Backstory
As I’ve been suspected to have Lyme disease, I have taken antibiotics for several months which have damaged my microbiome. Now I am taking antibacterial herbs.
From Email
* As my brain fog severely increased, I need your help to adjust my strategy. In addition, there are some specific questions:
I am contacting you as I have done a new microbiome analysis with BiomeSight. I haven’t been doing well in addition to my previous health issues. As I’ve been suspected to have Lyme disease, I have taken antibiotics for several months which have damaged my microbiome. Now I am taking antibacterial herbs.
As my brain fog severely increased, I need your help to adjust my strategy. In addition, there are some specific questions:
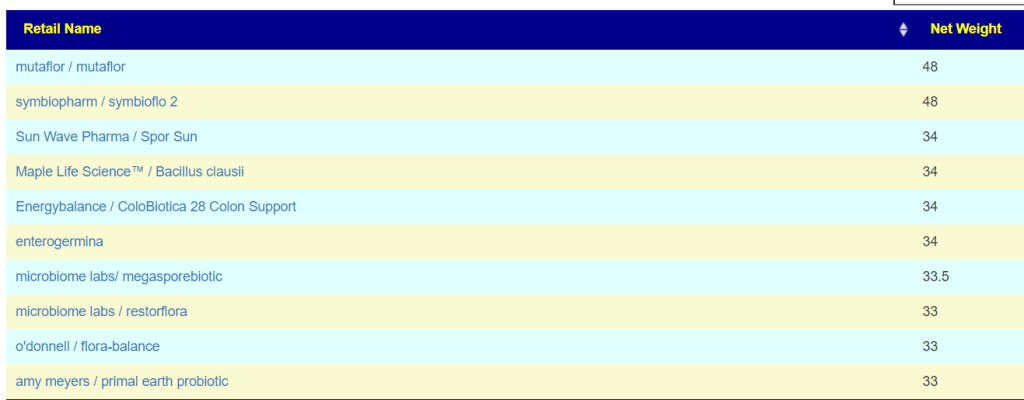
❔mutaflor isn’t among the suggestions done. Would it be a good thing to add it ?
❔how long should I wait between probiotics and antibacterial herbs ?
Analysis Of Data
I have a pretty fixed attitude to Lyme
- It’s Lyme only with a very clear laboratory result (i.e. tests for actual Borrelia species and strains and conforms to the rest of CDC criteria).
- “Chronic Lyme” is likely post-infection syndrome and the use of “Lyme antibiotics” can often do more harm than good. “Suspected Lyme” is a red flag that the medical practitioner is outside of their depth.
