A reader messaged me about some issues she was having
Hi, could I just have a quick question? I read in the Gut Health group on Facebook that you wrote that if there is too much, for example, lactobacillus, it can cause neurological problems. I suffer from anxiety and depression and was recommended a transplant of intestinal microflora, which made the condition 100 times worse and since then I can’t get out of it and the doctors don’t know what to do with it. I’m still trying to treat dysbiosis, but now I don’t know if the problem is one of the good bacteria? Thank you very much.
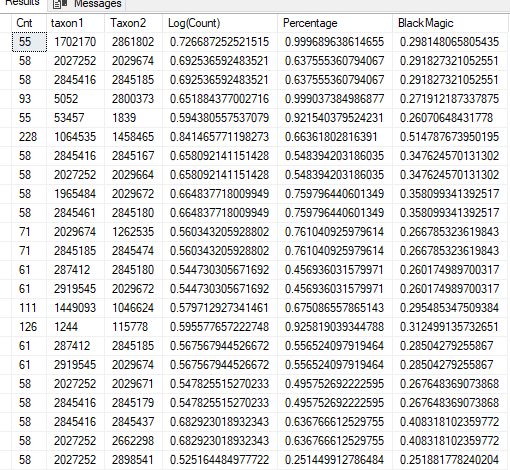
yes, I have a biomesight and a GI map, there is an overgrowth of Prevotela, Streptococus, Enterobacter and Citrobacter and a little bifido and lacto. I have yellow stools after the transplant, if I don’t take probiotics. But it seems that nothing works, diet, antimicrobials, probiotics, enemas with probiotics, prebiotics, nothing helps
Initial Comments
This person is not in the US. She lives in a place where Fecal Matter Transplants is allowed for many conditions than the US (where it is only authorized for Clostridioides difficile –after everything else has failed). I view FMT as Russian roulette hoping that a silver ballet will happen to end up in the cylinder. IMHO, before a FMT is done we need at least two shotgun microbiome tests done. One for each candidate donor and one for the recipient. These need to be carefully reviewed by a third party who is very well informed on the microbiome. Only the best donor will be used. After the FMT, monthly shotgun reports of the recipient microbiome should be done for at least 6 months.
Analysis
The first step is to look at predicted symptoms, most are neurological, with the two reported symptoms sitting high up the list.
- Comorbid: High Anxiety – [66.6%]
- General: Depression – [64.1%]
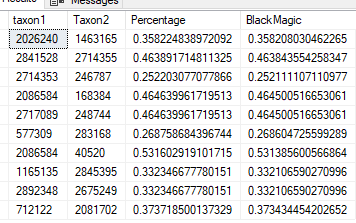
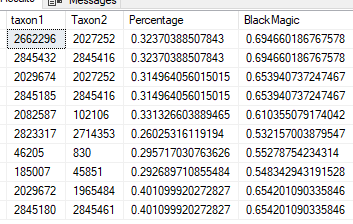
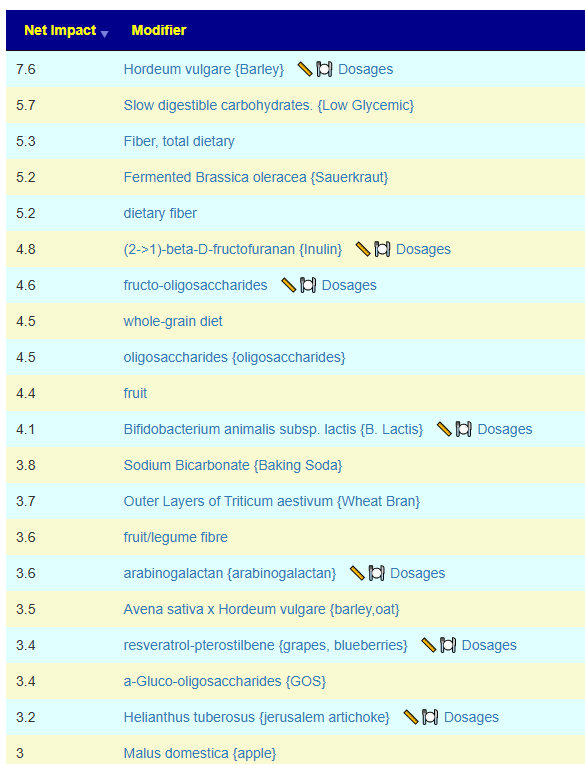
I marked all of the items with depression and anxiety and then asked for suggestions. The top items are shown below,
| (2->1)-beta-D-fructofuranan {Inulin} | Prebiotics and similar |
| oligosaccharides {oligosaccharides} | Prebiotics and similar |
| Outer Layers of Triticum aestivum {Wheat Bran} | Food (excluding seasonings) |
| laminaria digitata {Oarweed} | Food (excluding seasonings) |
| dietary fiber | Diet Style |
| β-lactoglobulin {Whey} | Food (excluding seasonings) |
| Fiber, total dietary | Diet Style |
| Pulvis ledebouriellae compositae {Bofutsushosan} | Herb or Spice |
| Orange Juice | Food (excluding seasonings) |
| ß-glucan {Beta-Glucan} | Prebiotics and similar |
The number of bacteria picked was below my comfort level, so I then did Novice: Just tell me what to take or avoid
While the items were technically different, they were very similar for example
Probiotics
There are two approaches for probiotics:
- Based on published studies (we actually do not have that many with good details on the impact)
- Based on KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes which uses the DNA of your microbiome and the probiotics.
