| Enzyme | Reference Mean | Study Mean | Z-Score |
| 2-acetylphloroglucinol C-acetyltransferase (2.3.1.272) | 177 | 28 | 7.9 |
| [cysteine desulfurase]-S-sulfanyl-L-cysteine:[molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein]-Gly-Gly sulfurtransferase (2.8.1.11) | 5231 | 1805 | 7.7 |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tellurite methyltransferase (2.1.1.265) | 5238 | 1938 | 7 |
| decenoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] Delta2-trans-Delta3-cis-isomerase (5.3.3.14) | 6010 | 2276 | 6.9 |
| tRNA-uridine65 uracil mutase (5.4.99.26) | 4052 | 1226 | 6.8 |
| coproporphyrinogen:oxygen oxidoreductase (decarboxylating) (1.3.3.3) | 3163 | 746 | 6.8 |
| donor:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase (1.11.1.21) | 3030 | 672 | 6.7 |
| 2-(1,2-epoxy-1,2-dihydrophenyl)acetyl-CoA isomerase (5.3.3.18) | 3097 | 1059 | 6.7 |
| 3-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA 3-epimerase (5.1.2.3) | 2951 | 696 | 6.7 |
| ATP:nicotinamide-nucleotide adenylyltransferase (2.7.7.1) | 5076 | 2200 | 6.7 |
| ATP:1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-nicotinamide 5′-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.22) | 5025 | 2187 | 6.6 |
| isocitrate glyoxylate-lyase (succinate-forming) (4.1.3.1) | 2955 | 730 | 6.6 |
| D-amino acid:quinone oxidoreductase (deaminating) (1.4.5.1) | 2485 | 686 | 6.5 |
| L-methionine:2-oxo-acid aminotransferase (2.6.1.88) | 2759 | 652 | 6.5 |
| 2-(glutathione-S-yl)-hydroquinone:glutathione oxidoreductase (1.8.5.7) | 3140 | 748 | 6.5 |
| D-glucose:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (1.1.5.2) | 2200 | 462 | 6.5 |
| methanesulfonate,FMNH2:oxygen oxidoreductase (1.14.14.34) | 2239 | 489 | 6.5 |
| alkanesulfonate,FMNH2:oxygen oxidoreductase (1.14.14.5) | 2239 | 489 | 6.5 |
| glutathione:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.8.1.7) | 5947 | 2494 | 6.5 |
| triphosphate phosphohydrolase (3.6.1.25) | 4494 | 2012 | 6.4 |
| S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.284) | 2862 | 759 | 6.4 |
| (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.35) | 3374 | 926 | 6.4 |
| ferredoxin:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.18.1.3) | 1992 | 455 | 6.4 |
