In an earlier post I cited supplements demonstrated in human clinical trials to lower blood pressure. A still earlier post looked at gut bacteria associated with hypertension and hypotension. I have collected the bacteria shifts reported from studies published on PubMed here
Literature of the microbiome bacteria
The following are the sources for the bacteria information
| Administration with Quinoa Protein Reduces the Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Modifies the Fecal Microbiota. Nutrients (Nutrients ) Vol: 13 Issue 7 Pages: Pub: 2021 Jul 17 Epub: 2021 Jul 17 Authors Guo H , Hao Y , Fan X , Richel A , Everaert N , Yang X , Ren G , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Changes of gut microbiome composition and metabolites associated with hypertensive heart failure rats. BMC microbiology (BMC Microbiol ) Vol: 21 Issue 1 Pages: 141 Pub: 2021 May 5 Epub: 2021 May 5 Authors Li L , Zhong SJ , Hu SY , Cheng B , Qiu H , Hu ZX , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Improvement of intestinal flora: accompany with the antihypertensive effect of electroacupuncture on stage 1 hypertension. Chinese medicine (Chin Med ) Vol: 16 Issue 1 Pages: 7 Pub: 2021 Jan 7 Epub: 2021 Jan 7 Authors Wang JM , Yang MX , Wu QF , Chen J , Deng SF , Chen L , Wei DN , Liang FR , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Associations between gut microbiota, faecal short-chain fatty acids, and blood pressure across ethnic groups: the HELIUS study. European heart journal (Eur Heart J ) Vol: 41 Issue 44 Pages: 4259-4267 Pub: 2020 Nov 21 Epub: Authors Verhaar BJH , Collard D , Prodan A , Levels JHM , Zwinderman AH , Bäckhed F , Vogt L , Peters MJL , Muller M , Nieuwdorp M , van den Born BH , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Changes in the Gut Microbiota are Associated with Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Japanese Subjects. Nutrients (Nutrients ) Vol: 12 Issue 10 Pages: Pub: 2020 Sep 30 Epub: 2020 Sep 30 Authors Takagi T , Naito Y , Kashiwagi S , Uchiyama K , Mizushima K , Kamada K , Ishikawa T , Inoue R , Okuda K , Tsujimoto Y , Ohnogi H , Itoh Y , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Human genetic determinants of the gut microbiome and their associations with health and disease: a phenome-wide association study. Scientific reports (Sci Rep ) Vol: 10 Issue 1 Pages: 14771 Pub: 2020 Sep 8 Epub: 2020 Sep 8 Authors Groot HE , van de Vegte YJ , Verweij N , Lipsic E , Karper JC , van der Harst P , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Differential Analysis of Hypertension-Associated Intestinal Microbiota. International journal of medical sciences (Int J Med Sci ) Vol: 16 Issue 6 Pages: 872-881 Pub: 2019 Epub: 2019 Jun 2 Authors Dan X , Mushi Z , Baili W , Han L , Enqi W , Huanhu Z , Shuchun L , Summary Html Article Publication |
| Critical Role of the Interaction Gut Microbiota – Sympathetic Nervous System in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. Frontiers in physiology (Front Physiol ) Vol: 10 Issue Pages: 231 Pub: 2019 Epub: 2019 Mar 8 Authors Toral M , Robles-Vera I , de la Visitación N , Romero M , Yang T , Sánchez M , Gómez-Guzmán M , Jiménez R , Raizada MK , Duarte J , Summary Html Article Publication |
