For the last decade I have been citing literature for the appropriate dosage levels of Vitamin D. The RDA level is not sufficient for a healthy microbiome — it is sufficient only to stop rickets from occurring.
Some old citations from 2015 Post
- “Several diseases have been linked to vitamin D deficiency, such as hypertension, diabetes, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain syndromes such as fibromyalgia. ” [2013]
- “Vitamin D deficiency was defined as a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations ≤20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L). The overall prevalence rate of vitamin D deficiency was 41.6%,” [2011]
- “Older adults are advised to maintain serum 25(OH)D concentrations >75 nmol/L.” [2006]
- Dr. Mercola recommends 45-50 ng/ml or 115-128 nmol/l [source]
- “Vitamin D intakes required to maintain serum 25(OH)D concentrations of >80 nmol/L in 97.5% of the sample[of men and women aged 20-40 y] were … 41.1μg/d (1640 IU), respectively.” [2008]
- “The clinical trial evidence shows that a prolonged intake of 250 mug (10,000 IU)/d of vitamin D(3) is likely to pose no risk of adverse effects in almost all individuals in the general population; this meets the criteria for a tolerable upper intake level.” [2007]
- “Evidence from clinical trials shows, with a wide margin of confidence, that a prolonged intake of 10,000 IU/d of vitamin D(3) poses no risk of adverse effects for adults,” [2009]
- NOTE: there was no evidence going 50% higher has any risks. The studies just tested the 10,000IU level.
- “Vitamin D, important for maintaining bone health in Crohn Disease[CD], may have potential as a treatment for the core inflammatory disease process. There is plausible evidence in favour of vitamin D as an anti-inflammatory from animal models, epidemiological and cross sectional studies of CD.”[2015]
- “Active Crohn’s disease was associated with low serum 25-OH vitamin D.”[2013]
- “In addition, low vitamin D has been associated with disease activity in CD patients, and supplementation appears to be beneficial in improving clinical scores and reducing inflammation.” [2014]
- “Vitamin D is an inexpensive supplement which has been shown to improve IBD outcomes.”[2014]
- “people with IBD may remain in remission longer when treated with oral vitamin D…suggest that vitamin D may modify the immune response in IBD.” [2015]
And from my 2017 post:
- “This study demonstrates for the first time a direct antiviral effect of vitamin D in an in vitro infectious virus production system.”[2011]
- “vitamin D is the environmental factor that most strongly influences autoimmune disease development.”[2015]
- “A significant negative correlation between vitamin D level and widespread pain index was found.”[2012] i.e. FM
- Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and BAFF Levels Are Associated with Disease Activity in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome [2017]. “Female SS patients had significantly lower vit D levels than controls” [2015]
- “Our findings showed that the high-dose supplementation of vitamin D[9 of 50000 IU cholecalciferol capsules for 3 months taken at weekly intervals] affects measures of systemic inflammation: reductions in High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein level and Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) distribution.” [2017]
- “The results of the meta-analysis of 10 trials involving a total of 924 participants showed that vitamin D supplementation significantly decreased the circulating hs-CRP level by 1.08 mg/L” [2014]
This is a good technical discussion: Vitamin D3 Deficiency Results in Dysfunctions of Immunity with Severe Fatigue and Depression in a Variety of Diseases [2014]
I mentioned a formula from 2010 in the first post. Fortunately, there are several Vitamin D calculator available. I put in the numbers from the above post below
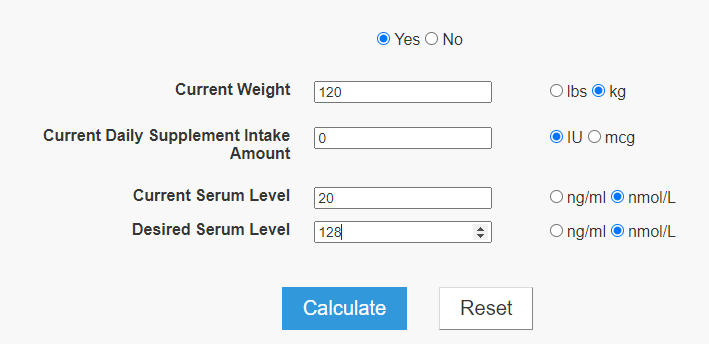
The numbers agree with my 2015 calculated example. 10,000 IU/day over 3 months
The factor not considered is age. Vitamin D absorption decreases with age;
- Relationship between age-related decreases in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and skeletal muscle mass in Japanese women [2020] which reports what appears to reflect decreased ability to absorb with age:
- Males 15% drop in the ability to absorb once you get over 50.
- Females 45% drop in the ability to absorb once you get over 50.
- This suggests that the dosage computed by the calculator needs to be doubled for a female over 50.