We have agreement on the following top choices:
- Mutaflor *
- bifidobacterium bifidum {B. bifidum} *
- Bacillus Subtilis *
- Lactobacillus johnsonii *
- Levilactobacillus brevis {L.brevis} *
- Lactiplantibacillus pentosus {L. pentosus}*
- Brevibacillus laterosporus {B. laterosporus }*
- Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI 588 {Miyarisan}*
- bacillus licheniformis {b. licheniformis}
We should note that there are probiotics that should be avoid, including
- Saccharomyces boulardii
- Bacillus coagulans
- bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum
- Bifidobacterium breve
- bifidobacterium longum
- Lactobacillus gasseri
- bifidobacterium infantis
- Ligilactobacillus salivarius
- Lactobacillus plantarum
- lactobacillus rhamnosus
The failure to understand that all probiotics are not created equal is a common problem. Often I have heard “I tried probiotics and it did not work”. That is not surprising because often they are sold with dozen of species in one bottle — “because the more species you have, the better your sales will be” from manufacturers and influencers.
You need to get specific species and ideally recently manufactured. A bottle of probiotics stored in an unrefrigerated warehouse for 12 months may have very few viable bacteria left. When they get to a retail store, they may be put into a refrigerator — but that is too late.
Where do I get the probiotics?
I prefer single species — and where I get mine?
- Single species with (almost) no fillers. There are precisely three sources that I use:
- Custom Probiotics :they list all of their strains — many are researched. No other ingredients just the bacteria.
- Maple Life Science™: No strains yet, but shipments usually have manufactured date within 4 weeks of arrival (i.e. FRESH). Contains FOS
- Bulk Probiotics: US based Newbie — but has some species not available at the other two sites. No other ingredients just the bacteria. Specifically, Lactobacillus Jensenii that has great potential for Crohn’s disease.
- NOTE: none of these sell though retail outlets. This keeps their costs down and their product fresh.
Another Alternative to get Suggestions
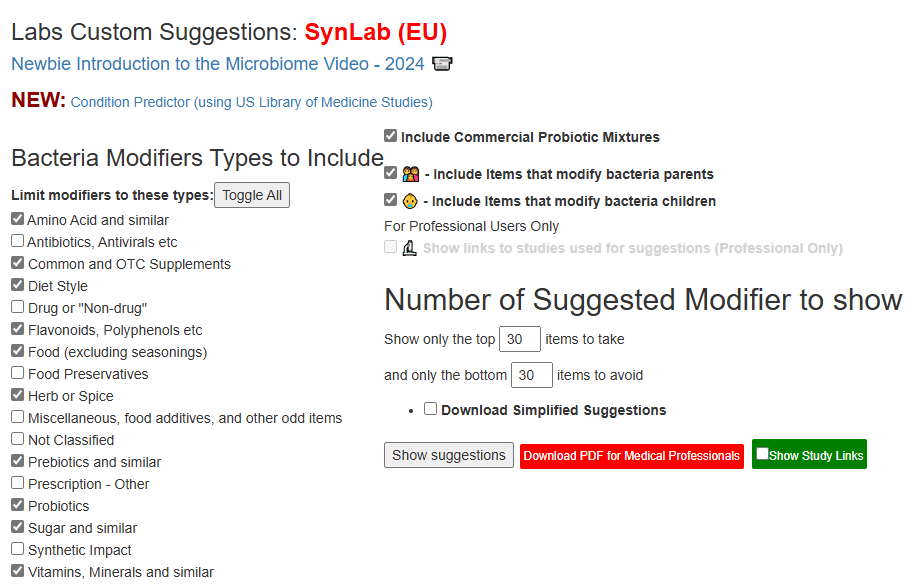
On the old UI we have this section and we have enough studies for Depression show up.