| acyl-CoA:sn-glycerol-3-phosphate 1-O-acyltransferase (2.3.1.15) | 3270 | 1139 | 6.4 |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tRNA (cytidine32/uridine32-2′-O)-methyltransferase (2.1.1.200) | 3316 | 1093 | 6.3 |
| [50S ribosomal protein L16]-L-Arg81,2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase (3R-hydroxylating) (1.14.11.47) | 3334 | 1114 | 6.3 |
| choline:acceptor 1-oxidoreductase (1.1.99.1) | 2748 | 562 | 6.3 |
| acetyl-CoA:glyoxylate C-acetyltransferase [(S)-malate-forming] (2.3.3.9) | 3116 | 950 | 6.3 |
| siroheme ferro-lyase (sirohydrochlorin-forming) (4.99.1.4) | 2565 | 539 | 6.2 |
| deoxyribocyclobutadipyrimidine pyrimidine-lyase (4.1.99.3) | 4156 | 1337 | 6.2 |
| acetyl-CoA:[elongator tRNAMet]-cytidine34 N4-acetyltransferase (ATP-hydrolysing) (2.3.1.193) | 3309 | 1094 | 6.2 |
| 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3′-triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (3.6.1.67) | 3607 | 1299 | 6.2 |
| n/a (3.4.11.23) | 3312 | 1083 | 6.2 |
| acetyl-CoA:dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-galactose N-acetyltransferase (2.3.1.210) | 2766 | 673 | 6.2 |
| ATP:N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.59) | 3263 | 1071 | 6.2 |
| L-2,4-diaminobutanoate carboxy-lyase (propane-1,3-diamine-forming) (4.1.1.86) | 2127 | 304 | 6.2 |
| chorismate pyruvate-lyase (4-hydroxybenzoate-forming) (4.1.3.40) | 2596 | 567 | 6.2 |
| protein dithiol:quinone oxidoreductase (disulfide-forming) (1.8.5.9) | 3557 | 1276 | 6.2 |
| fatty acyl-[acyl-carrier protein]:alpha-Kdo-(2->4)-alpha-Kdo-(2->6)-(acyl)-[lipid IVA] O-acyltransferase (2.3.1.243) | 3322 | 1097 | 6.2 |
| ATP:L-threonine O3-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.177) | 2358 | 350 | 6.1 |
| ditrans-octacis-undecaprenyl-diphosphate:alpha-D-Kdo-(2->4)-alpha-D-Kdo-(2->6)-lipid-A phosphotransferase (2.7.4.29) | 2852 | 1008 | 6.1 |
| D-sorbitol-6-phosphate:NAD+ 2-oxidoreductase (1.1.1.140) | 2447 | 677 | 6.1 |
| diacylglycerol-3-phosphate phosphohydrolase (3.1.3.4) | 3284 | 1105 | 6.1 |
| 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate phosphohydrolase (3.1.3.81) | 3284 | 1105 | 6.1 |
| (R)-lactate:quinone 2-oxidoreductase (1.1.5.12) | 2328 | 510 | 6.1 |
| (S)-lactate:ferricytochrome-c 2-oxidoreductase (1.1.2.3) | 2368 | 544 | 6.1 |
| methyl DNA-base, 2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase (formaldehyde-forming) (1.14.11.33) | 2304 | 475 | 6.1 |