In addition to classic role of vitamin D in musculoskeletal health over the last decade it was shown that low blood serum concentrations of 25(OH)D are associated with a number of non-skeletal disorders including cancer, high blood pressure, age-related cognitive decline, disorders of the immune and reproductive systems, etc. The prevention of the development of these diseases is reached under considerably higher concentrations of the vitamin in the blood serum, than is necessary to maintain the normal state of the bone tissue, to regulate calcium absorption and homeostasis
[Physiological needs and effective doses of vitamin D for deficiency correction. Current state of the problem [2017]
“Vitamin D was first discovered as the curative agent for nutritional c, and its classical actions are associated with calcium absorption and bone health. However, vitamin D exhibits a number of extra-skeletal effects, particularly in innate immunity. Notably, it stimulates production of pattern recognition receptors, anti-microbial peptides, and cytokines, which are at the forefront of innate immune responses. They play a role in sensing the microbiota, in preventing excessive bacterial overgrowth, and complement the actions of vitamin D signaling in enhancing intestinal barrier function. Vitamin D also favours tolerogenic rather than inflammogenic T cell differentiation and function. Compromised innate immune function and overactive adaptive immunity, as well as defective intestinal barrier function, have been associated with IBD. Importantly, observational and intervention studies support a beneficial role of vitamin D supplementation in patients with Crohn’s disease, a form of IBD. This review summarizes the effects of vitamin D signaling on barrier integrity and innate and adaptive immunity in the gut, as well as on microbial load and composition. Collectively, studies to date reveal that vitamin D signaling has widespread effects on gut homeostasis, and provide a mechanistic basis for potential therapeutic benefit of vitamin D supplementation in IBD.”
Vitamin D signaling in intestinal innate immunity and homeostasis [2017]
- Molecular basis of vitamin D action in inflammatory bowel disease [2022]
- Vitamin D Modulates Intestinal Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. [2020]
- Immunomodulatory Properties of Vitamin D in the Intestinal and Respiratory Systems. [2023]
There is no appropriate dosage to take without lab results. I know females over 50 that freaked out their physician when they stated that they were taking 20,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily for the last 2 years. Lab tests were quickly ordered!! The lab tests showed her just above the middle of the normal range. The ability to absorb is significantly reduced with IBS, IBD, UC, Crohn’s disease, etc. It’s a matter of getting the labs, take an aggressive dosage for 6 months, retest and then adjust the dosage according to the new results.
“The biggest problem is that MDs are often behind the times and do not work from the latest literature. For example a single dosage of 600,000 IU of vitamin D is deemed safe on medscape, or 10,000 IU/day for months [source]. One of the studies above cited an average of 60,000 IU/day for 3 months! [2017]”
From my 2017 post
Target Dosages?
At least 128 nmol/l or 50 ng/mL. You want to be at the TOP of the normal range. You will get push back from MD with higher level because of medical myth that above this is toxic. I say myth because there is no evidence in the literature. There were issues with Vitamin D2 supplements which was sold for a while because it was cheap to produce and is chemically different.
Of 20,308 measurements, 8 percent of the people who had their vitamin D measured had levels greater than 50 ng/mL, and less than 1 percent had levels over 100 ng/mL.
“We found that even in those with high levels of vitamin D over 50 ng/mL, there was not an increased risk of hypercalcemia, or elevated serum calcium, with increasing levels of vitamin D,” says study co-author Thomas D. Thacher, M.D., a family medicine expert at Mayo Clinic. [2015]
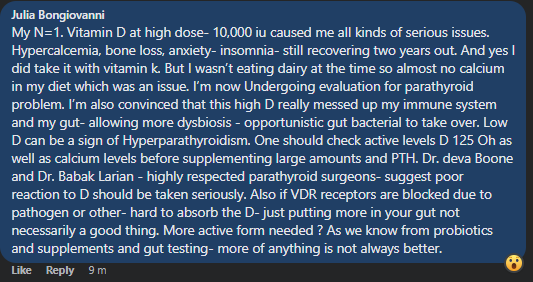
Of course, there are some rare DNA mutations that could cause problems with that level. One person’s experience with the details. If you have adverse reaction — get the additional tests described below.
Vitamin D Is Not as Toxic as Was Once Thought: A Historical and an Up-to-Date Perspective [2015]
“(Obese adults require doses 2-3 times higher.)”
“The evidence is clear that vitamin D toxicity is one of the rarest medical conditions and is typically due to intentional or inadvertent intake of extremely high doses of vitamin D (usually in the range of >50,000-100,000 IU/d for months to years).”
Hmmm. I have been trying to take D3 supplements unsuccessfully for years. Everytime I try it makes me feel like I have a bad flu the following day. This happens with even just a dose of 400iu. Anyone have a clue why this could be happening and how to get around it?
You may wish to read this article published this week on Vitamin D issues.
https://www.newscientist.com/article/2372443-having-naturally-high-vitamin-d-levels-may-protect-against-psoriasis/