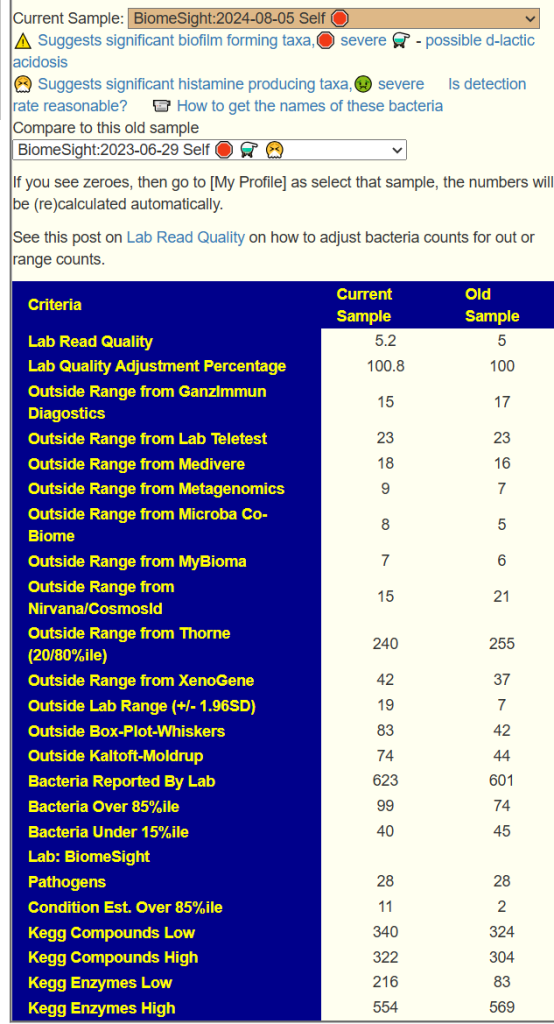
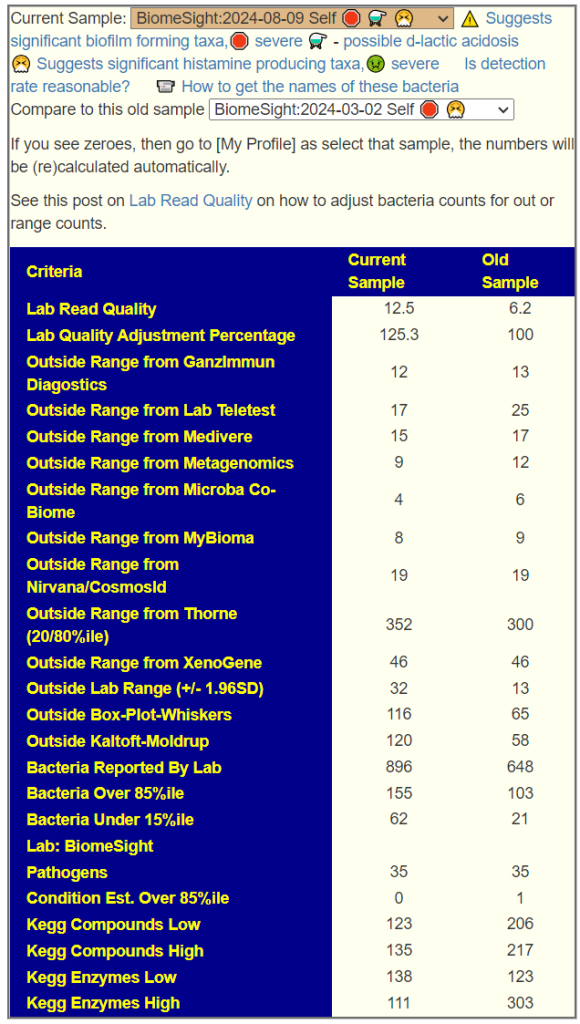
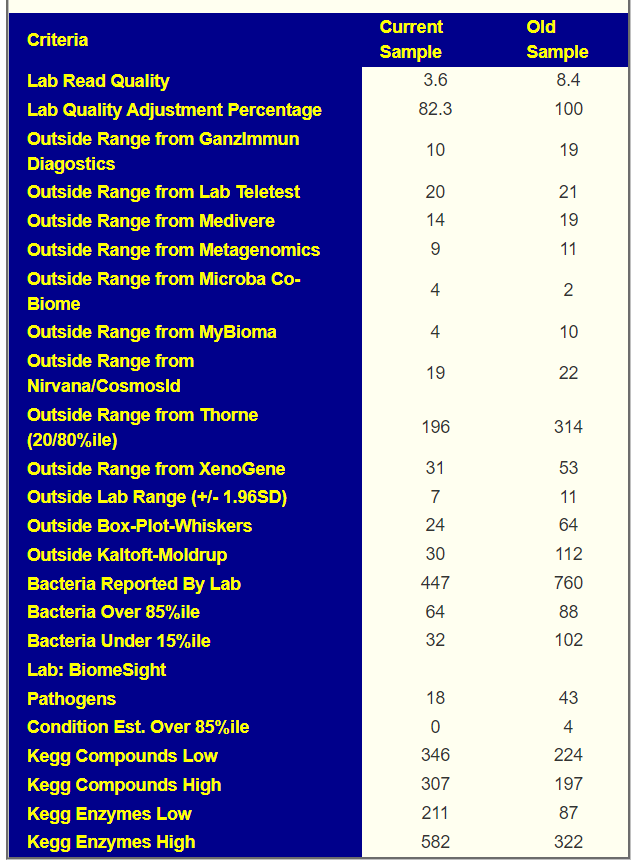
We have three samples available. There was some apparent improvements from earlier samples (
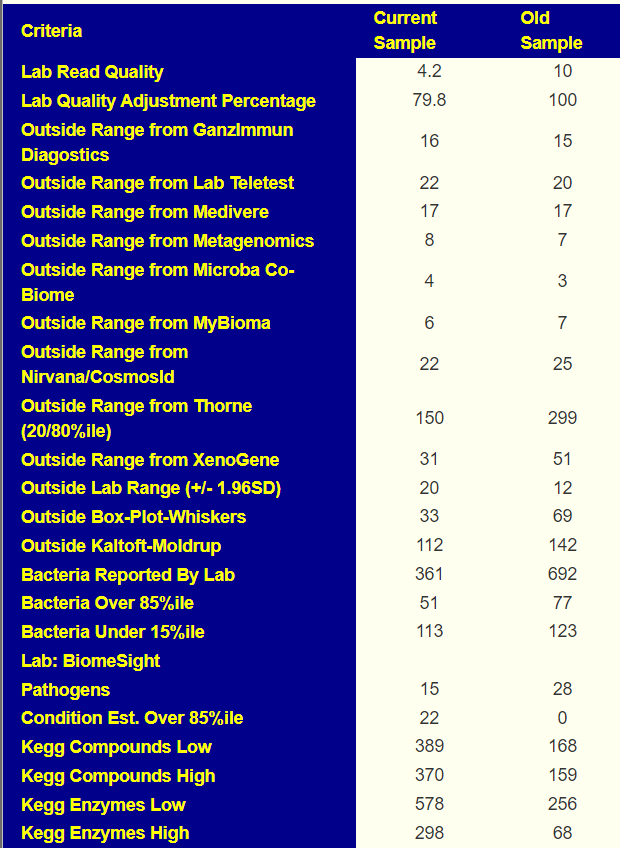
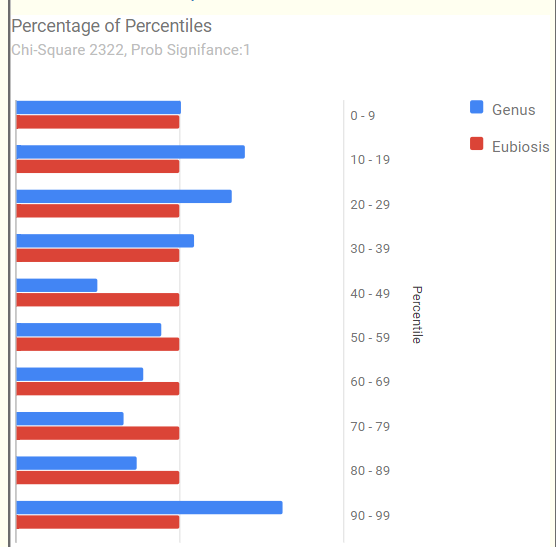
Comparing current sample to the first sample is shown below. The number of bacteria reported is almost half of the prior test, making comparison difficult, but my impression is that there was some improvement.
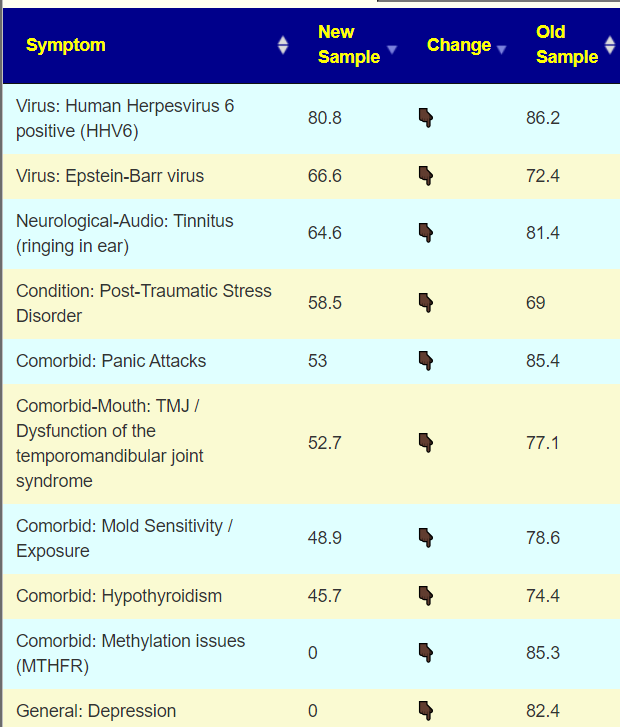
