On top of different labs interpreting samples in different manner which I have covered in the posts below, there is an additional issue to compound determining if a level of bacteria is normal or not!
- The taxonomy nightmare before Christmas…
- The taxonomy nightmare before Christmas … Episode II
- The taxonomy nightmare before Christmas… Episode III
I described it in my 2017 post, and updating information here.
One of the common misconception is that there is a “normal” microbiome that can be used as a reference. Below is a chart from “Metagenomic sequencing of fecal DNA[2016]“. Diet and environment makes a major impact on the distribution and volume of the bacteria.
- “In a study of gut bacteria of children in Burkina Faso (in Africa), Prevotella made up 53% of the gut bacteria, but were absent in age-matched European children.”[2010]
The chart below is for healthy individuals in 12 different countries. In some cases neighboring very similar countries (Sweden [SE] and Denmark [DK]) have very different compositions.
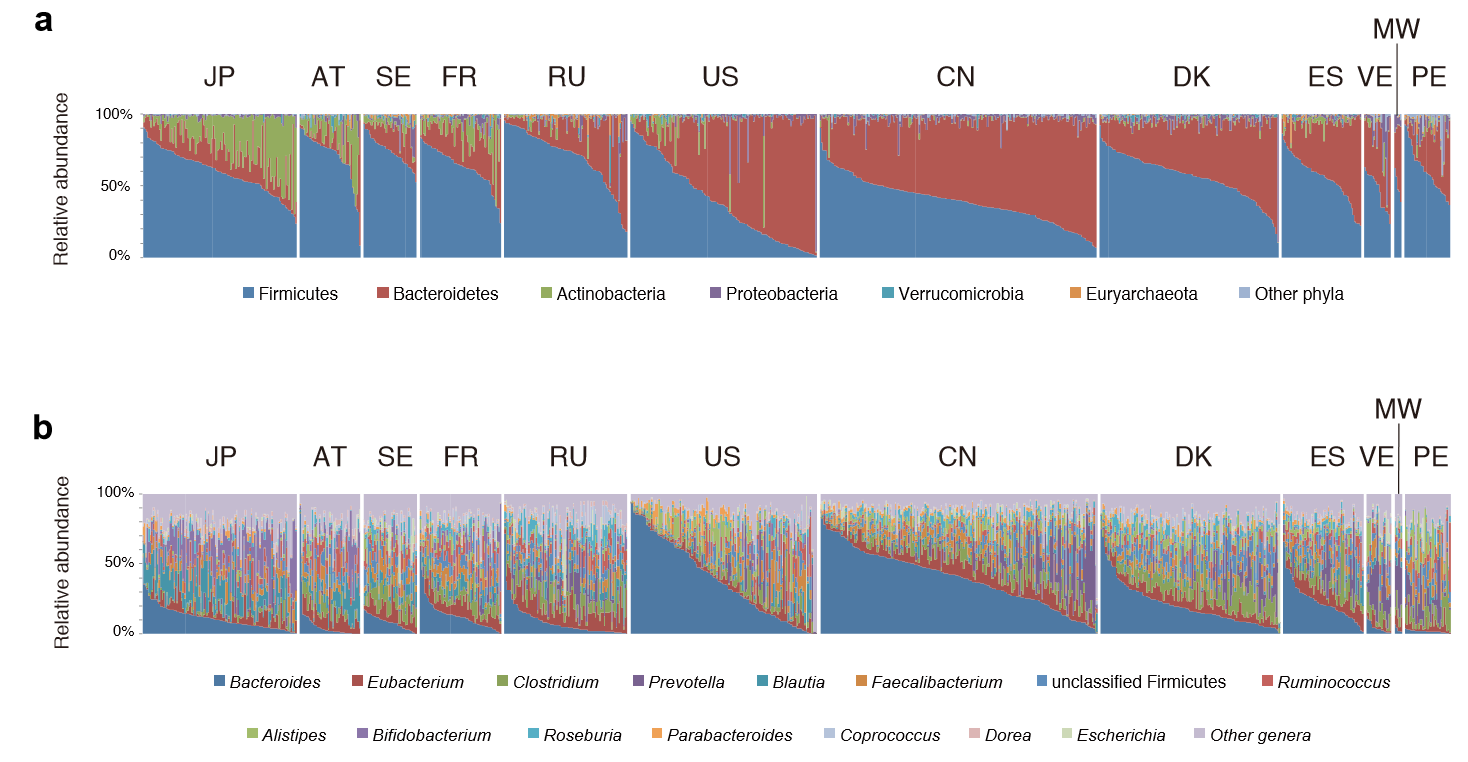
This great variation means that testing the microbiome can only be done as group of individuals living in the same area with similar eating habits…. If you are a vegetarian living in Australia, the reference ranges provided by your Australian lab are very questionable for you to use.