| ATP:D-ribulose-5-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.19) | 2435 | 543 | 6.1 |
| (2S,3S)-2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.3.1.28) | 2240 | 476 | 6.1 |
| D-mannitol-1-phosphate:NAD+ 5-oxidoreductase (1.1.1.17) | 2672 | 727 | 6 |
| 2-O-(alpha-D-mannopyranosyl)-D-glycerate D-mannohydrolase (3.2.1.170) | 1248 | 396 | 6 |
| S-formylglutathione hydrolase (3.1.2.12) | 2402 | 554 | 6 |
| gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine:spermidine amidase (3.5.1.78) | 3189 | 1059 | 6 |
| gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine:spermidine ligase (ADP-forming) [spermidine is numbered so that atom N-1 is in the amino group of the aminopropyl part of the molecule] (6.3.1.8) | 3189 | 1059 | 6 |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine:23S rRNA (uracil747-C5)-methyltransferase (2.1.1.189) | 3257 | 1112 | 6 |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine:uridine in tRNA 3-[(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl]transferase (2.5.1.25) | 1704 | 303 | 6 |
| succinate-semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.24) | 2416 | 449 | 6 |
| Fe(II)-siderophore:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.16.1.9) | 2344 | 447 | 6 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, taurine-importing) (7.6.2.7) | 2185 | 521 | 6 |
| geraniol:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.183) | 2470 | 466 | 6 |
| ATP:N-acyl-D-mannosamine 6-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.60) | 3204 | 1098 | 5.9 |
| L-serine:[L-seryl-carrier protein] ligase (AMP-forming) (6.2.1.72) | 2199 | 454 | 5.9 |
| galactarate hydro-lyase (5-dehydro-4-deoxy-D-glucarate-forming) (4.2.1.42) | 3015 | 963 | 5.9 |
| propanoyl-CoA:phosphate propanoyltransferase (2.3.1.222) | 1738 | 358 | 5.9 |
| ATP:thiamine phosphotransferase (2.7.1.89) | 2372 | 492 | 5.9 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, putrescine-importing) (7.6.2.16) | 2302 | 503 | 5.9 |
| ubiquinol:oxygen oxidoreductase (superoxide-forming) (1.10.3.17) | 2232 | 475 | 5.9 |
| S-adenosyl-L-methionine:23S rRNA (guanine1835-N2)-methyltransferase (2.1.1.174) | 2258 | 485 | 5.9 |
| riboflavin:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase (1.5.1.41) | 2323 | 491 | 5.9 |