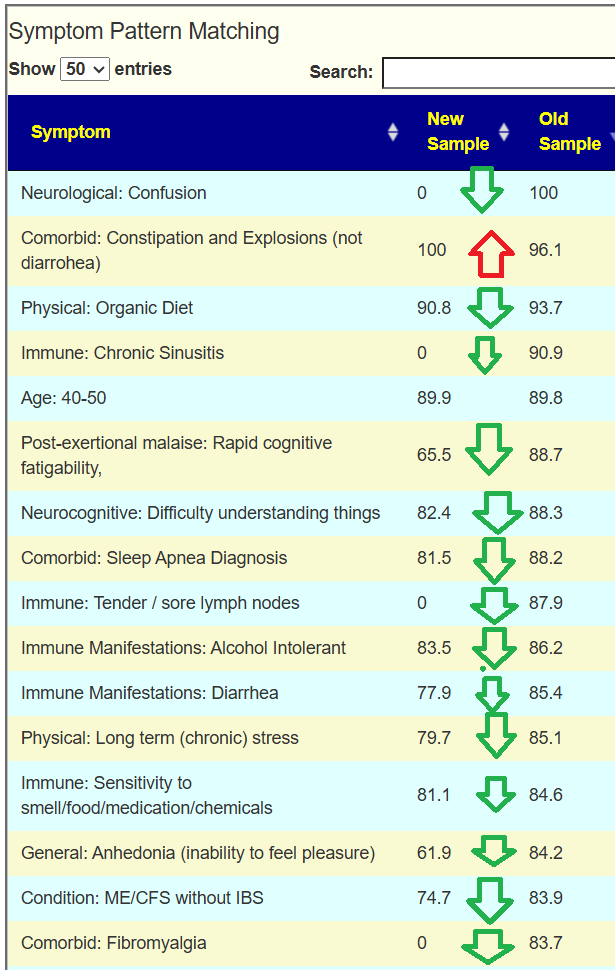
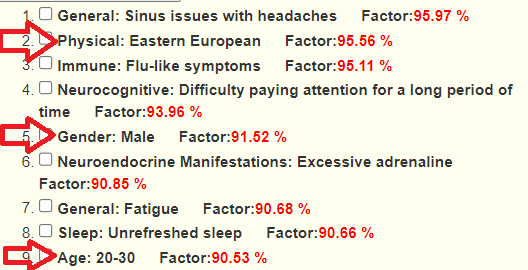
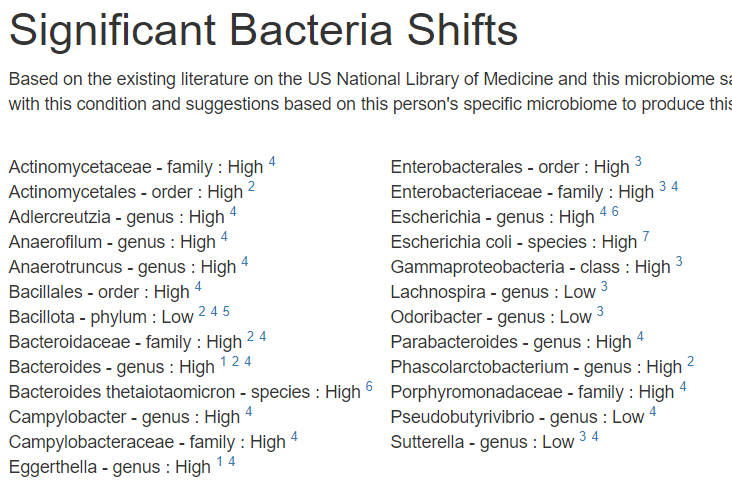
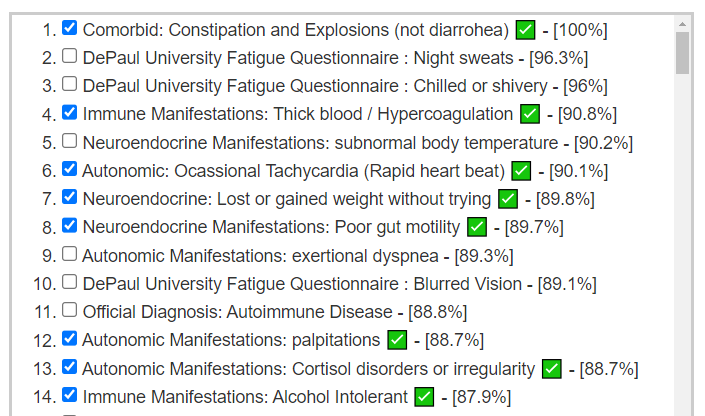
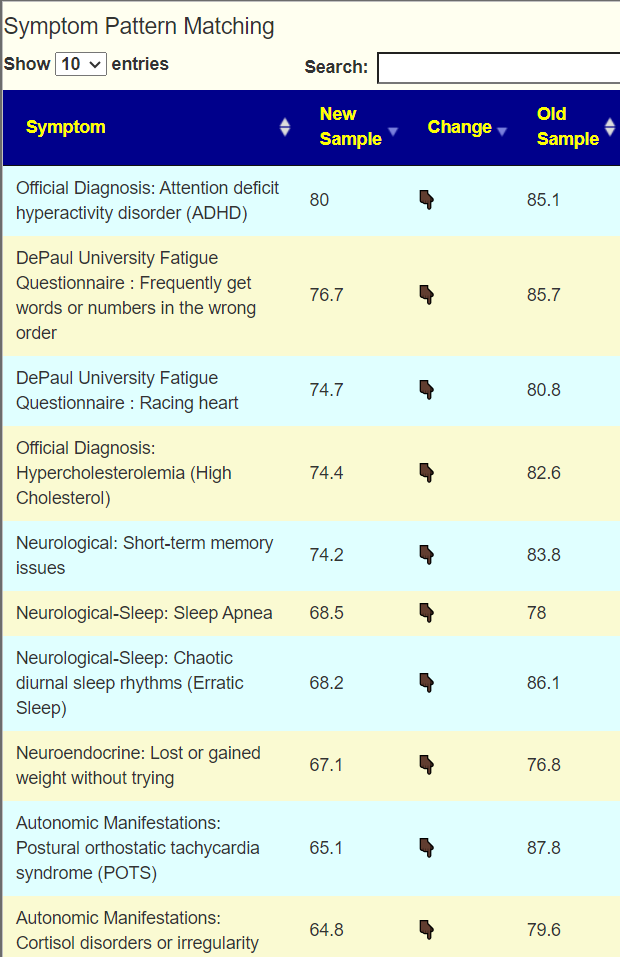
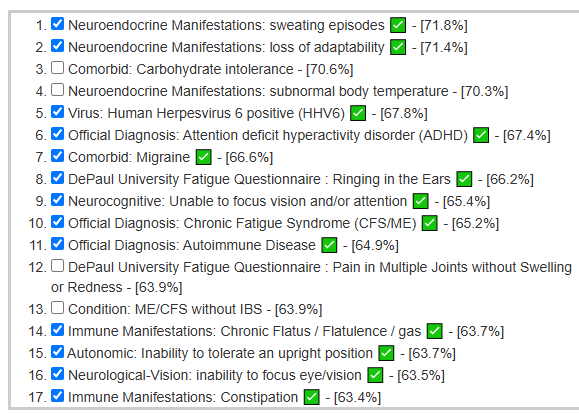
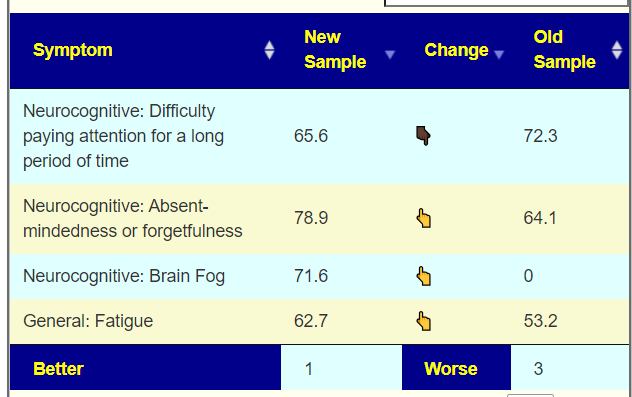
Looking at the new symptom matching comparison , we see some significant drops.
Going Forward
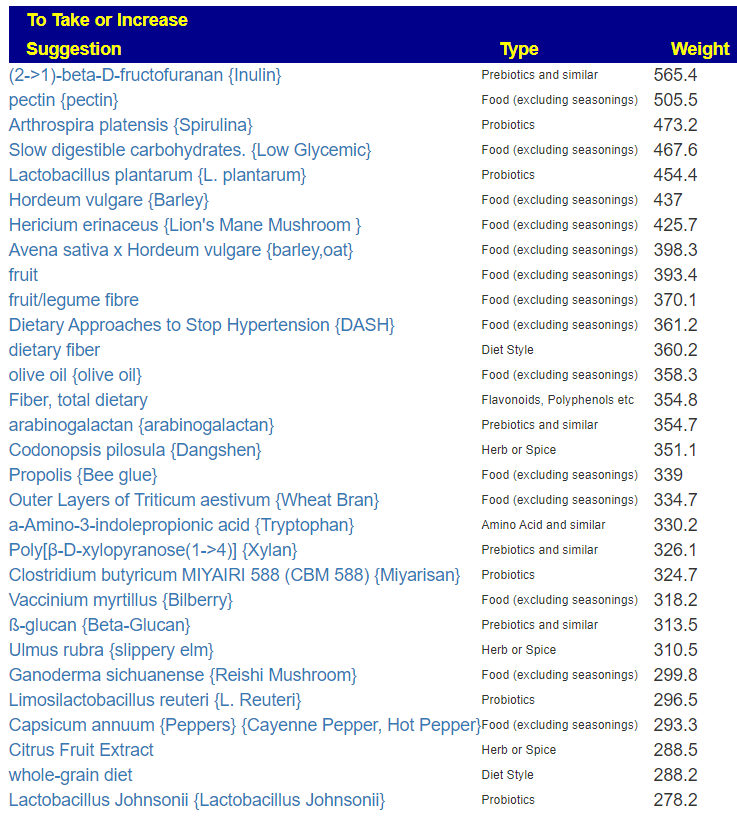
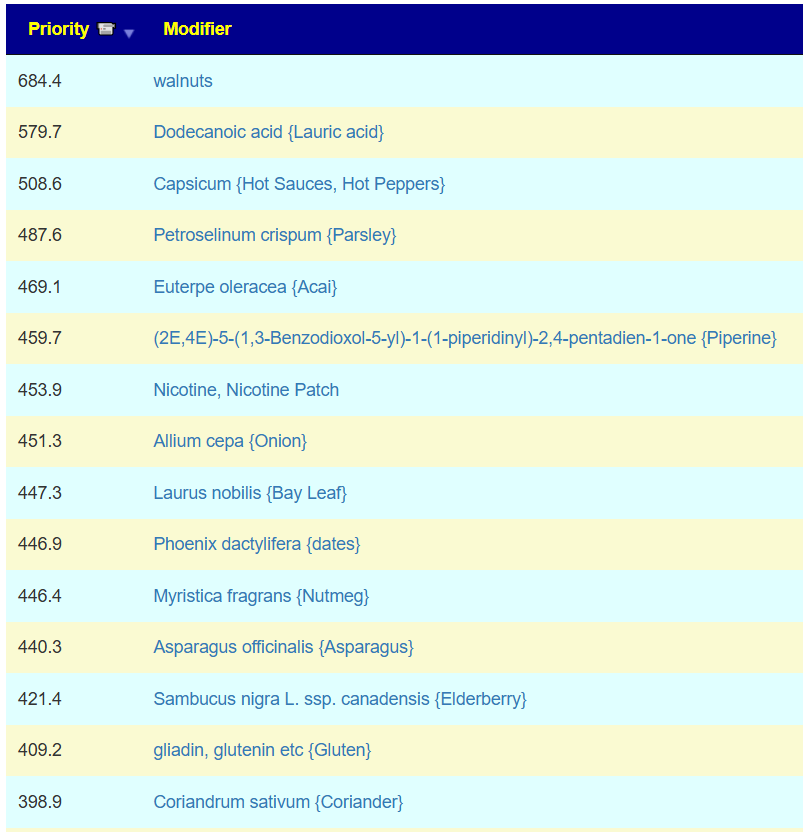
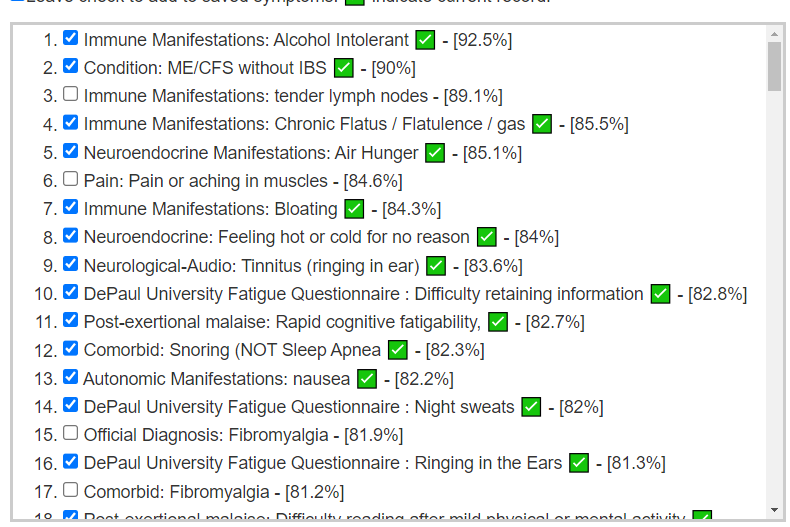
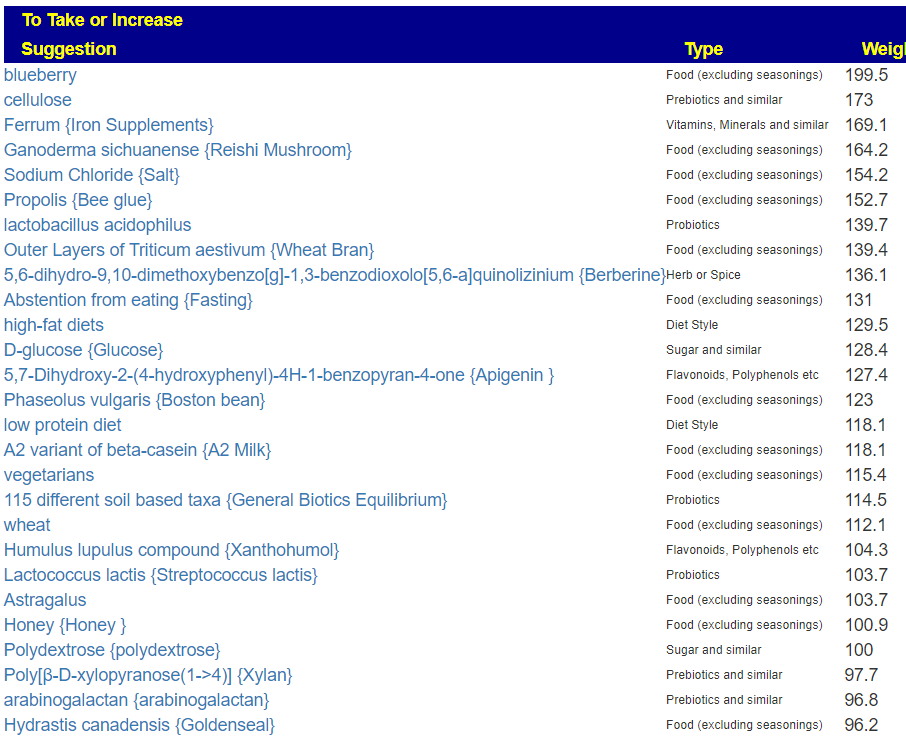
Since symptoms have been entered, we will go with [Beginner-Symptoms: Select bacteria connected with