An individual result without reference from people with the same eating habits and possibly ethnic background is very fuzzy to interpret. Yes, highlights may be common — like low E.Coli, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria…. but they likely apply to no more than 80-90%, the other CFS patients may have different shifts.
Then we also find that DNA also impacts the microbiome,
Host genetic variation drives phenotype variation, and this study solidifies the notion that our microbial phenotype is also influenced by our genetic state. We have shown that the host genetic effect varies across taxa and includes members of different phyla. The host alleles underlying the heritability of gut microbes, once identified, should allow us to understand the nature of our association with these health-associated bacteria, and eventually to exploit them to promote health.Human genetics shape the gut microbiome , 2014
People have asked me, “Did you get your microbiome done, what was it?” My honest answer was “No, such testing was not available when I last had CFS. I simply assumed that my pattern would be an appropriate match to that reported from the 1998 Australian studies”
Age changes the microbiome
” DNA of the Clostridium leptum group and pathogenic Enterobactericeae increase in the gut microbiome with age and can be detected in the same individual’s coronary plaques along with pathogenic Streptococcus spp., associating with more severe coronary atherosclerosis. ” [2019]

The presence of the Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium, Bacteroides group, and Clostridium cluster XIVa decreased with age up to 66-80 years of age, with differences reaching statistical significance for the latter group. Interestingly, the levels of some of these microorganisms recovered in the very old age group (>80 years), with these older individuals presenting significantly higher counts of Akkermansia and Lactobacillus group than adults and the younger elderly.
Age-Associated Changes in Gut Microbiota and Dietary Components Related with the Immune System in Adulthood and Old Age: A Cross-Sectional Study. [2019]
- Differences in the gut Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio across age groups in healthy Ukrainian population [2020]
- The Inuit gut microbiome is dynamic over time and shaped by traditional foods [2017]
Latitude changes the Microbiome
Latitude means the distance from the equator. This may be due to sunlight-vitamin D levels.
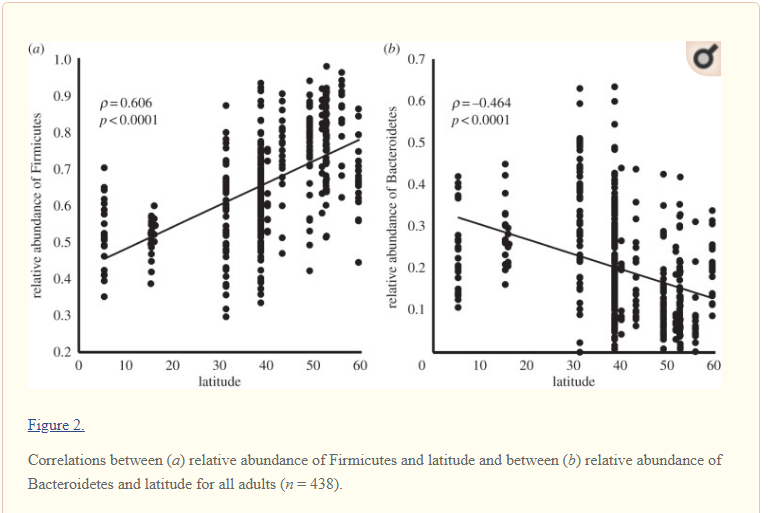
These changes in the microbiome, also impacts symptoms, for example The Association of Latitude and Altitude with COVID-19 Symptoms: A VIRUS: COVID-19 Registry Analysis. [2022]
If you exercised recently impacts the microbiome
Underlying these macro-level microbial alterations were demonstrable increases in select bacterial genera such as Veillonella (+14,229%) and Streptococcus (+438%) concomitant with reductions in Alloprevotella (-79%) and Subdolingranulum (-50%). To our knowledge, this case study shows the most rapid and pronounced shifts in human gut microbiome composition after acute exercise in the human literature.
