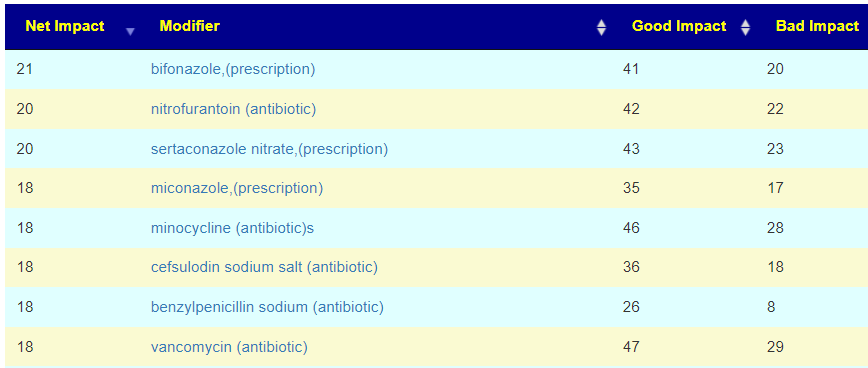
| Net | Modifier2 | Good Impact | Bad Impact |
| 24 | bacillus subtilis (probiotics) | 34 | 10 |
| 21 | lactobacillus casei (probiotics) | 30 | 9 |
| 20 | pomegranate | 27 | 7 |
| 19 | resistant starch | 34 | 15 |
| 19 | whey | 22 | 3 |
| 19 | bifidobacterium longum (probiotics) | 22 | 3 |
| 18 | pediococcus acidilactic (probiotic) | 21 | 3 |
| 17 | brown rice | 23 | 6 |
| 17 | wheat | 24 | 7 |
| 17 | oregano (origanum vulgare, oil) | | 24 | 7 |
| 16 | almonds/ almond skins | 18 | 2 |
| 15 | soy | 25 | 10 |
| 15 | vitamin d | 29 | 14 |
| 14 | walnuts | 27 | 13 |
| 14 | whole-grain barley | 22 | 8 |
| 14 | pectin | 22 | 8 |
| 14 | wheat bran | 24 | 10 |
| 14 | Cacao | 21 | 7 |
| 14 | dietary fiber | 14 | 0 |
| 14 | lactobacillus plantarum,xylooligosaccharides,(prebiotic) (probiotics) | 16 | 2 |
| 14 | lactobacillus reuteri (probiotics) | 27 | 13 |
| 14 | fish oil | 17 | 3 |
| 14 | proline (amino acid) | 19 | 5 |
| 14 | bifidobacterium bifidum (probiotics) | 25 | 11 |
| 13 | lactobacillus paracasei (probiotics) | 22 | 9 |
| 13 | lactobacillus acidophilus (probiotics) | 22 | 9 |
| 13 | Human milk oligosaccharides (prebiotic, Holigos, Stachyose) | 28 | 15 |
| 12 | raffinose(sugar beet) | 16 | 4 |
| 12 | lauric acid(fatty acid in coconut oil,in palm kernel oil,) | 17 | 5 |
| 12 | high fiber diet | 20 | 8 |
| 12 | rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary) | 25 | 13 |
| 12 | Conjugated Linoleic Acid | 14 | 2 |
| 12 | Alpha-Ketoglutarate | 18 | 6 |
| 12 | Burdock Root | 16 | 4 |
| 11 | glycine | 17 | 6 |
| 11 | Glucomannan | 11 | 0 |
| 11 | pea (fiber, protein) | 16 | 5 |
| 11 | fructo-oligosaccharides (prebiotic) | 26 | 15 |
| 11 | lactobacillus rhamnosus (probiotics) | 23 | 12 |
| 11 | lactobacillus rhamnosus gg (probiotics) | 19 | 8 |
| 11 | lactobacillus casei shirota (probiotics) | 13 | 2 |
| 11 | fat | 20 | 9 |
| 11 | bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum,(probiotics) | 15 | 4 |
| 11 | bifidobacterium infantis,(probiotics) | 17 | 6 |
| 11 | polyphenols | 14 | 3 |
| 11 | saccharomyces boulardii (probiotics) | 20 | 9 |
| 11 | oligofructose (prebiotic) | 12 | 1 |
| 11 | apple | 21 | 10 |
| 11 | whole grain,bran | 11 | 0 |
| 10 | vsl#3 (probiotics) | 14 | 4 |