symptoms]. This results in 29 bacteria being identified (about 8% of the bacteria – my preferred range is 4- 12% being flagged to be of concern).
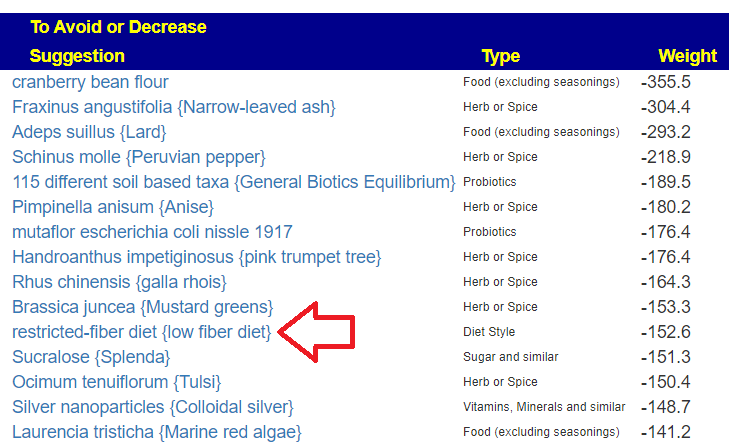
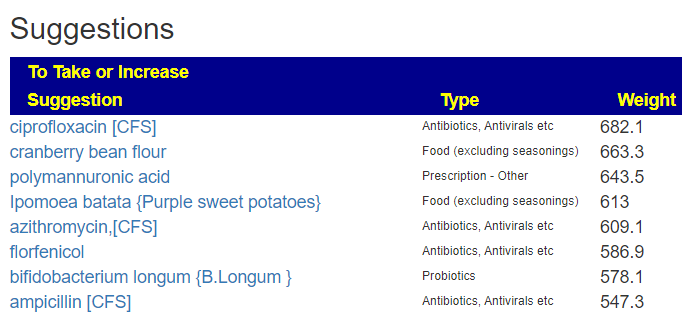
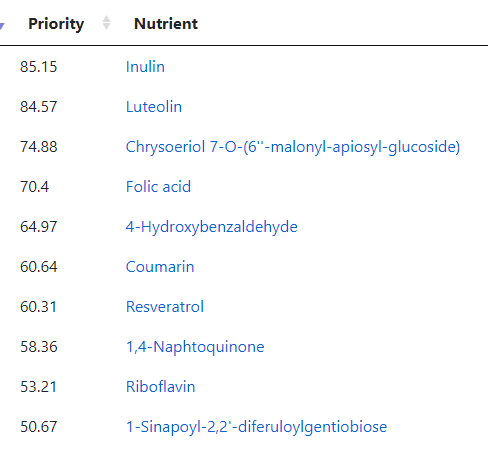
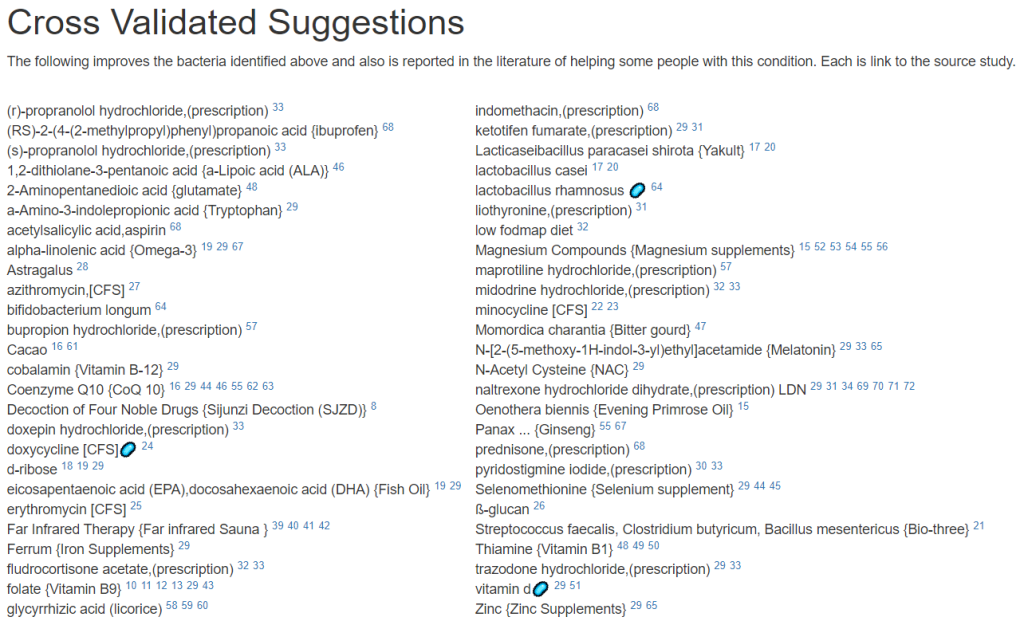
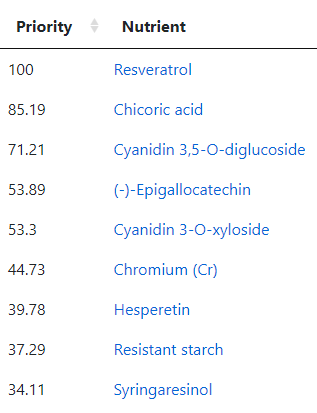
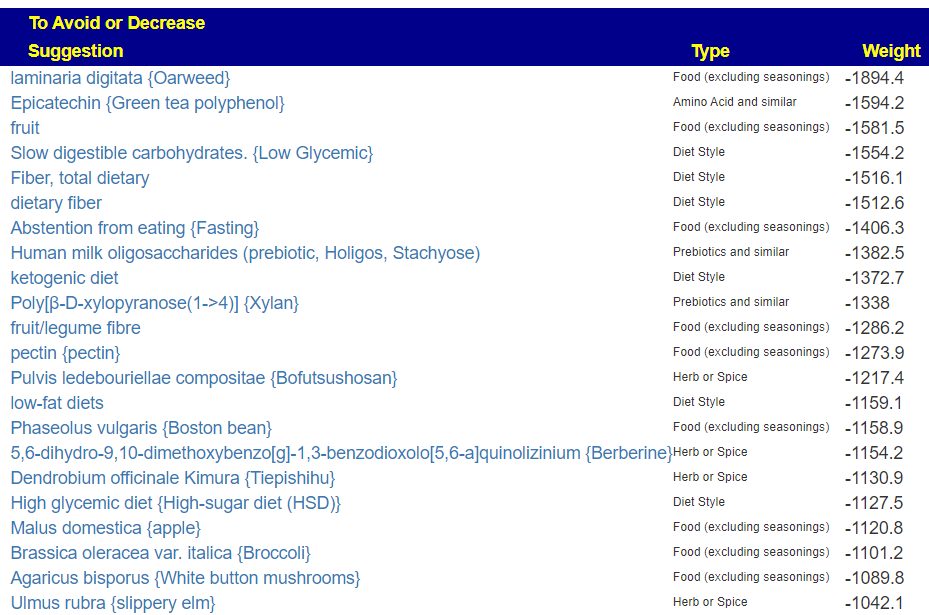
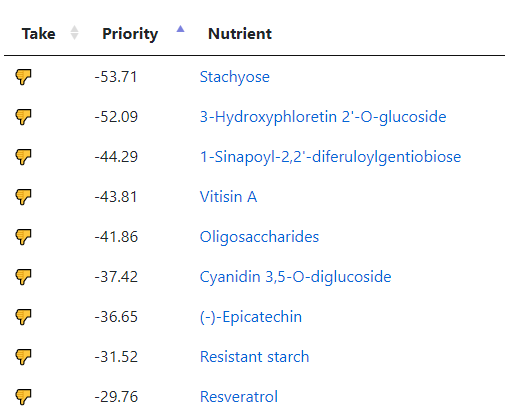
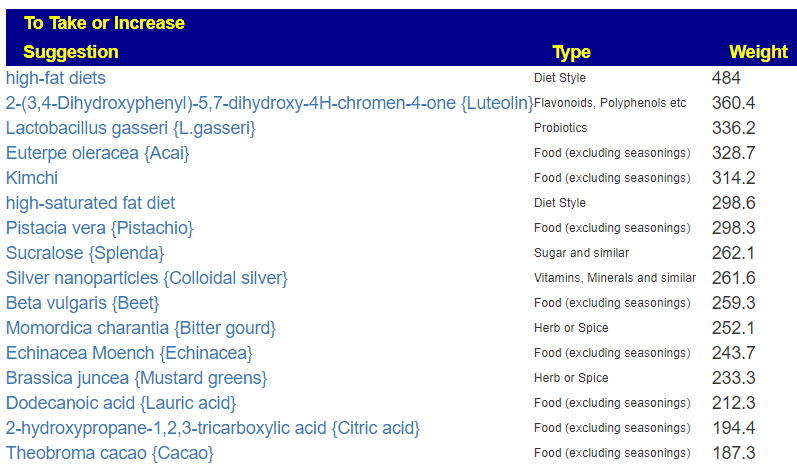
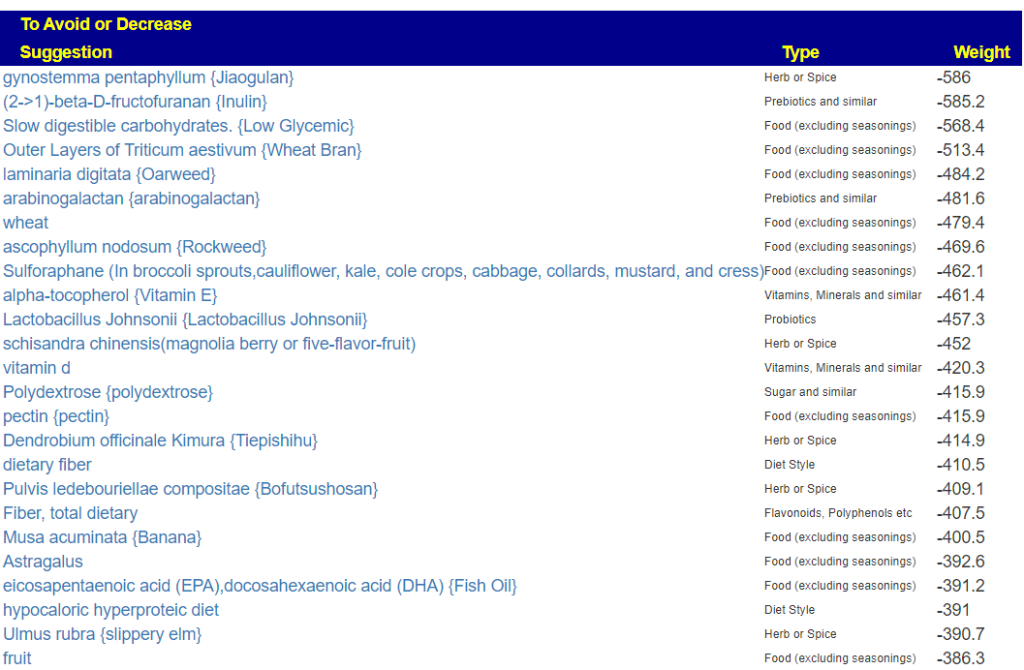
The top suggestions are below which are heavy in fiber and beta-glucan. A common pattern with post-infection syndrome.