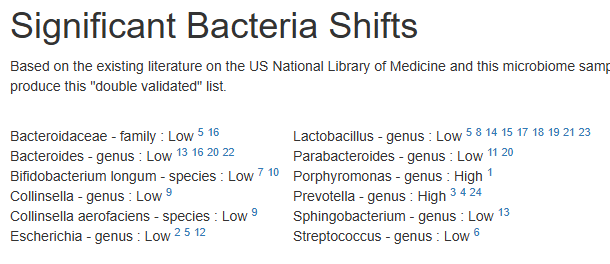
With this sample, we have the following bacteria matches against published studies (with links to the studies).
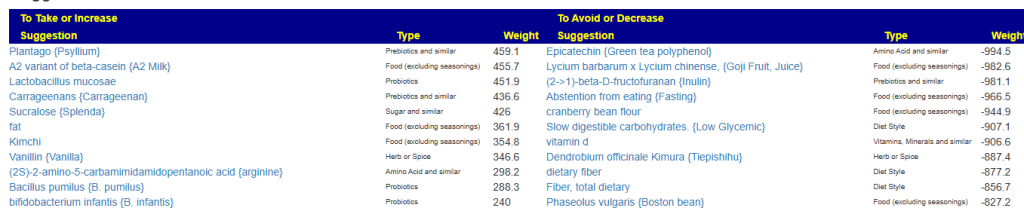
This results in the suggestions below. Each suggestion has also been reported in studies to help depression. This means that the odds of them working is pretty good.

Treatment Suggestions for
This report is for Reader using this sample BiomeSight:2022-10-25 Self 🛑 . It uses their reported medical conditions, microbiome sample, US National Library of Medicine, and a fuzzy logic expert system to compute recommendations balancing study reliability and contraindications. These suggestions should always be reviewed by a medical professional before starting.
NOTA BENE: This is working solely from published studies. Other suggestions algorithms are available on Microbiome Prescription. The URL above may be sent to your MD if you wish to share it.
The reported condition(s) are
This person has a significant amount of bacteria known to form biofilms
Substances with a 🦠 are reported to reduce biofilms. See for studies.
- Depression – Depressive Disorder
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Some studies suggest that omega-3 supplements, particularly those rich in EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), might have modest benefits as adjuncts to traditional treatments for depression. Omega-3s are essential for brain health, and they may have some mood-stabilizing properties.
- Vitamin D: Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with depression. While the exact relationship is complex and not fully understood, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels through supplements or exposure to sunlight may support overall mental health.
- B Vitamins: Some B vitamins, such as B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are involved in neurotransmitter synthesis and may have a role in mood regulation. Folate deficiency, in particular, has been linked to depressive symptoms.
- Probiotics: The gut-brain connection has led to studies exploring the potential impact of probiotics on mental health. Research suggests that gut health may influence mood, and some studies propose that certain probiotics might have a modest effect on reducing depressive symptoms. However, more research is needed to determine specific strains, dosages, and their impact on depression.
Significant Bacteria Shifts
Based on the existing literature on the US National Library of Medicine and this microbiome sample, we have the following matches for bacteria shifts. There is a growing body of literature finding that the effectiveness of interventions depends on the existing microbiome. We filter by documented interventions that helps some with this condition and suggestions based on this person’s specific microbiome to produce this “double validated” list.
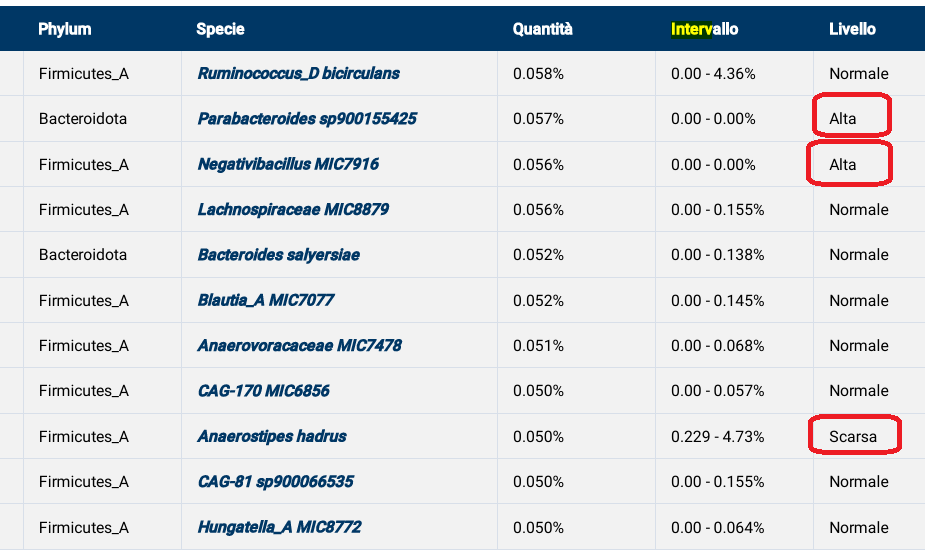
Bacteroidaceae – family : Low 5 16 Bacteroides – genus : Low 13 16 20 22 Bifidobacterium longum – species : Low 7 10 Collinsella – genus : Low 9 Collinsella aerofaciens – species : Low 9 Escherichia – genus : Low 2 5 12 | Lactobacillus – genus : Low 5 8 14 15 17 18 19 21 23 Parabacteroides – genus : Low 11 20 Porphyromonas – genus : High 1 Prevotella – genus : High 3 4 24 Sphingobacterium – genus : Low 13 Streptococcus – genus : Low 6 |
Cross Validated Suggestions
The following improves the bacteria identified above and also is reported in the literature of helping some people with this condition. Each is link to the source study.