| 10 | naringenin(grapefruit) (Flavonoid) | 13 | 3 |
| 10 | lupin seeds (anaphylaxis risk, toxic if not prepared properly) | 20 | 10 |
| 10 | magnesium | 12 | 2 |
| 10 | red wine | 23 | 13 |
| 10 | broad beans | 20 | 10 |
| 10 | fasting | 16 | 6 |
| 10 | lactobacillus plantarum (probiotics) | 28 | 18 |
| 10 | inulin (prebiotic) | 26 | 16 |
| 10 | enterococcus faecium (probiotic) | 15 | 5 |
| 10 | hou-po-da-huang-tang | 11 | 1 |
| 9 | Goji (berry,juice) | 15 | 6 |
| 9 | fruit/legume fibre | 16 | 7 |
| 9 | oligosaccharides (prebiotic) | 12 | 3 |
| 9 | banana | 10 | 1 |
| 9 | bifidobacterium adolescentis,(probiotics) | 12 | 3 |
| 9 | bifidobacterium animalis lactis (probiotics) | 16 | 7 |
| 9 | anise | 13 | 4 |
| 9 | triphala | 34 | 25 |
| 9 | zinc | 27 | 18 |
| 9 | vitamin a | 23 | 14 |
| 8 | trametes versicolor( mushroom) | 10 | 2 |
| 8 | red chiles (Capsicum) | 8 | 0 |
| 8 | xylooligosaccharide (prebiotic) | 9 | 1 |
| 8 | thyme | 15 | 7 |
| 8 | trametes versicolor(Turkey tail mushroom) | 10 | 2 |
| 8 | peppermint | 13 | 5 |
| 8 | persimmon tannin | 9 | 1 |
| 8 | resistant maltodextrin | 16 | 8 |
| 8 | selenium | 9 | 1 |
| 8 | mediterranean diet | 21 | 13 |
| 8 | omega-3 fatty acids | 14 | 6 |
| 8 | palm kernel meal | 12 | 4 |
| 8 | bifidobacterium catenulatum,(probiotics) | 10 | 2 |
| 8 | bacillus subtilis natto (probiotics) | 9 | 1 |
| 8 | cinnamon (oil. spice) | 21 | 13 |
| 8 | high resistant starch | 12 | 4 |
| 8 | green tea | 14 | 6 |
| 8 | jerusalem artichoke (prebiotic) | 11 | 3 |
| 8 | ketogenic diet | 18 | 10 |
| 8 | noni | 12 | 4 |
| 8 | Acacia Gum | 9 | 1 |
| 8 | bacillus,lactobacillus,streptococcus,saccharomyces probiotic | 8 | 0 |
| 8 | yogurt | 8 | 0 |
| 8 | sarcodiotheca gaudichaudii (red sea weed) | 11 | 3 |
| 8 | brown algae | 11 | 3 |
| 8 | Soymilk | 8 | 0 |
| 7 | plantago asiatica l. | 12 | 5 |
| 7 | lactose | 11 | 4 |
| 7 | Codonopsis pilosula | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | rosa rugosa | 11 | 4 |
| 7 | dietary phytoestrogens (isoflavones) | 12 | 5 |
| 7 | chicken | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | sialyllactose (oligosaccharide ) (prebiotic) | 11 | 4 |
| 7 | polygonatum kingianum(Orange Flower Solomon’s Seal.) | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (prebiotic) | 20 | 13 |