| DIFFERENCES IN MICROBIOME IN RAT MODELS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE. South African journal of surgery. Suid-Afrikaanse tydskrif vir chirurgie (S Afr J Surg ) Vol: 55 Issue 2 Pages: 71 Pub: 2017 Jun Epub: Authors Thiba A , Umar CA , Myende S , Nweke E , Rumbold K , Candy G , Summary |
| Altered Gut Microbiome Profile in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979) (Hypertension ) Vol: Issue Pages: HYPERTENSIONAHA11914294 Pub: 2020 Feb 24 Epub: 2020 Feb 24 Authors Kim S , Rigatto K , Gazzana MB , Knorst MM , Richards EM , Pepine CJ , Raizada MK , Summary Publication Publication |
| Intestinal Flora Modulates Blood Pressure by Regulating the Synthesis of Intestinal-Derived Corticosterone in High Salt-Induced Hypertension. Circulation research (Circ Res ) Vol: Issue Pages: Pub: 2020 Feb 13 Epub: 2020 Feb 13 Authors Yan X , Jin J , Su X , Yin X , Gao J , Wang X , Zhang S , Bu P , Wang M , Zhang Y , Wang Z , Zhang Q , Summary Publication Publication |
| Exercise and food supplement of vitamin C ameliorate hypertension through improvement of gut microflora in the spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life sciences (Life Sci ) Vol: 269 Issue Pages: 119097 Pub: 2021 Mar 15 Epub: 2021 Jan 19 Authors Li Y , Zafar S , Salih Ibrahim RM , Chi HL , Xiao T , Xia WJ , Li HB , Kang YM , Summary Publication |
| Enterococcus faecalis contributes to hypertension and renal injury in Sprague-Dawley rats by disturbing lipid metabolism. Journal of hypertension (J Hypertens ) Vol: 39 Issue 6 Pages: 1112-1124 Pub: 2021 Jun 1 Epub: Authors Zhu Y , Liu Y , Wu C , Li H , Du H , Yu H , Huang C , Chen Y , Wang W , Zhu Q , Wang L , Summary Publication |
| Bifidobacterium reduction is associated with high blood pressure in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie (Biomed Pharmacother ) Vol: 140 Issue Pages: 111736 Pub: 2021 Aug Epub: 2021 May 23 Authors Lakshmanan AP , Shatat IF , Zaidan S , Jacob S , Bangarusamy DK , Al-Abduljabbar S , Al-Khalaf F , Petroviski G , Terranegra A , Summary Publication |
| Gut microbiome diversity and composition is associated with hypertension in women. Journal of hypertension (J Hypertens ) Vol: Issue Pages: Pub: 2021 May 10 Epub: 2021 May 10 Authors Louca P , Nogal A , Wells PM , Asnicar F , Wolf J , Steves CJ , Spector TD , Segata N , Berry SE , Valdes AM , Menni C , Summary Publication |
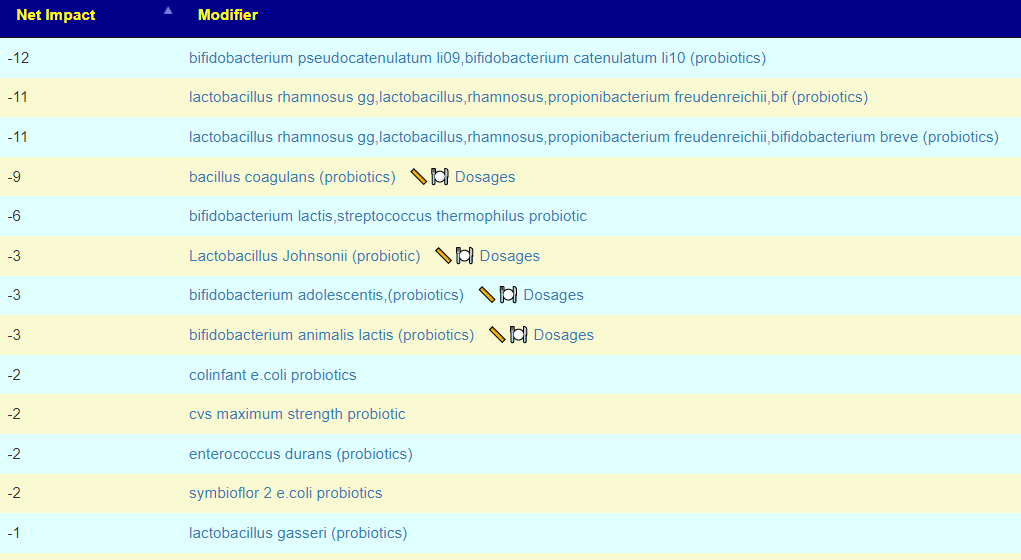
Probitotics
From Theoretical Model
These are based on the bacteria reported above and an AI engine on the impact of various probiotics (in order of confidence). Links to dosages found to be sufficient to cause changes in clinical trails are after each. It is a common mistake to take ‘homeopathic” dosage, that is, if a product contains one of these, then that is sufficient. This thinking is akin to thinking that a squirt gun is sufficient to put out a wildfire!
