This post is an update of an earlier post. It deals mainly with non-prescription items. Some prescription items can have adverse effects on the microbiome seen with other conditions. “No medical condition is an Island“
After reviewing reviewed tested supplements, we use the Three-Legged-Stool model to get additional candidates and then check if there are studies supporting their use.
Prescription Responder and Non-Responders
I came across this 2021 article that was investigating DNA/SNP and hypertension drugs.
“Drug effectiveness was defined as 10% decrease in systolic blood pressure at 1 week follow-up. “
Genomic markers associated with successful treatment of hypertension with lisinopril: A pilot study [2021]
If you do not see that type of response, there may be genetics involved.
Base List
This base list comes from my 2019 review, “Hypertension – What we know” with most items coming from Nutrients and Nutraceuticals for the Management of High Normal Blood Pressure: An Evidence-Based Consensus Document. [2019] All of these are based on actual human clinical studies and not on rodent studies. See above for amount of impact for each substance. Current studies suggests that impact is linearly cummative.
| Pycnogenol | 100–200 mg |
| Lycopene | 15–50 mg |
| Melatonin | 2–5 mg |
| Coenzyme Q10 | 100–300 mg |
| Resveratrol | >300 mg |
| Magnesium | 500-1000mg |
| Cocoa flavonoids | 200 mg |
| Calcium | 1500–2000 mg |
| Potassium | 4–5 gr |
| L-Arginine | 10-20 gr |
| Taurine | 1-2 gr |
| Quercetin | 150 mg [2009] |
Additional items are discussed in Role of natural herbs in the treatment of hypertension, 2011, but with less critical review.
Candidate Modelled Substances
For modelling substances for a condition, I often use a three legged tool as shown below
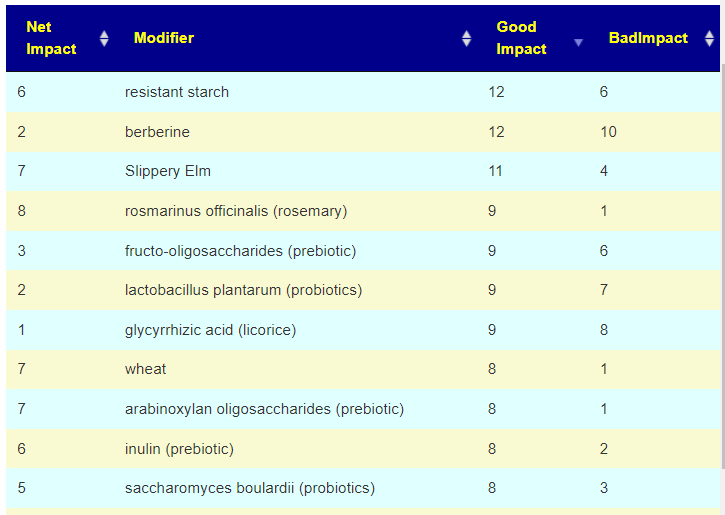
Items were ranked by number of bacteria favorability impacted. The top 3 suggested modifiers are below. The next step is to see if there is any literature. [Good Impact: Bad Impact]
- resistant starch [12:6]
- berberine [12:10]
- Studies suggests lowering [2021]
- Slippery Elm ( Ulmus macrocarpa ) [11:4]
- Lowers in Rodent studies [2008]
The next 4 items contains one surprise – licorice is usually associated with increase of BP
- lactobacillus plantarum (probiotics) [9:7]
- glycyrrhizic acid (licorice) [9:8}
- rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary) [9:1]
- “Both blood pressure variables of SBP and DBP reflect the clinically significant antihypotensive effect of Rosemary essential oil that was maintained throughout the treatment period. ” [2014]
- fructo-oligosaccharides (prebiotic) [9:6]
- Nothing
The next items
- zinc [8:3]
- saccharomyces boulardii (probiotics) [8:3]
- nothing
- wheat [8:1] – complex, ancient varieties appear to have benefits
- arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (prebiotic) [8:1]
- nothing
- inulin (prebiotic) [8:2]
- Inulin Supplementation Reduces Systolic Blood Pressure in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy [2019] SBP: -4 mm Hg
- lactobacillus salivarius (probiotics) [7:1]
- Nothing
- vitamin a [7:2]
- Inverse association between dietary vitamin A intake and new-onset hypertension[2021] “Our results emphasized the importance of maintaining relatively higher vitamin A intake levels for the prevention of hypertension.”
- oregano (origanum vulgare, oil) |[7:2]
- Nothing
We do see some items from our first list, with predictions tending to agree. Remember that we are doing a naïve count by bacteria and dealing with fuzzy data
- quercetin [6:2]
- resveratrol (grape seed/polyphenols/red wine) [6:5]
- melatonin supplement [5:8]
- magnesium [4:0]
- Cacao [3:1]
Bottom Line
This illustrates the use of the three legged stool approach for treating conditions. The use of microbiome appears to produce an extended list of candidates substances that appears to be in general agreement with studies. Each candidate substance should be researched because we have a complex mixture of bacteria.
These modelled suggestions have been added to MicrobiomePrescription
To address the questions above, we performed deep metagenomic sequencing of stool samples from 196 participants of healthy control, pHTN, and HTN; took metabolomic analyses of their metabolic profiles, further constructed a disease classifier for pHTN and HTN based on GM and metabolites; and demonstrated the crucial role of disordered GM in triggering thigh BP by human fecal microbiota transplantation into GF mice. To identify whether gut microbial changes are associated with HTN, we performed shotgun metagenomic sequencing of fecal samples from a cohort of 196 Chinese individuals. The cohort consisted of 41 healthy controls, 56 subjects with pHTN, and 99 patients with primary HTN. All the participants were from a cohort study among employees of the Kailuan Group Corporation. The Kailuan study is a prospective cohort study focusing on the Kailuan community in Tangshan, a large modern city in northern China. All the subjects in the hypertension group were newly diagnosed hypertensive patients prior to antihypertensive treatment. Patients suffering from cancer, heart failure, renal failure, smoking, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and chronic inflammatory disease were all excluded. Drugs including statins, aspirin, insulin, metformin, nifedipine, and metoprolol were not used on the patients, and other drug consumption was not compared because the sample size was quite small. Individuals were also excluded if they had received antibiotics or probiotics within the last 8В weeks. Other than SBP and DBP, there was no significant difference in other clinical parameters among groups, except for fasting blood glucose level (FBG) (