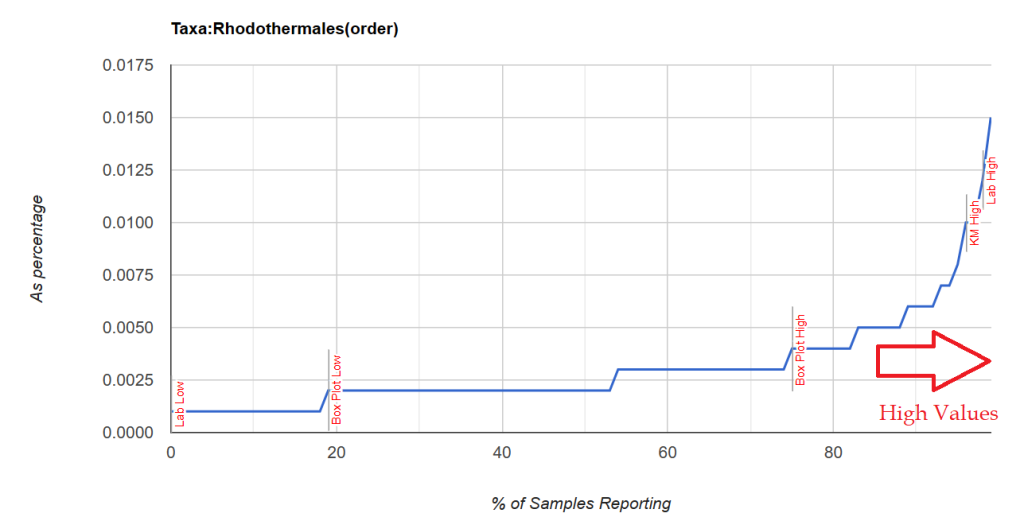
This is an update Jason Hawrelak Criteria for Healthy Gut. His criteria is based on percentages and used by medical practitioners around the world. I have three significant collections of samples and decided to find out how these percentages translate to percentile for each lab.
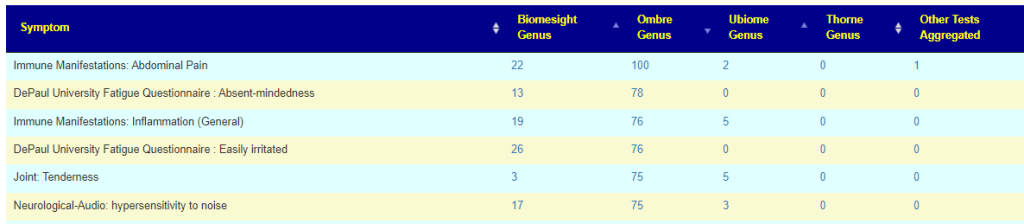
They are similar and not similar. For example 50% of people will have low Akkermansia using uBiome while Biomesight increases it to 77%. Alistipes — are never out of range for Biomesight while 90% of people using uBiome would be too high.
| Taxa Name | Taxa Rank | Percentage | uBiome Percentile | Ombre Percentile | Biomesight Percentile |
| Akkermansia | genus | 1 – 5 | 48 – 80 | 71 – 91 | 77 – 93 |
| Alistipes | genus | 0 – 0.3 | 0 – 10 | 0 – 33 | 0 – 100 |
| Bacteroides | genus | 0 – 20 | 0 – 32 | 0 – 48 | 0 – 45 |
| Bacteroidia | class | 0 – 35 | 0 – 24 | 0 – 40 | 0 – 45 |
| Bifidobacterium | genus | 2.5 – 5 | 78 – 91 | 78 – 87 | 90 – 95 |
| Bilophila wadsworthia | species | 0 – 0.15 | 0 – 32 | 0 – 43 | 0 – 44 |
| Blautia | genus | 5 – 10 | 15 – 60 | 32 – 72 | 24 – 69 |
| Desulfovibrio | genus | 0 – 0.15 | 0 – 46 | 0 – 42 | 0 – 72 |
| Escherichia coli | species | 0 – 0.1 | 0 – 100 | 0 – 75 | 0 – 88 |
| Eubacterium | genus | 0 – 15 | 0 – 100 | 0 – 99 | 0 – 100 |
| Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | species | 10 – 15 | 80 – 95 | 50 – 69 | 46 – 69 |
| Fusobacterium | genus | 0 – 0.01 | 0 – 40 | 0 – 66 | 0 – 72 |
| Lactobacillus | genus | 0.01 – 1 | 23 – 93 | 9 – 75 | 46 – 99 |
| Methanobrevibacter | genus | 0 – 0.01 | 0 – 7 | 0 – 33 | 0 – 33 |
| Oxalobacter | genus | 0.01 – 1 | 0 – 100 | 38 – 100 | 35 – 100 |
| Prevotella | genus | 0 – 25 | 0 – 100 | 0 – 89 | 0 – 88 |
| Pseudomonadota | phylum | 0 – 4 | 0 – 52 | 0 – 76 | 0 – 54 |
| Roseburia | genus | 5 – 10 | 51 – 86 | 85 – 96 | 81 – 95 |
| Ruminococcus | genus | 0 – 15 | 0 – 100 | 0 – 98 | 10- 95 |
This post is intended to illustrate that percentages cannot be determined by one lab and applied to another. Percentile appears to be more robust.


Recent Comments