- bacillus subtilis (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages — Confirmed in Animal Studies
- lactobacillus rhamnosus (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages – Animal studies
- lactobacillus plantarum (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages -slight impact sometimes
- lactobacillus reuteri (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
- lactobacillus acidophilus (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
- saccharomyces boulardii (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
- bifidobacterium bifidum (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
- bifidobacterium longum (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
- lactobacillus casei (probiotics) 📏🍽️ Dosages
From Animal Studies
Often animal studies do NOT replicate to humans, so care need to be taken. Where it available, the strain is give with a link to the study.
- Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 (LC40) [2021]
- Bifidobacterium breve CECT7263 (BFM) [2021]
- ” The fermentation of beans with Bacillus Subtilis B060 may therefore constitute a successful strategy for producing a functional food with antihypertensive activity.” [2014]
- “water extracts of Bacillus subtilis-fermented pigeon pea (100 mg/kg body weight) significantly improved systolic blood pressure (21 mmHg) and diastolic blood pressure (30 mmHg) in spontaneously hypertensive rats.” [2015]
- ” treatment of model rats with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevented aggravation of hypertension by reducing blood TMAO levels, modulating Th1/Th2 cytokine imbalance and suppressing phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2, Akt and mTOR.”[2019]
From Human Studies
- NO EFFECT from Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 [2031] -dosage was sufficient
- “The clinical significance of blood pressure-lowering effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum supplementation is not considerable; ” [2020]
- “Our meta-analysis showed a modest but a significant reduction in SBP and DBP in patients with hypertension, particularly in those with diabetes mellitus, following probiotic supplementation. This effect was associated with treatment duration, dosage, and the age of subject but was not associated with single or multiple strains usage. Additionally, probiotic supplement had a beneficial effect in reducing BMI and blood glucose.” [2020]
- “Lactobacillus consumption significantly reduced systolic blood pressure (SBP) by -2.74 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) by -1.50 mmHg when comparing with the control group.” Dosage above 5 Billion CFU per day. [2020]
- “Probiotic consumption significantly changed systolic BP by -3.56 mm Hg and diastolic BP by -2.38 mm Hg compared with control groups.” After 8 weeks at 10+ Billion CFU/day [2014] No strains or species specified
- “Lactobacillus para casei LPC-37, Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001, Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM, and Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 (109 CFU of each strain) for 8 weeks….Probiotic supplementation lowered, although without statistical significance, systolic BP by about 5 mmHg and diastolic BP by about 2 mmHg in hypertensive women.” [2020]
- Saccharomyces boulardii – no effect [2012]
- Bifidobacterium reduction is associated with high blood pressure in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus [2021] — this does not mean the probiotics will have significant effect because bifidobacterium rarely persist and are gone in hours. However, the consumption of oat bran, reduces BP and increases bifidobacterium [2021]
Bottom Line
Bacillus subtilis (especially the Natto strain) appears to be most effective, both from a theoretical and animal study point of view. The theoretical model appears to work reasonably. Probiotic consumption appears to do no harm from clinical studies — however, the theoretical model indicates some may increase the microbiome shifts in the wrong direction.
Using supplements and changing diet (i.e. having oat bran daily) will have a far greater impact.
Recent Comments