SIBO or Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth was first proposed as a medical condition in 1970. The first use of breath tests for it was around 1974. The key things to remember is that this condition was the naming of a collection of symptoms. The name reflected the speculation on the general cause without any specifics. Over the years, this condition has been broken down in 6 general subsets depending on the results of breath test (and a potential 7th, if the symptoms are there but no positive breath test results).
Assuming that it is a bacteria overgrowth — which bacteria is overgrown? The breath test does not provide evidence on which specific bacteria a person has.
Based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, we see many suspect bacteria. Worse still, it may not be a single species overgrowth but several.
- Hydrogen Levels (H2) – 595 species
- Methane Levels (CH4) – 622 species
- hydrogen sulfide (H2S) – 3817 species
The clinical practice is often applying a simple logic “If it is an overgrowth, we just toss the appropriate antibiotic at it and it is solved!”. Experience has shown that some are generally effective, i.e.
- Rifaximin was 78% effective [2023]
- Amoxicillin (500 mg 3 times a day per, during the first month), followed by ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice a day per, during the second month) and metronidazole (500 mg 3 times a day per, during the third month) about 56% effective [2023]
With effective usually being defined as symptom improvement not remission. Reporting adverse reaction is poorly done.
The reality that using herbs, oil of.. , tinctures, etc. have the same problem as antibiotics. With the evidence above there is not way to determine which ones will be effective for the individual.
There is a recognized and accepted way to better determine the bacteria involved: Small Intestine Aspirate. This is a quasi-surgical procedure to take a sample from the Small Intestine.
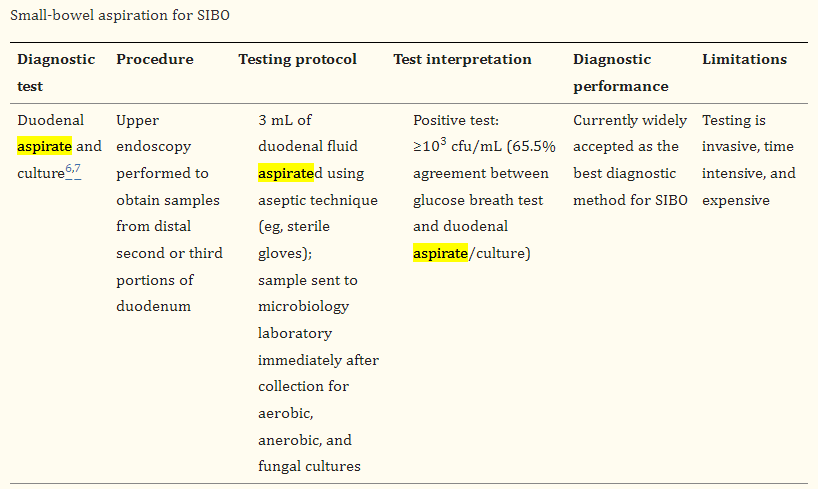
The gotcha is the handling of the sample, the treating physician or the lab may do one of several possible things:
- Just report the quantity (confirming an overgrowth) — most common
- Classic culturing of the sample — which will report on the culturable bacteria (most are NOT culturable)
- 16s testing of the sample – better resolution
- Shotgun testing of the sample — best resolution
Cost issues can be complicated by insurance companies not covering the costs in most situations.
The Downstream Proposal
Whatever is in the small bowel or intestine eventually makes it way thru the entire system and ends up in a stool. The amount will likely differ because of passages through multiple environments.
The motivation for this post was a reader telling me that his hydrogen sulfide levels have become a problem. His latest sample had a significant amount of them. This suggests that 16s sampling can be helpful for detecting the species involved and thus treatment suggestions based on the bacteria that appear to be in overgrowth (by virtue of the breath test elements).
The video below takes you through the process.
A Walkthru
Note that the top antibiotics suggested from Microbiome Prescription are those used for treating SIBO.
Suggested Readings
Many older articles have stale information, the following are very recent publications.
- Small-bowel aspiration during upper esophagogastroduodenoscopy: Rao technique [2021]
- Unravelling the controversy with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth [2023]
- Evaluation of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth [2023] “SIBO was conventionally defined as a total bacterial count >100,000 colony forming units (CFU) per mL on quantitative culture of upper gut aspirate. The threshold for the diagnosis of SIBO has been reduced to >1000 CFU per mL of aspirate recently.” That is 100x decrease of the amount need to get the diagnosis!
- Association between Gut Dysbiosis and the Occurrence of SIBO, LIBO, SIFO and IMO [2023] “The subject literature is extensive but of limited quality.”
- Diagnosis by Microbial Culture, Breath Tests and Urinary Excretion Tests, and Treatments of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth [2023]
- Understanding Our Tests: Hydrogen-Methane Breath Testing to Diagnose Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth [2023]
This is really helpful walk-thru. Just a theory, I wonder whether lack of stomach acid could be responsible here, eg. Thiamine is highly recommended and it is often reported that it is important for stomach acid, and therefore with deficiency overgrowth occurs due to excess fermentation. Perhaps something like thiamine and digestive enzymes could improve/resolve this.
Interesting speculation. I checked PubMed and no association has been made in any study.
I did find “in those patients with abnormal glucose-hydrogen breath tests, antibiotic therapy with oral thiamine is effective therapy.”
2007, https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Fulltext/2007/09002/Treatment_of_Symptomatic_Small_Intestinal.230.aspx
This implies (reading between the lines) the thiamine has likely been tried and by itself, it was found ineffective.