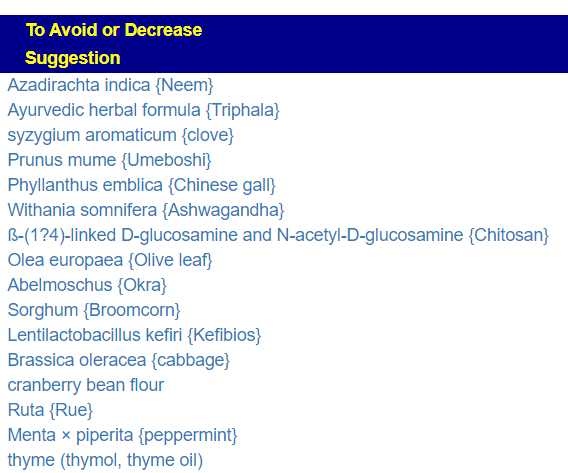
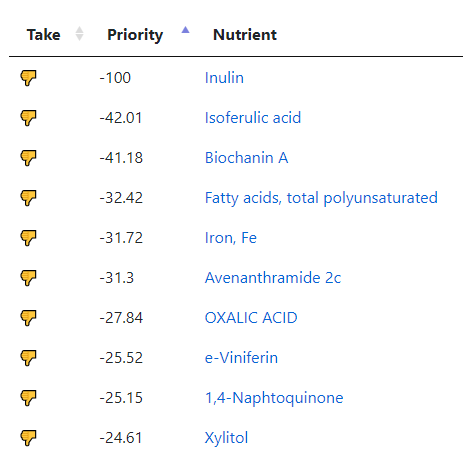
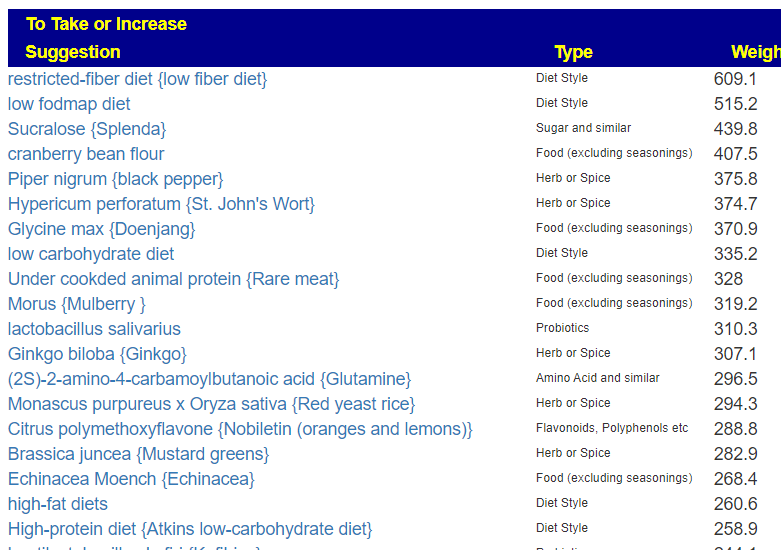
The avoids echo this high fiber approach
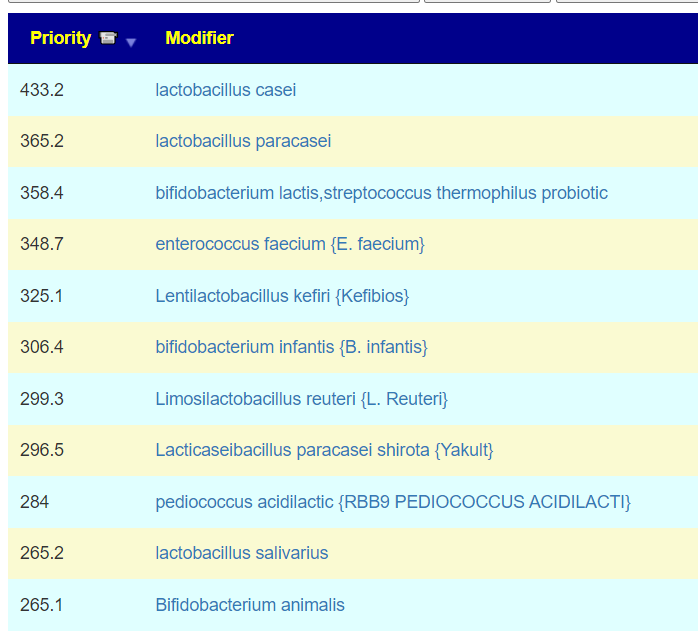
Probiotics
We actually have three lists to compare:
- To take (with some possible adverse interactions)
- Positive effect with no known risk of adverse interactions
- aor / probiotic-3 [69]
- Lactobacilos Reuteri [55]
- miyarisan [64]
- bioflorin [56]
- Lactobacillus salivarius [41]
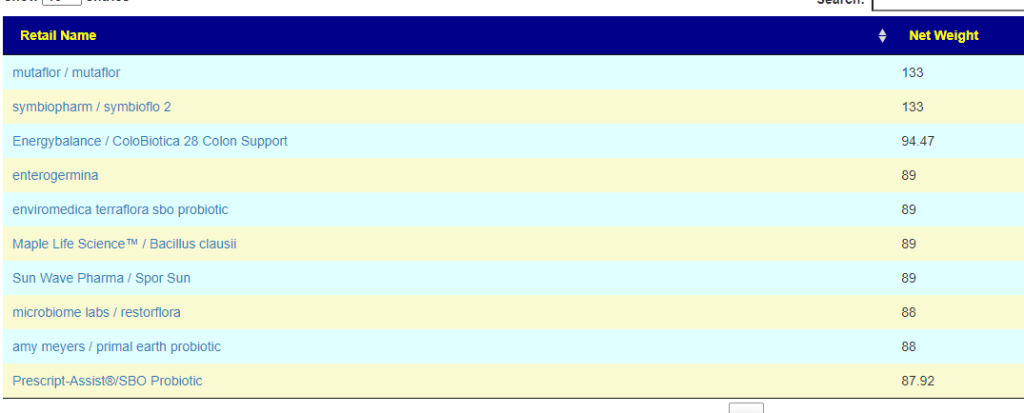
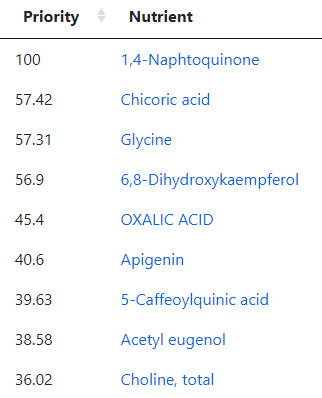
- Probiotics computed from KEGG compounds found deficient (low). Top ones were
- mutaflor / mutaflor (E.Coli) [133]
- Energybalance / ColoBiotica 28 Colon Support [95]
- Bacillus clausii [89]
The numbers in the [ ] are the number of compound that are low that the probiotic produces. Enzymes shortage usually leads me towards probiotics because they are producers of many enzymes. Most of these enzymes are not available as supplements. When there are shortages, bacteria misbehaves… “when the manager is empty, horses bite”
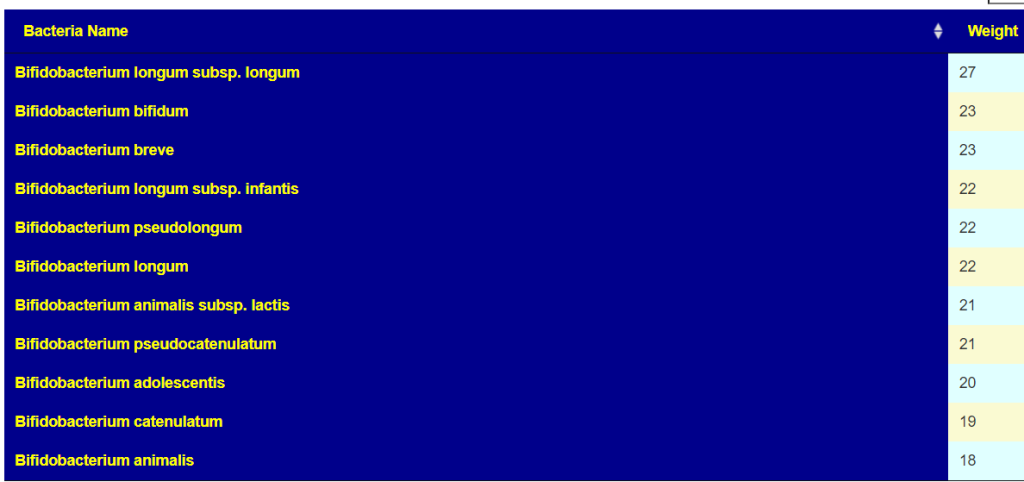
My suggestion for rotations (1 probiotic for 1-2 weeks and then move on to the next)
Alternative Paths
At this point, we branch into two additional paths — one by using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) data on compound being produce and consumed by your microbiome. With KEGG we look for probiotics that can provide enzymes etc that you are deficient in. Why these alternative paths? Simple, there is not enough data available so we use inference.