Rapid gut microbiome changes in a world-class ultramarathon runner. 2019
- The influence of exercise training volume alterations on the gut microbiome in highly-trained middle-distance runners.[2022]
- Four men in a boat: Ultra-endurance exercise alters the gut microbiome. [2019]
Season Changes Microbiome
Seasonal variation in gut microbiota composition: cross-sectional evidence from Ukrainian population [2020]
Some Population Studies
“We analyzed the combined microbiome data from five previous studies with samples across five continents. We clearly demonstrate that there are no consistent bacterial taxa associated with either Bacteroides– or Prevotella-dominated communities across the studies. By increasing the number and diversity of samples, we found gradients of both Bacteroides and Prevotella and a lack of the distinct clusters in the principal coordinate plots originally proposed in the “enterotypes” hypothesis. The apparent segregation of the samples seen in many ordination plots is due to the differences in the samples’ Prevotella and Bacteroides abundances and does not represent consistent microbial communities within the “enterotypes” and is not associated with other taxa across studies.” [2016]
” All Egyptian gut microbial communities belonged to the Prevotella enterotype, whereas all but one of the U.S. samples were of the Bacteroides enterotype.
- The intestinal environment of Egyptians was characterized by higher levels of short-chain fatty acids, a higher prevalence of microbial polysaccharide degradation-encoding genes, and a higher proportion of several polysaccharide-degrading genera.
- Egyptian gut microbiota also appeared to be under heavier bacteriophage pressure.
- In contrast, the gut environment of U.S. children was rich in amino acids and lipid metabolism-associated compounds; contained more microbial genes encoding protein degradation, vitamin biosynthesis, and iron acquisition pathways; and was enriched in several protein- and starch-degrading genera.
- Levels of 1-methylhistamine, a biomarker of allergic response, were elevated in U.S. guts, as were the abundances of members of Faecalibacterium and Akkermansia, two genera with recognized anti-inflammatory effects.
- The revealed corroborating differences in fecal microbiota structure and functions and metabolite profiles between Egyptian and U.S. teenagers are consistent with the nutrient variation between Mediterranean and Western diets.” [2017]
“This suggests that similarities between the Inuit diet and the Western diet (low fiber, high fat) may lead to a convergence of community structures and diversity. However, certain species and strains of microbes have significantly different levels of abundance and diversity in the Inuit, possibly driven by differences in diet.” [2017]
- A Korean-Style Balanced Diet Has a Potential Connection with Ruminococcaceae Enterotype and Reduction of Metabolic Syndrome Incidence in Korean Adults. [2021]
- Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts. [2023]
For a Worked Example Using Dr. Jason Hawrelak Recommendations, see The taxonomy nightmare before Christmas… Episode III
Bottom Line
There is no clear definitive benefit from doing an individual microbiome testing — there is no definitive reference ranges. This is an inconvenient truth about the microbiome testing – rarely talked about and typically ignore.
My training is in statistics and artificial intelligence where there is no concept of definitive, just probability and fuzzy data.
The path that I have walked down on my Microbiome Prescription site accepts this problem and use a wide variety of methods (familiar to some of those people who are very well practiced and experienced in probability, statistics and artificial intelligence) to maximize the odds that suggestions will improve a person’s health. Both the simplified logic of influencers and the naïve application of the “hottest new” artificial intelligence fad are ignored. Many people cannot get their minds wrapped around the nature of this problem, IMHO.
This latter issue persists even if you get lab test results to agree.
” This work supports that sex is a critical factor in colonic bacterial composition of an aged, genetically-heterogenous population. Moreover, this study establishes that the effectiveness of dietary interventions for health maintenance and disease prevention via direct or indirect manipulation of the gut microbiota is likely dependent on an individual’s sex, age, and genetic background. ” [2019]


Recent Comments