| 5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]quinolizinium {Berberine} 64 3,3′,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone {Quercetin} 41 3,5,7-trihydroxy flavanone-7-rhamnoglucoside {Hesperidin} 31 a-Amino-3-indolepropionic acid {Tryptophan} 72 Agaricus bisporus {White button mushrooms} 31 Akkermansia muciniphila {Pendulum Probiotic} 43 62 66 74 81 92 alpha-linolenic acid {Omega-3} 34 35 41 48 arabinogalactan {arabinogalactan} 86 Bifidobacterium breve {B. breve} 46 89 bifidobacterium infantis {B. infantis} 78 Biotin {Vitamin B7} 76 blueberry 41 Caffeine 41 Camellia sinensis {oolong tea} 48 Citrus limon {Lemon} 47 Coffee 41 coptis chinensis {Chinese goldthread } 49 Crocus sativus {Saffron} 44 48 Cuminum cyminum {Cumin} 48 dietary fiber 41 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA),docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) {Fish Oil} 41 48 Epicatechin {Green tea polyphenol} 41 folate {Vitamin B9} 33 34 fruit 32 40 Glycine max x Aspergillus oryzae {Miso} 41 green tea 41 Hericium erinaceus {Lion’s Mane Mushroom } 68 Heyndrickxia coagulans {B. coagulans} 25 26 Hypericum perforatum {St. John’s Wort} 41 48 Ipomoea batata {Purple sweet potatoes} 31 kefir 90 Kimchi 31 Lacticaseibacillus casei {L. casei} 77 Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus {l. rhamnosus}🦠 54 63 84 87 93 lactobacillus acidophilus {L. acidophilus} 49 50 51 lactobacillus helveticus {L. helveticus} 49 67 82 lactobacillus helveticus,lactobacillus rhamnosus 80 84 Lactobacillus plantarum {L. plantarum} 41 49 53 55 | Lactococcus lactis {Streptococcus lactis}🦠 44 Lentinula edodes {Shiitake Mushroom} 31 Levilactobacillus brevis {L.brevis} 42 Limosilactobacillus fermentum {L. fermentum} 88 long-term, moderate-intensity exercise {exercise} 65 71 low carbohydrate diet 41 low-fat diets 40 Lycium barbarum x Lycium chinense, {Goji Fruit, Juice} 48 Malus domestica {apple} 70 Mixture of Vitamin B? {B Vitamins} 27 Musa acuminata {Banana} 31 Nigella sativa {black cumin}🦠 56 nuts 40 41 oligosaccharides {oligosaccharides} 80 Phaseolus vulgaris {Boston bean} 40 Pisces {Fish} 32 41 polyphenols 41 Pulses, Beans 40 Pyroguaiac acid {Guaiacol} 70 resveratrol-pterostilbene {grapes, blueberries} 41 resveratrol-pterostilbene x Quercetin {quercetin x resveratrol} 41 Rhodiola rosea {Rosavin} 48 Rubus {Raspberries} 41 52 SAM-e 41 Selenomethionine {Selenium supplement} 85 Solanum tuberosum {Potatoes} 73 soy 40 41 ß-glucan {Beta-Glucan} 57 58 59 60 tea 91 Traditional Mediterranean diet {Mediterranean diet} 40 Vaccinium {Cranberry} 41 vegetable 32 40 vegetarians 40 vitamin d🦠 27 28 29 30 41 69 Whole Cow milk {Whole Milk} 31 whole-grain diet 40 yogurt 41 |
Bottom Line
There is no definitive right way to determine how to correct a dysbiosis. We just do not have enough studies. Above, you have two main approach (with some overlap of suggestions)
- Working off the microbiome that are too high or too low.
- We cross check probiotics suggestions using KEGG data
- Working off the microbiome using only peer reviewed studies for one condition: depression.
- This report should have high creditability with most medical types — because all of the evidence used to make the report is cited.











Recent Comments