| 7 | bacillus pumilus | 9 | 2 |
| 7 | lactobacillus gasseri (probiotics) | 16 | 9 |
| 7 | glutamate | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | foeniculum vulgare (Fennel) | 12 | 5 |
| 7 | dates | 9 | 2 |
| 7 | black raspberries | 12 | 5 |
| 7 | arabinogalactan (prebiotic) | 8 | 1 |
| 7 | garlic (allium sativum) | 20 | 13 |
| 7 | neem | 13 | 6 |
| 7 | methyl gallate | 10 | 3 |
| 7 | polysorbate 80 | 11 | 4 |
| 7 | Vitamin B-12 (Cyanocobalamin) | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | blueberry | 12 | 5 |
| 6 | buckwheat | 8 | 2 |
| 6 | vitamin b2(Riboflavin) | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | germinated barley food-stuff | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | schinus molle (herb) | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | raw potato starch | 10 | 4 |
| 6 | sesame cake/meal | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | safflower oil | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | barley | 25 | 19 |
| 6 | chicory (prebiotic) | 8 | 2 |
| 6 | chrysanthemum morifolium | 12 | 6 |
| 6 | fibre-rich macrobiotic ma-pi 2 diet | 13 | 7 |
| 6 | daesiho-tang | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | lactobacillus salivarius (probiotics) | 16 | 10 |
| 6 | lactobacillus brevis (probiotics) | 9 | 3 |
| 6 | Lactobacillus Johnsonii (probiotic) | 12 | 6 |
| 6 | Oyster Mushroom | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | corn | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | sesame | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | rye | 7 | 1 |
| 6 | grape fiber | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | chondrus crispus (red sea weed) | 9 | 3 |
| 5 | xylaria hypoxylon (fungi) | 7 | 2 |
| 5 | lactobacillus sakei (probiotics) | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | purple sweet potatoes | 9 | 4 |
| 5 | d-ribose | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | Whole Milk | 6 | 1 |
| 5 | brassica juncea | 9 | 4 |
| 5 | galla rhois | 8 | 3 |
| 5 | Kiwifruit | 7 | 2 |
| 5 | lactobacillus acidophilus,cellobiose (probiotics) | 6 | 1 |
| 5 | gum arabic (prebiotic) | 6 | 1 |
| 5 | chamomile (chamaemelum nobile) | 8 | 3 |
| 5 | cabbage | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | barley,oat | 15 | 10 |