| D-erythrose 4-phosphate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.72) | 2267 | 485 | 5.9 |
| CDP-diacylglycerol phosphatidylhydrolase (3.6.1.26) | 2239 | 499 | 5.9 |
| D-glucarate hydro-lyase (5-dehydro-4-deoxy-D-glucarate-forming) (4.2.1.40) | 2953 | 1125 | 5.9 |
| 6-phospho-D-gluconate hydro-lyase (2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-gluconate-forming) (4.2.1.12) | 2260 | 495 | 5.8 |
| ATP:propanoate phosphotransferase (2.7.2.15) | 2215 | 469 | 5.8 |
| isochorismate pyruvate-hydrolase (3.3.2.1) | 2164 | 473 | 5.8 |
| (3Z/3E)-alk-3-enoyl-CoA (2E)-isomerase (5.3.3.8) | 2225 | 487 | 5.8 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, L-arabinose-importing) (7.5.2.12) | 2214 | 473 | 5.8 |
| n/a (3.4.24.55) | 2279 | 492 | 5.8 |
| diacylphosphatidylethanolamine:alpha-D-Kdo-(2->4)-alpha-D-Kdo-(2->6)-lipid-A 7”-phosphoethanolaminetransferase (2.7.8.42) | 2371 | 500 | 5.8 |
| 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate:L-serine ligase (6.3.2.14) | 2179 | 611 | 5.8 |
| 2-O-(alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-glycerate:phosphate alpha-D-glucosyltransferase (configuration-retaining) (2.4.1.352) | 1217 | 249 | 5.8 |
| pyrimidine-5′-nucleotide phosphoribo(deoxyribo)hydrolase (3.2.2.10) | 2222 | 495 | 5.8 |
| 6-sulfo-alpha-D-quinovosyl diacylglycerol 6-sulfo-D-quinovohydrolase (3.2.1.199) | 1113 | 222 | 5.8 |
| (9Z)-hexadec-9-enoyl-[acyl-carrier protein]:Kdo2-lipid IVA O-palmitoleoyltransferase (2.3.1.242) | 2356 | 502 | 5.8 |
| [RNA]-adenosine-cytidine 5′-hydroxy-adenosoine ribonucleotide-3′-[RNA fragment]-lyase (cyclicizing; [RNA fragment]-3′-cytidine-2′,3′-cyclophosphate-forming and hydrolysing) (4.6.1.21) | 2312 | 470 | 5.8 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, D-allose-importing) (7.5.2.8) | 2146 | 431 | 5.8 |
| 6-methoxy-3-methyl-2-(all-trans-polyprenyl)-1,4-benzoquinol,acceptor:oxygen oxidoreductase (5-hydroxylating) (1.14.99.60) | 2180 | 540 | 5.8 |
| NADPH:NAD+ oxidoreductase (Si-specific) (1.6.1.1) | 2204 | 490 | 5.8 |
| taurine, 2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase (sulfite-forming) (1.14.11.17) | 2122 | 496 | 5.8 |
| (deoxy)cytidine 5′-triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (3.6.1.65) | 2307 | 500 | 5.7 |