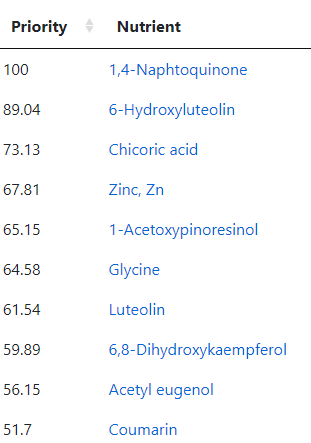
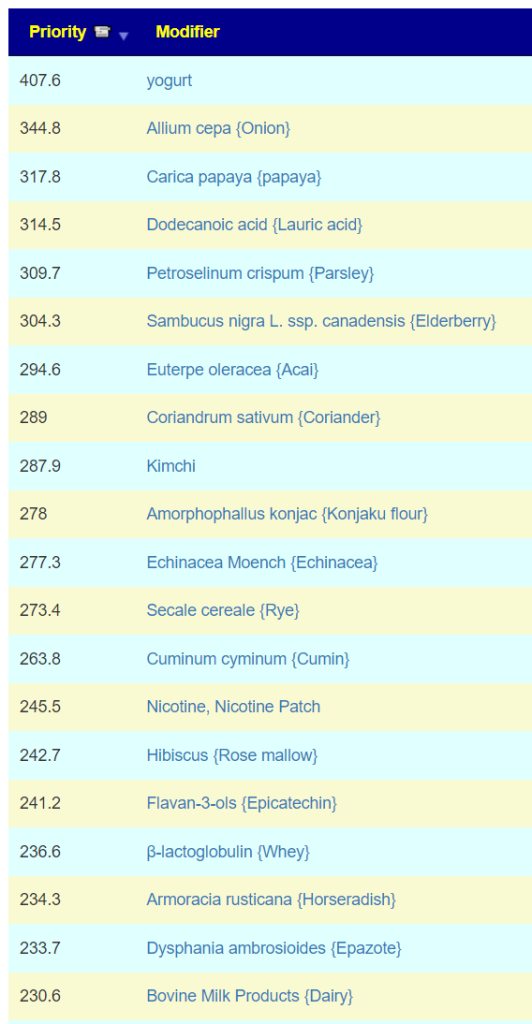
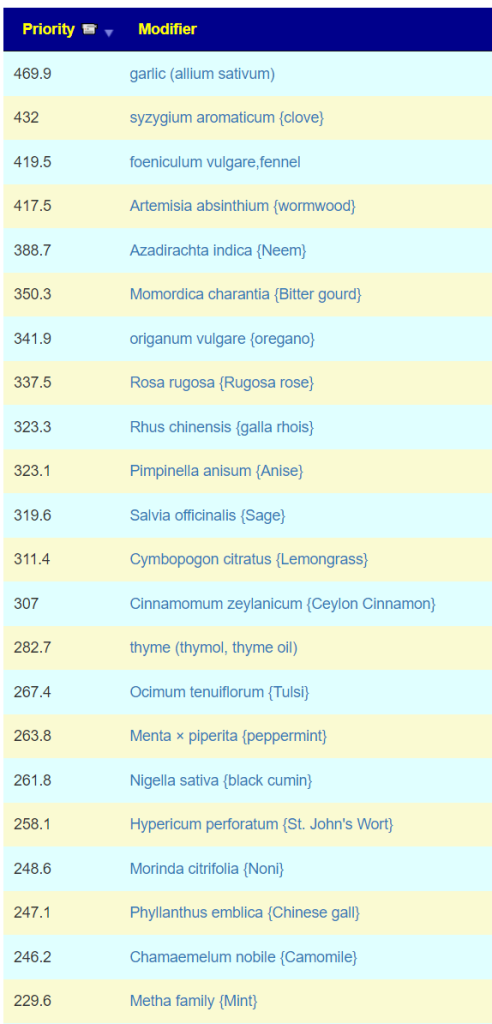
The second path is going to the food site to identify foods rich in suggested nutrients. The foods may not have been used in studies, but the dominant nutrients in the foods may have been studied.
KEGG
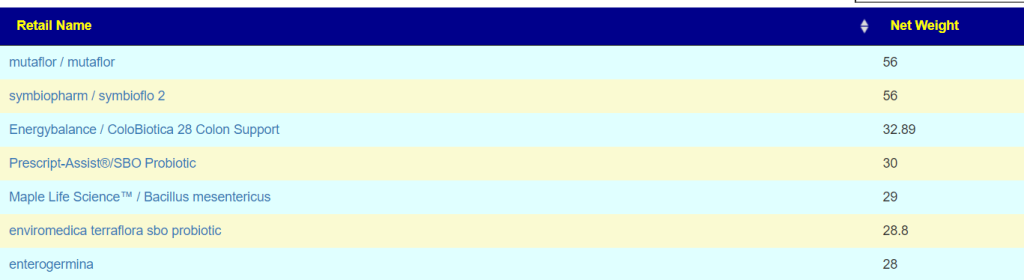
The top suggestions are below. #1 item is common for ME/CFS, Mutaflor is available in some countries in Europe, I warn people that it may cause a major die-off / herx reaction. Symbioflor 2 is the same probiotic species but at ~ 1/100 of the BCFU and unlikely to cause die off. These are reasonable “2nd rank” probiotics to try. The evidence is by inference and not direct study.