| 5 | basil | 6 | 1 |
| 5 | bacillus (probiotics) | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | rhubarb | 14 | 9 |
| 5 | navy bean | 15 | 10 |
| 5 | n-acetyl-d-glucosamine | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | oats | 7 | 2 |
| 5 | bifidobacterium lactis bb12 (probiotics) | 10 | 5 |
| 5 | green-lipped mussel | 11 | 6 |
| 5 | genistein | 8 | 3 |
| 5 | salt (sodium chloride) | 8 | 3 |
| 4 | saccharomyces cerevisiae (probiotics) | 9 | 5 |
| 4 | sesuvium portulacastrum herb | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | tulsi | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | vegetable | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | resveratrol (grape seed/polyphenols/red wine) | 24 | 20 |
| 4 | tannic acid | 10 | 6 |
| 4 | marijuana | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | pea protein | 7 | 3 |
| 4 | mutaflor escherichia coli nissle 1917 (probiotics) | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | moderate-protein moderate-carbohydrate | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | marjoram | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | rosa canina | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | plantain bananas | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | bifidobacterium longum bb536 (probiotics) | 13 | 9 |
| 4 | black beans | 7 | 3 |
| 4 | chitosan,(sugar) | 20 | 16 |
| 4 | glucose (sugar) | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | fruit | 7 | 3 |
| 4 | koji aspergillus oryzae | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | laminaria digitata(oarweed – seaweed) | 9 | 5 |
| 4 | Psyllium (Plantago Ovata Husk) | 13 | 9 |
| 4 | Beet | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Bifidobacterium animalis | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | wasabi | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | fucoidan | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | punicic acid | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | asparagus | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Vitamin E | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Vitamin B | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | lemon | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | western diet | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | allium cepa | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Spearmint(mentha spicata) | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Mango ginger(curcuma amada) | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | cinnamomum zeylanicum | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | cinnamomum tamala | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | Exercise | 10 | 6 |
| 4 | potatoes | 10 | 6 |
| 4 | bifidobacterium breve (probiotic) | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | spirulina(cyanobacteria) | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | low protein diet | 12 | 8 |
| 4 | papaya | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | bean | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | fenugreek | 7 | 3 |
| 4 | quercetin,resveratrol | 13 | 9 |
| 4 | rosehip tea | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | pomegranate blossom tea | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | grape polyphenols | 13 | 9 |
| 4 | hypericum scabrum herb | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | high amylose cornstarch | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | maize | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | mannitol | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | tabebuia impetiginosa (taheebo) bark | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | vitex negundo (herb) | 4 | 0 |
| 3 | nigella sativa seed (black cumin) | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | whole-grain wheat | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | sorghum | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | lactulose | 14 | 11 |
| 3 | bifidobacterium longum,lactobacillus helveticus (probiotics) | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | Curcumin | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | White-leaved Savory(micromeria fruticosa) | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | amaranth | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | Agavins (agave sugar) | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | avocado peel | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | Slippery Elm | 30 | 27 |
| 3 | Gallic acid | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | Ajwain (trachyspermum ammi) | 6 | 3 |
| 3 | Taxifolin | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | Ginseng | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | Lithium | 9 | 6 |
| 3 | Dendrobium officinale | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | lactobacillus fermentum (probiotics) | 10 | 7 |
| 3 | low animal protein diet | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | l-sorbose | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | fraxinus angustifolia (narrow-leafed ash) | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | capsaicin (hot pepper) | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | coriander oil | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | enterococcus durans (probiotics) | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | aspartame (sweetner) | 9 | 6 |
| 3 | animal-based diet | 14 | 11 |
| 3 | polymannuronic acid | 17 | 14 |
| 3 | momordia charantia(bitter melon, karela, balsam pear, or bitter gourd) | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | low processed foods diet | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | lychee fruit (nephelium longan) | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | xylan (prebiotic) | 13 | 10 |
| 3 | xylitol | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | sunflower oil | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | syzygium aromaticum (clove) | 7 | 4 |
| 3 | galacto-oligosaccharides (prebiotic) | 19 | 16 |
| 2 | oolong tea polyphenols | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | oolong teas | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | tomato powder | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | tea | 18 | 16 |
| 2 | vitamim e | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | oligofructose-enriched inulin (prebiotic) | 11 | 9 |
| 2 | oregano essential oil | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | paenibacillus polymyxa (prescript assist) (probiotics) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | olea europaea (olive leaf) | 5 | 3 |