| 2-(all-trans-polyprenyl)phenol,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (6-hydroxylating) (1.14.13.240) | 2178 | 535 | 5.7 |
| dTDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-fucose:N-acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminouronyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-ditrans,octacis-undecaprenol N-acetylfucosaminyltransferase (2.4.1.325) | 2308 | 507 | 5.7 |
| ATP:[isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)] phosphotransferase (2.7.11.5) | 2142 | 516 | 5.7 |
| 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate:[aryl-carrier protein] ligase (AMP-forming) (6.2.1.71) | 2118 | 604 | 5.7 |
| 5,6,7,8-tetrahydromonapterin:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.5.1.50) | 2159 | 476 | 5.7 |
| glutathione gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase (5-oxo-L-proline producing) (4.3.2.7) | 2158 | 500 | 5.7 |
| iron(III)-enterobactin hydrolase (3.1.1.108) | 2204 | 491 | 5.7 |
| N,N’-diacetylchitobiose acetylhydrolase (3.5.1.105) | 2304 | 508 | 5.7 |
| N-succinyl-L-glutamate amidohydrolase (3.5.1.96) | 2172 | 518 | 5.7 |
| protein-Npi-phospho-L-histidine:N-acetyl-D-muramate Npi-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.192) | 2283 | 474 | 5.7 |
| 4-alpha-D-[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucano]trehalose glucanohydrolase (trehalose-producing) (3.2.1.141) | 1335 | 181 | 5.7 |
| acetyl-CoA:N6-hydroxy-L-lysine 6-acetyltransferase (2.3.1.102) | 708 | 159 | 5.6 |
| 4-aminobutanoate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (2.6.1.19) | 3600 | 1155 | 5.6 |
| ATP:(S)-4,5-dihydroxypentane-2,3-dione 5-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.189) | 1415 | 220 | 5.6 |
| inosine/xanthosine 5′-triphosphate phosphohydrolase (3.6.1.73) | 2071 | 496 | 5.6 |
| 6-deoxy-6-sulfofructose-1-phosphate 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropane-1-sulfonate-lyase (glycerone-phosphate-forming) (4.1.2.57) | 1346 | 295 | 5.6 |
| protein-Npi-phospho-L-histidine:2-O-alpha-mannopyranosyl-D-glycerate Npi-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.195) | 1163 | 234 | 5.6 |
| 2,3-dihydroxypropane-1-sulfonate:NAD+ 3-oxidoreductase (1.1.1.373) | 1341 | 295 | 5.6 |
| 4-aminobutanal:NAD+ 1-oxidoreductase (1.2.1.19) | 2237 | 491 | 5.6 |