Food
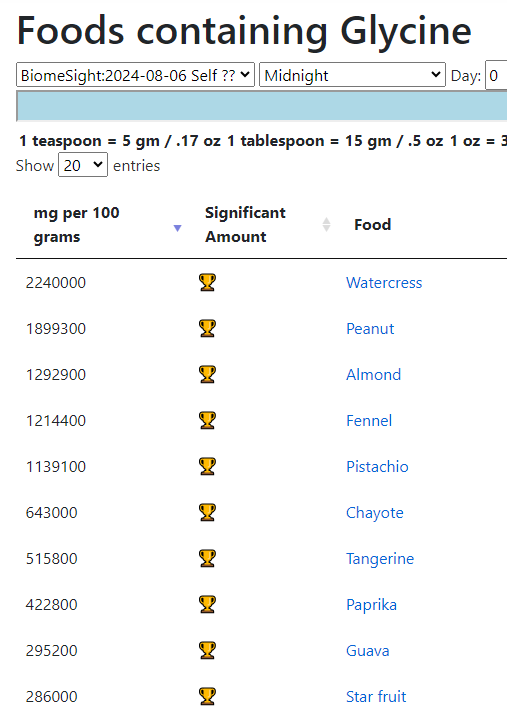
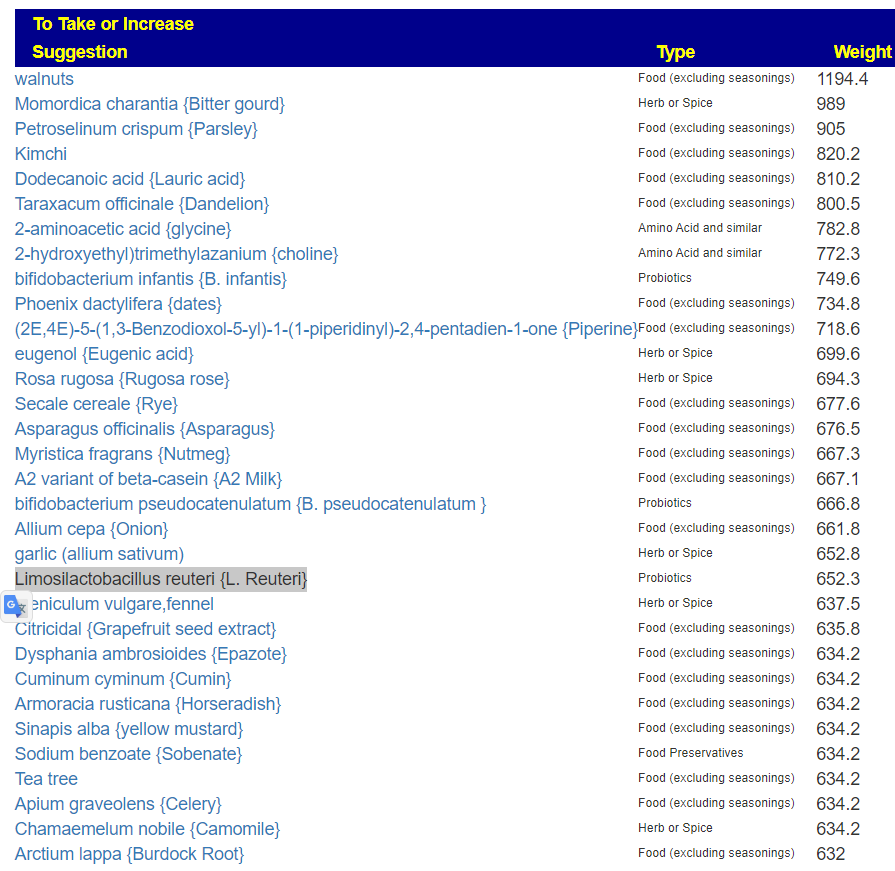
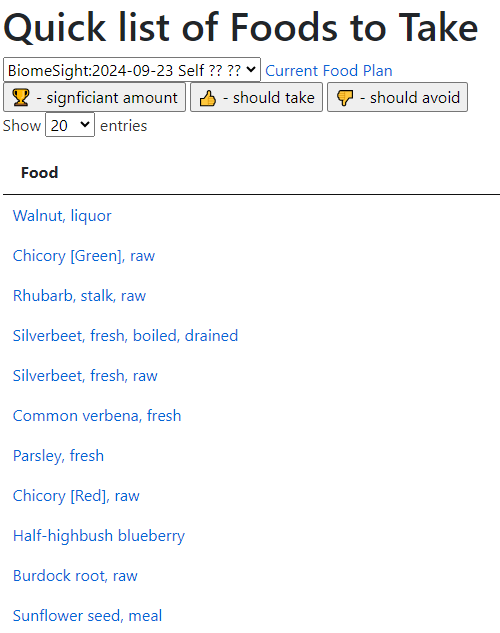
Going to the food site, we find walnuts, almonds,cocao/dark chocolate, and beef at the top of the list. The following food groups should be added to the menu also:
Questions
❔ Brain fog
- Usually this is due to d-lactic acid which is produced by some Lactobacillus species but not by Bifidobacterium and others. You may wish to skip those in the above list. Thick blood is another common cause for brain fog.
Other things to try (assuming d-lactic is the cause):- Sodium Bicarbonate (baking soda)
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1) – Low on Avoid list
- Calcium Supplements – Low on suggestions list
❔mutaflor isn’t among the suggestions done. Would it be a good thing to add it ?
- Mutaflor is at present on the avoid list but top of the KEGG list. It is worth doing a short trial to resolve if it is good or bad for you. I put it at the bottom of the list, in the hope that the other probiotics would cause changes that it can use.
❔how long should I wait between probiotics and antibacterial herbs ?
- Typically I suggest 2-3 weeks of probiotics and then a switch. Above we have a variety of nuts (remember peanuts are not nuts) and other foods that are not deemed antibacterial. My general impression of the suggestions is that encouraging good bacteria (instead of killing bad bacteria) is the desired direction.
Postscript and Reminder
As a statistician with relevant degrees and professional memberships, I present data and statistical models for evaluation by medical professionals. I am not a licensed medical practitioner and must adhere to strict laws regarding the appearance of practicing medicine. My work focuses on academic models and scientific language, particularly statistics. I cannot provide direct medical advice or tell individuals what to take or avoid.My analyses aim to inform about items that statistically show better odds of improving the microbiome. All suggestions should be reviewed by a qualified medical professional before implementation. The information provided describes my logic and thinking and is not intended as personal medical advice. Always consult with your knowledgeable healthcare provider.
Implementation Strategies
- Rotate bacteria inhibitors (antibiotics, herbs, probiotics) every 1-2 weeks
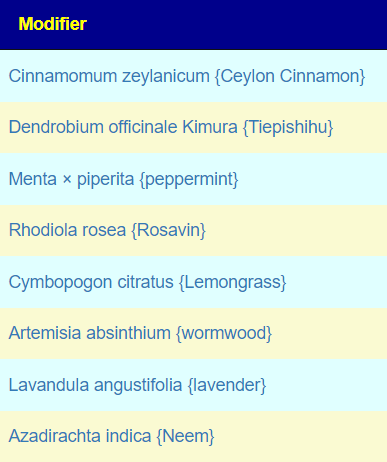
- Some herbs/spices are compatible with probiotics (e.g., Wormwood with Bifidobacteria)
- Verify dosages against reliable sources or research studies, not commercial product labels. This Dosages page may help.
- There are 3 suppliers of probiotics that I prefer: Custom Probiotics , Maple Life Science™, Bulk Probiotics: see Probiotics post for why
Professional Medical Review Recommended
Individual health conditions may make some suggestions inappropriate. Mind Mood Microbes. outlines some of what her consultation service considers:
A comprehensive medical assessment should consider:
- Terrain-related data
- Signs of low stomach acid, pancreatic function, bile production, etc.
- Detailed health history
- Specific symptom characteristics (e.g., type and location of bloating)
- Potential underlying conditions (e.g., H-pylori, carbohydrate digestion issues)
- Individual susceptibility to specific probiotics
- Nature of symptoms (e.g., headache type – pressure, cluster, or migraine)
- Possible histamine issues
- Colon acidity levels
- SCFA production and acidification needs
A knowledgeable medical professional can help tailor recommendations to your specific health needs and conditions.











Recent Comments