| 2 | mint | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | satureia montana(Winter savory) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | (+)-catechin | 4 | 2 |
| 2 | abies alba mill. (silver fir) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | bioflorin,enterococcus faecium sf 68,(probiotics) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | bacopa monnieri | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | carum carvi (Caraway) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | catechol | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | choline deficiency | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | chitooligosaccharides (prebiotic) | 14 | 12 |
| 2 | chaga (mushroom) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | grapes | 4 | 2 |
| 2 | l-phenylalanine | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | l-arginine | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | lemon oil | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | lemongrass oil | 5 | 3 |
| 2 | lactobacillus helveticus,lactobacillus rhamnosus (probiotics) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Pork | 8 | 6 |
| 2 | camellia | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | rice bran | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | Tryptophan | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | nobiletin | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Konjaku flour | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | lactobacillus helveticus | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | bacillus laterosporus (probiotic) | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | Immortelle(helichrysum italicum) | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | milk thistle(silybum marianum) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | bandicoot berry(leea indica) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Bacillus clausii (Probiotics) | 4 | 2 |
| 2 | bifidobacterium (probiotics) | 6 | 4 |
| 2 | xylopia aethiopica (herb) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | cylicodiscus gabunensis (mimosaceae) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | d-fructose (sugar) | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | lactobacillus paracasei,lactobacillus acidophilus,bifidobacterium animalis (probiotics) | 3 | 1 |