| N-succinyl-L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.71) | 2135 | 535 | 5.6 |
| protein-dithiol:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase (1.8.1.8) | 2151 | 540 | 5.6 |
| succinyl-CoA:acetyl-CoA C-succinyltransferase (2.3.1.174) | 1445 | 205 | 5.6 |
| succinyl-CoA:L-arginine N2-succinyltransferase (2.3.1.109) | 2135 | 536 | 5.6 |
| 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.91) | 1461 | 221 | 5.6 |
| 2-oxepin-2(3H)-ylideneacetyl-CoA hydrolase (3.3.2.12) | 1461 | 221 | 5.6 |
| N2-succinyl-L-arginine iminohydrolase (decarboxylating) (3.5.3.23) | 2134 | 536 | 5.6 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, nitrate-importing) (7.3.2.4) | 1523 | 142 | 5.6 |
| 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3′-triphosphate 2′-epimerase (5.1.99.7) | 1928 | 468 | 5.5 |
| N4-acetylcytidine amidohydrolase (3.5.1.135) | 2966 | 1096 | 5.5 |
| N2-succinyl-L-ornithine:2-oxoglutarate 5-aminotransferase (2.6.1.81) | 2254 | 677 | 5.5 |
| (1->4)-alpha-D-glucan 1-alpha-D-glucosylmutase (5.4.99.15) | 1319 | 183 | 5.5 |
| ATP:2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-galactonate 6-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.58) | 1536 | 299 | 5.5 |
| 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-galactonate D-glyceraldehyde-3-phospho-lyase (pyruvate-forming) (4.1.2.21) | 1538 | 299 | 5.5 |
| (S)-ureidoglycolate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.350) | 1729 | 436 | 5.5 |
| ATP:D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphotransferase (2.7.1.28) | 1512 | 115 | 5.5 |
| ATP:glycerone phosphotransferase (2.7.1.29) | 1512 | 115 | 5.5 |
| FAD AMP-lyase (riboflavin-cyclic-4′,5′-phosphate-forming) (4.6.1.15) | 1512 | 115 | 5.5 |
| tRNA 2-(methylsulfanyl)-N6-prenyladenosine37,donor:oxygen 4-oxidoreductase (trans-hydroxylating) (1.14.99.69) | 1565 | 158 | 5.5 |
| S-methyl-5′-thioadenosine:phosphate S-methyl-5-thio-alpha-D-ribosyl-transferase (2.4.2.28) | 3673 | 1543 | 5.4 |
| primary-amine:oxygen oxidoreductase (deaminating) (1.4.3.21) | 1495 | 217 | 5.4 |
| UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinose:ditrans,octacis-undecaprenyl phosphate 4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinosyltransferase (2.4.2.53) | 2107 | 573 | 5.4 |
| (2S)-2-hydroxy-3,4-dioxopentyl phosphate aldose-ketose-isomerase (5.3.1.32) | 1529 | 259 | 5.4 |
| acyl-CoA:acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (2.3.1.16) | 3869 | 1876 | 5.4 |
| 2,3-didehydroadipoyl-CoA:acetyl-CoA C-didehydroadipoyltransferase (double bond migration) (2.3.1.223) | 1516 | 224 | 5.4 |
| 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose N-formyltransferase (2.1.2.13) | 2048 | 470 | 5.4 |
| UDP-alpha-D-glucuronate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (decarboxylating) (1.1.1.305) | 2048 | 470 | 5.4 |
| 4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl ditrans,octacis-undecaprenyl-phosphate:lipid IVA 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinopyranosyltransferase (2.4.2.43) | 2044 | 473 | 5.4 |
| 5-(methylsulfanyl)-D-ribulose-1-phosphate 4-hydro-lyase [5-(methylsulfanyl)-2,3-dioxopentyl-phosphate-forming] (4.2.1.109) | 1552 | 181 | 5.3 |
| UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (2.6.1.87) | 2070 | 480 | 5.3 |
| phenylacetyl-CoA:oxygen oxidoreductase (1,2-epoxidizing) (1.14.13.149) | 1375 | 278 | 5.3 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, D-xylose-transporting) (7.5.2.10) | 1473 | 308 | 5.3 |
| 5-(methylsulfanyl)-2,3-dioxopentyl-phosphate phosphohydrolase (isomerizing) (3.1.3.77) | 1689 | 121 | 5.3 |
| N-benzoylamino-acid amidohydrolase (3.5.1.32) | 1712 | 408 | 5.3 |
| phenylacetaldehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.39) | 1391 | 271 | 5.3 |
| L-glutamate:putrescine ligase (ADP-forming) (6.3.1.11) | 1902 | 448 | 5.3 |
| iron(III)-salmochelin complex hydrolase (3.1.1.109) | 727 | 159 | 5.3 |
| 2-O-(alpha-D-mannosyl)-3-phosphoglycerate phosphohydrolase (3.1.3.70) | 2061 | 498 | 5.3 |
| 4-(gamma-L-glutamylamino)butanoate amidohydrolase (3.5.1.94) | 1914 | 445 | 5.3 |
| GDP-alpha-D-mannuronate:mannuronan D-mannuronatetransferase (2.4.1.33) | 154 | 39 | 5.2 |
| [mannuronan]-beta-D-mannuronate 5-epimerase (5.1.3.37) | 154 | 39 | 5.2 |
| 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvate carboxy-lyase [(2-indol-3-yl)acetaldehyde-forming] (4.1.1.74) | 1802 | 138 | 5.2 |
| quinate:quinol 3-oxidoreductase (1.1.5.8) | 1523 | 124 | 5.2 |
| betaine-aldehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.2.1.8) | 2057 | 434 | 5.2 |