| 1 | galactose (milk sugar) | 12 | 11 |
| 1 | hydrogenated palm oil | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | bifidobacterium lactis,streptococcus thermophilus probiotic | 8 | 7 |
| 1 | galla chinensis (herb) | 10 | 9 |
| 1 | Sijunzi decoction | 4 | 3 |
| 1 | Baking Soda (Sodium Bicarbonate) | 7 | 6 |
| 1 | strawberry | 4 | 3 |
| 1 | Fiber, total dietary | 3 | 2 |
| 1 | Haritaki | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | quinoa | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | Cacoa flavonoids | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | lactobacillus kefiri (NOT KEFIR) | 11 | 10 |
| 1 | grape seed extract | 8 | 7 |
| 1 | fumarate | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | ginger | 10 | 9 |
| 1 | doenjang (fermented bean paste) | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | aloe vera | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | ashwagandha (withania somnifera) | 3 | 2 |
| 1 | bacillus licheniformis,(probiotics) | 10 | 9 |
| 1 | ß-glucan | 17 | 16 |
| 1 | salvia officinalis (sage) | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | plant-rich diet | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | peppermint (spice, oil) | 5 | 4 |
| 1 | moderate-carbohydrate diet | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | magnolia bark | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | peganum harmala (rue) | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | thyme oil | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | thyme (thymol, thyme oil) | 8 | 7 |
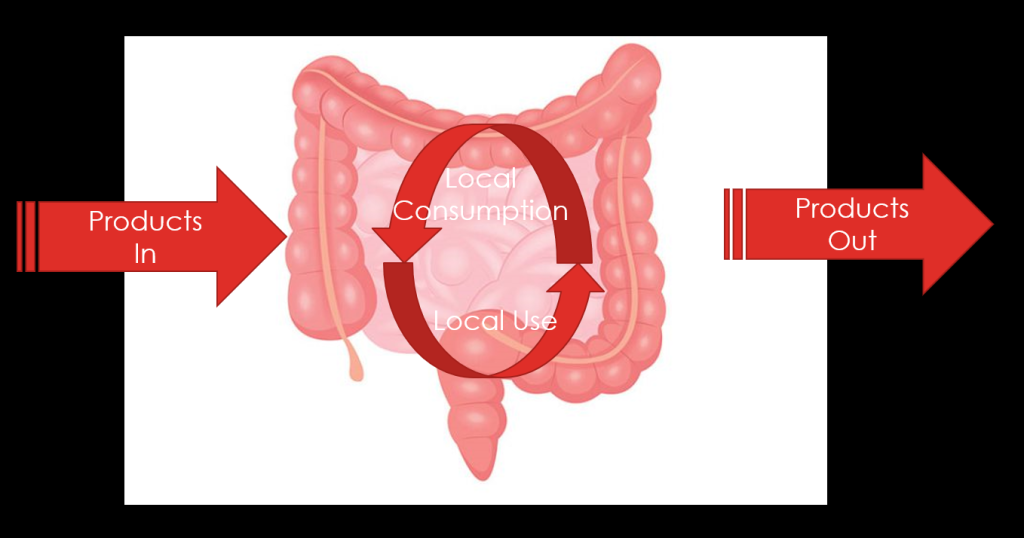
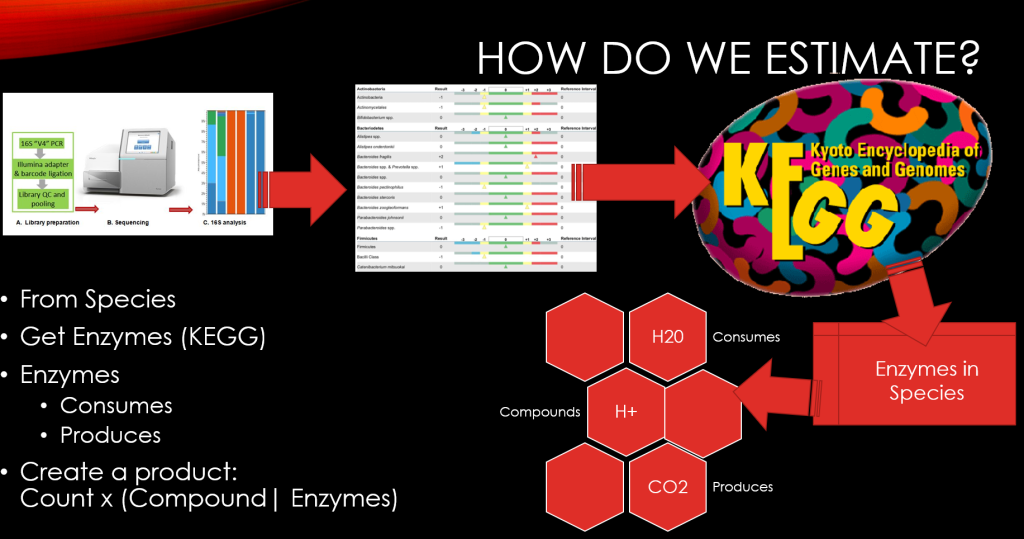
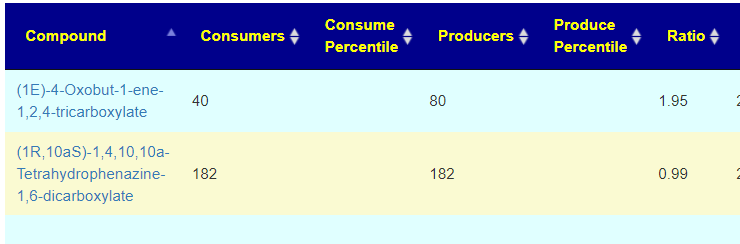
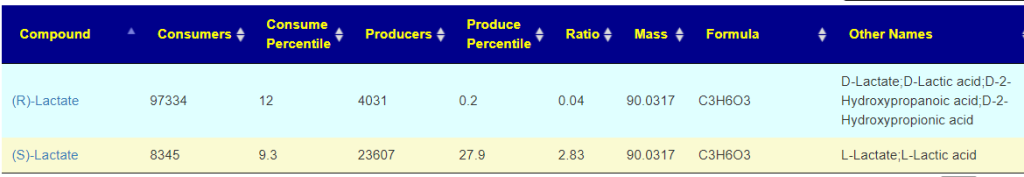
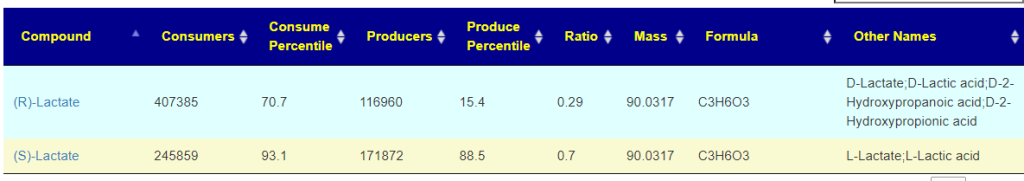
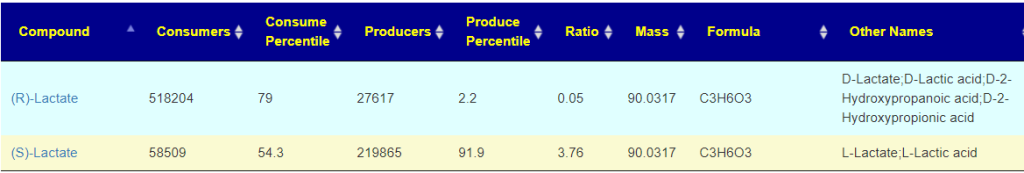
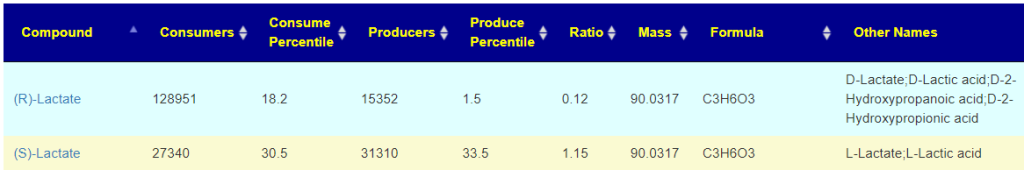




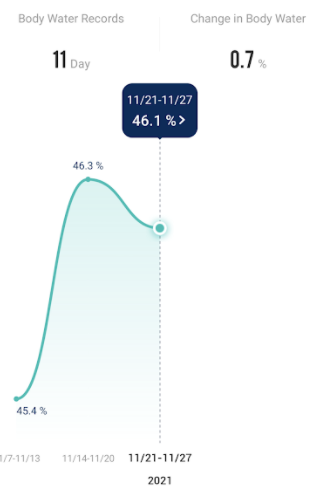
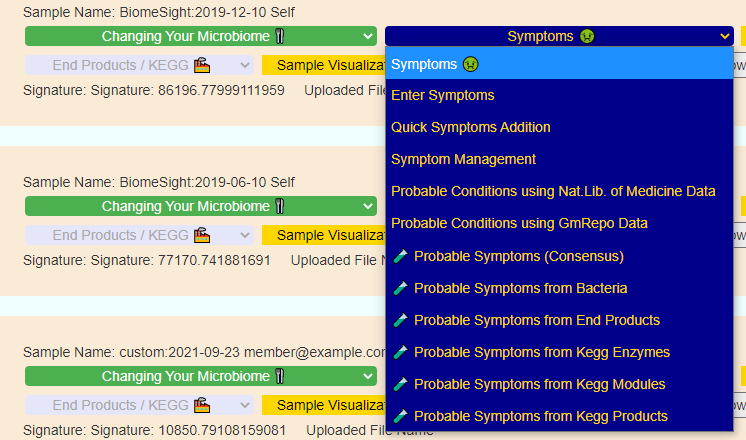
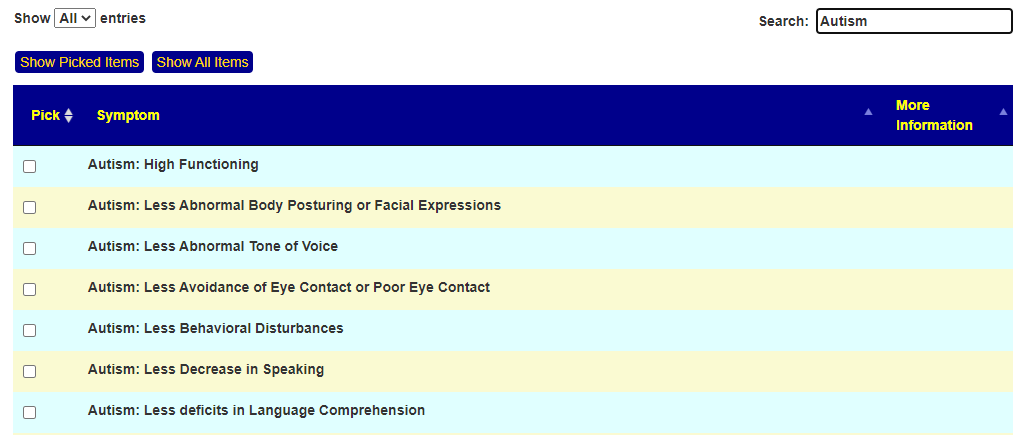
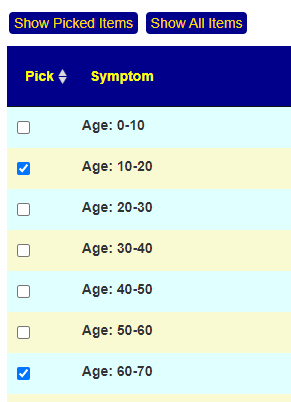
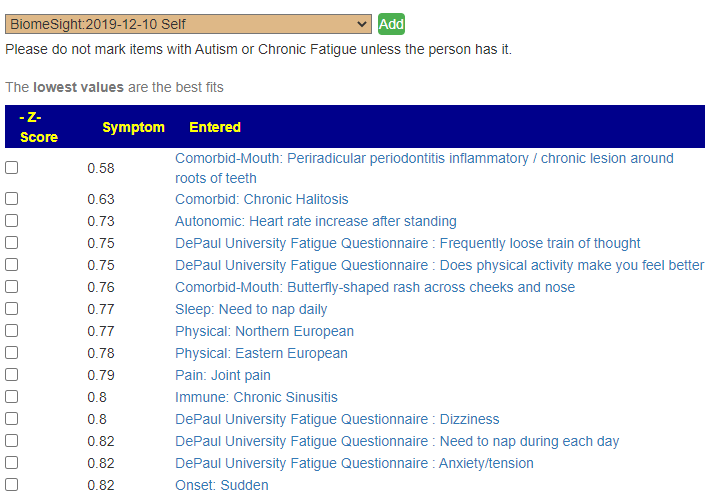
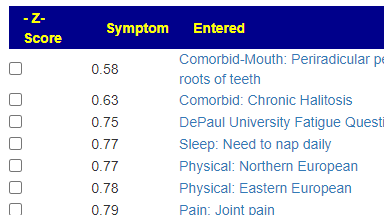
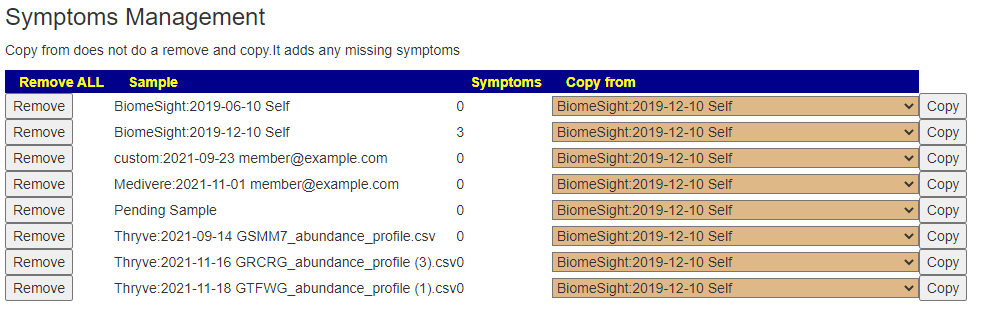
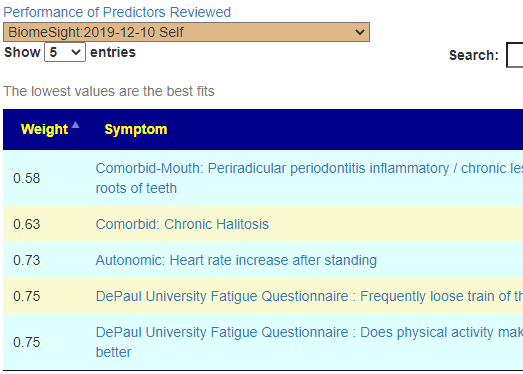
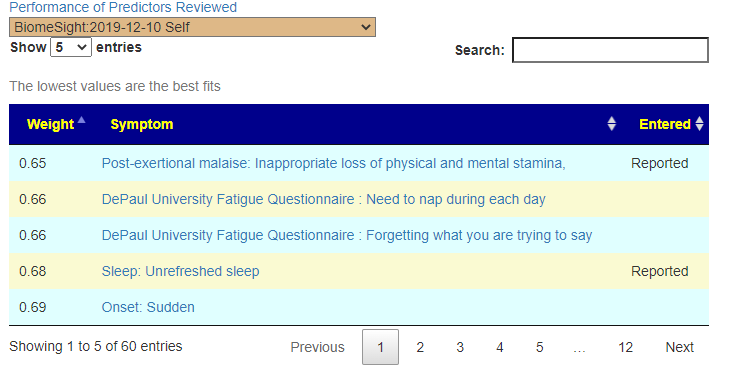
Recent Comments