| catechol:oxygen 2,3-oxidoreductase (ring-opening) (1.13.11.2) | 3240 | 1416 | 5.2 |
| 1,2-dihydroxy-5-(methylsulfanyl)pent-1-en-3-one:oxygen oxidoreductase (formate- and CO-forming) (1.13.11.53) | 1714 | 283 | 5.2 |
| 1,2-dihydroxy-5-(methylsulfanyl)pent-1-en-3-one:oxygen oxidoreductase (formate-forming) (1.13.11.54) | 1714 | 283 | 5.2 |
| ATP phosphohydrolase (ABC-type, thiamine-importing) (7.6.2.15) | 3503 | 1300 | 5.2 |
| citrate:N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine ligase (AMP-forming) (6.3.2.38) | 797 | 193 | 5.1 |
| RX:glutathione R-transferase (2.5.1.18) | 2968 | 1025 | 5.1 |
| N2-citryl-N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine:N6-acetyl-N6-hydroxy-L-lysine ligase (AMP-forming) (6.3.2.39) | 795 | 193 | 5.1 |
| putrescine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (2.6.1.82) | 3168 | 1490 | 5.1 |
| UDP-alpha-D-glucose:enterobactin 5′-C-beta-D-glucosyltransferase (configuration-inverting) (2.4.1.369) | 807 | 200 | 5.1 |
| 4-hydroxybutanoate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.61) | 2322 | 607 | 5.1 |
| D-xylonate hydro-lyase (2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabinonate-forming) (4.2.1.82) | 621 | 178 | 5 |
| D-glycerate:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.60) | 1888 | 516 | 5 |
| galactitol-1-phosphate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.251) | 997 | 277 | 5 |
| alkylmercury mercury(II)-lyase (alkane-forming) (4.99.1.2) | 577 | 115 | 5 |
| (S)-2-hydroxyglutarate:quinone oxidoreductase (1.1.5.13) | 2192 | 670 | 5 |
| (R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA:NADP+ oxidoreductase (1.1.1.36) | 523 | 154 | 5 |
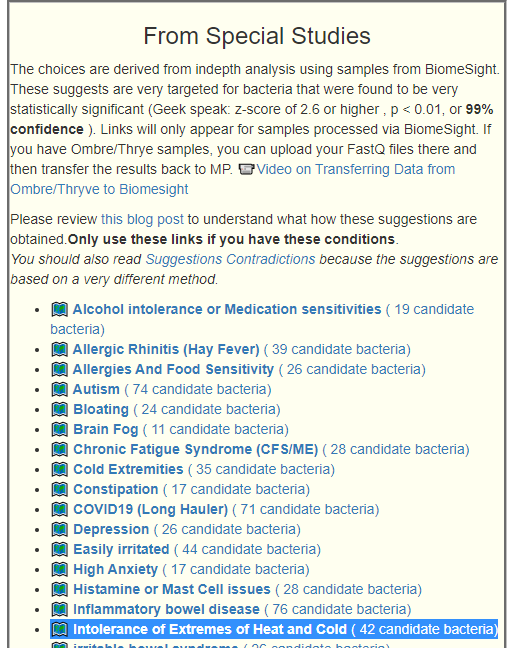
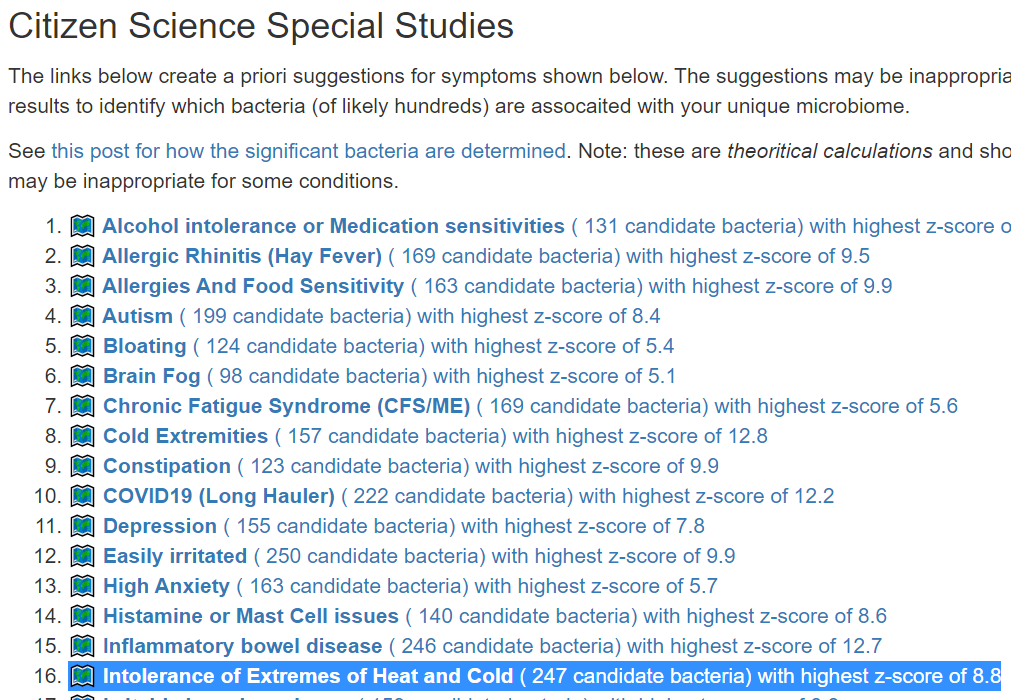
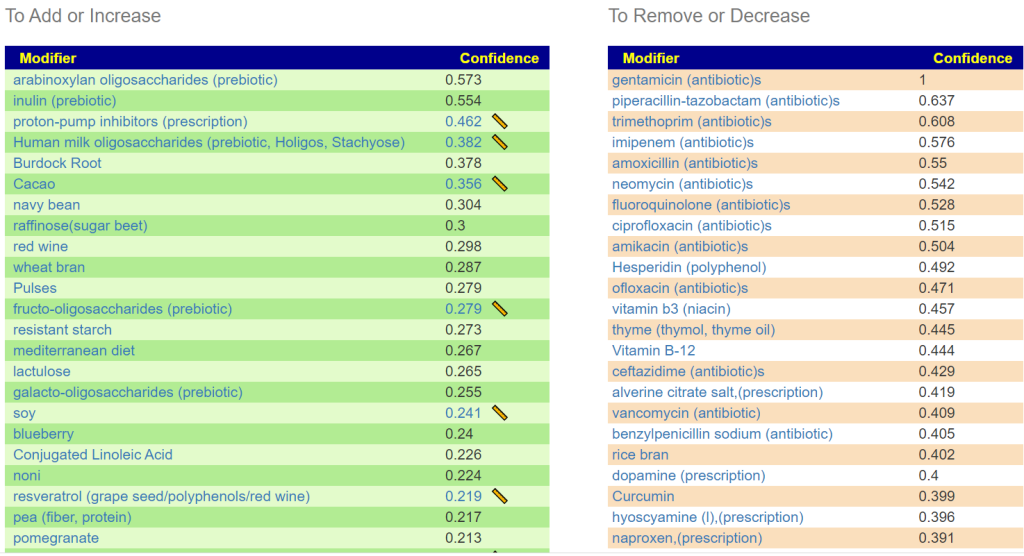
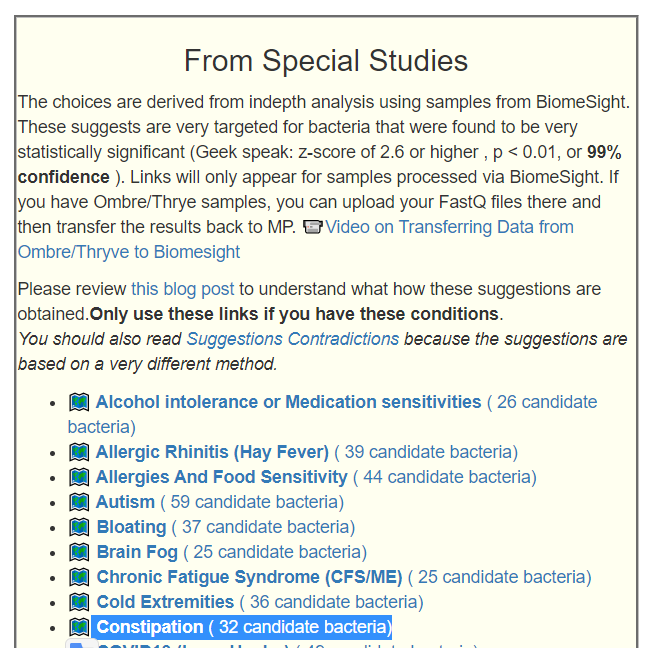

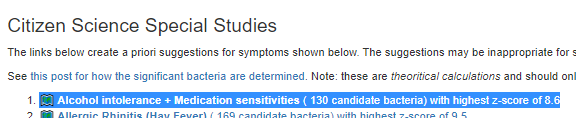
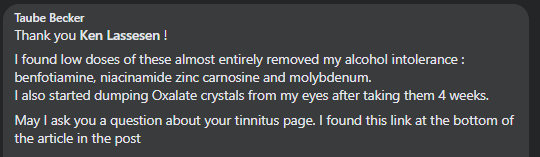
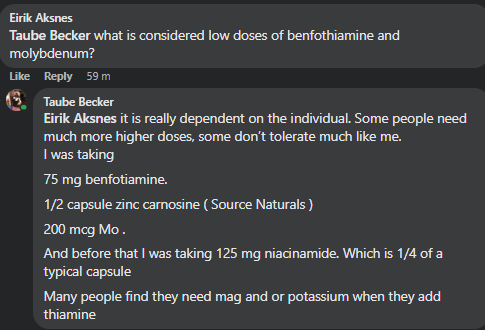
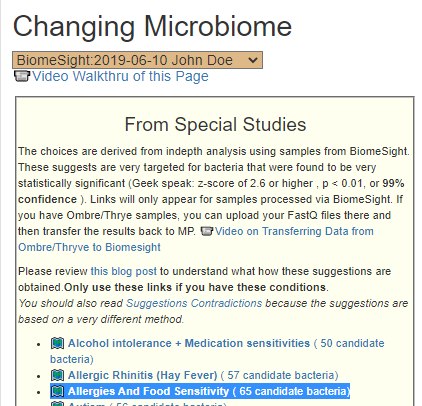

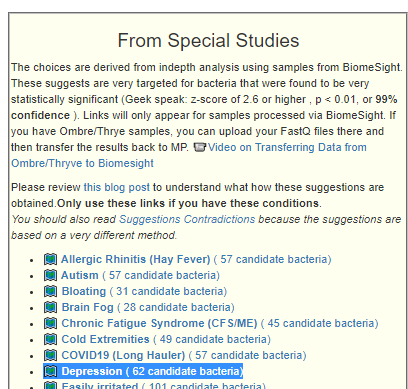
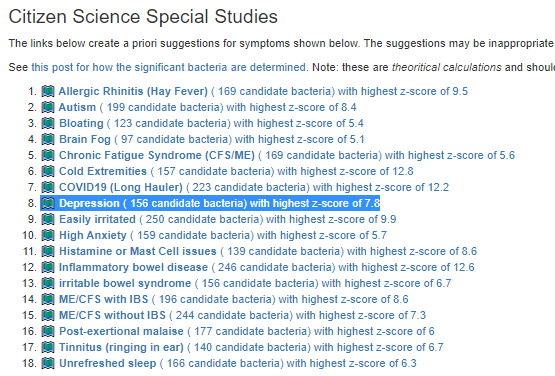

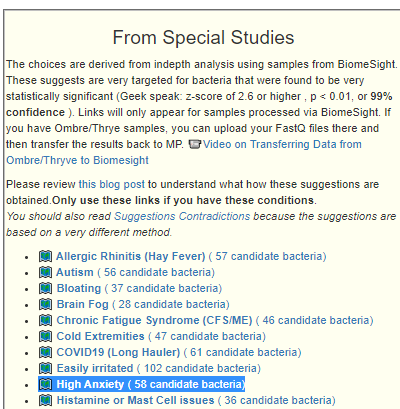
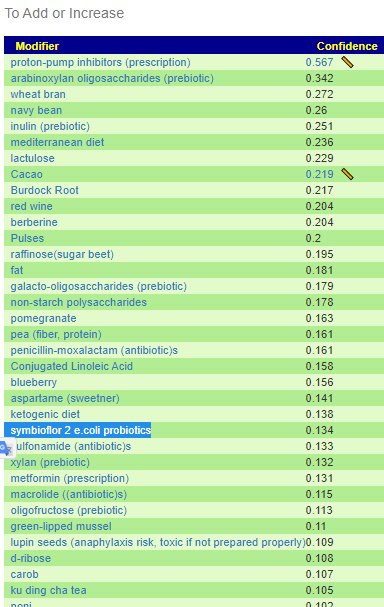
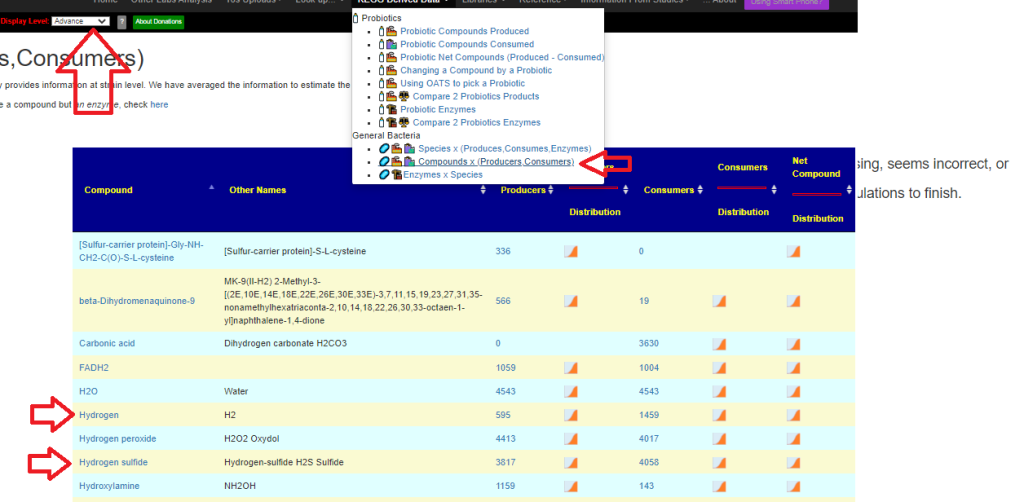
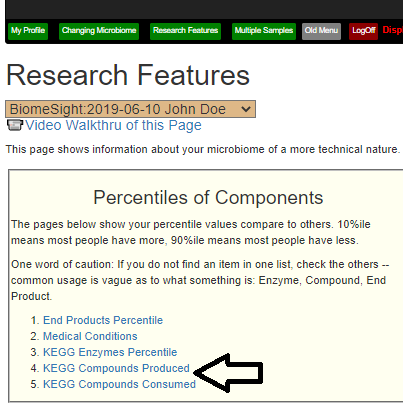
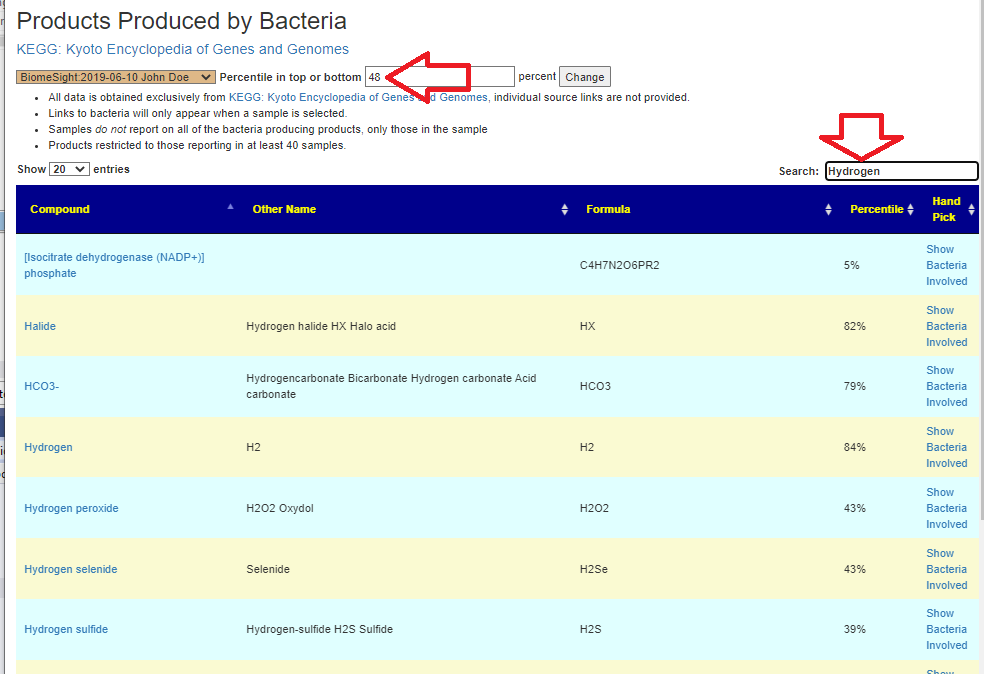
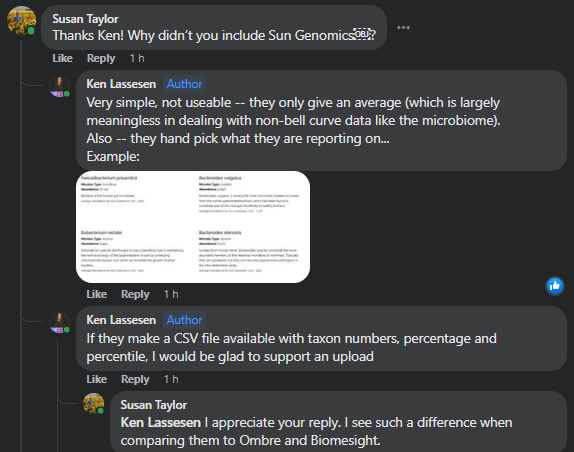


Recent Comments