The human microbiome industry is experiencing significant growth and attracting substantial investor interest. According to recent market reports, the human microbiome market is poised for remarkable expansion in the coming years.
Market Growth and Potential
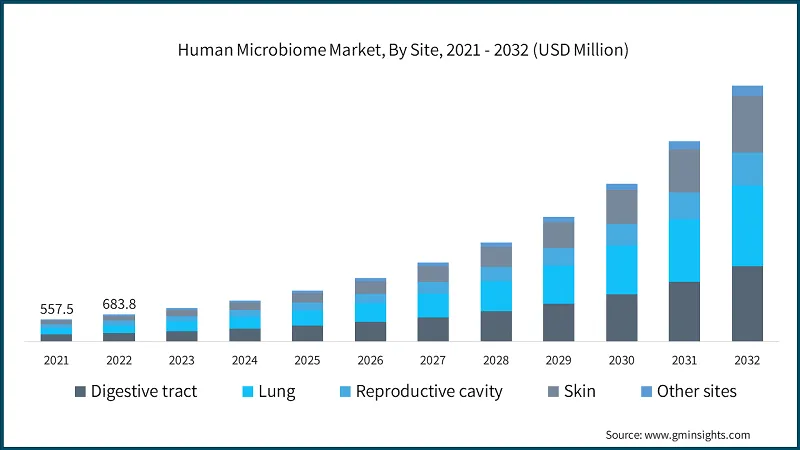
The human microbiome market was valued at USD 824.4 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 6.47 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.7%1. This impressive growth trajectory underscores the increasing recognition of the microbiome’s role in human health and disease management. [Human Microbiome Market Size & Forecast Report, 2024 – 2032]
Key Drivers
Several factors are fueling the rapid growth of the microbiome industry:
- Rising prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases: The growing incidence of chronic conditions has highlighted the potential of microbiome-based solutions in disease management.
- Demand for precision medicine: The microbiome’s pivotal role in personalizing treatment strategies has gained significant attention.
- Technological advancements: Progress in areas such as next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics has accelerated research and development in the field.
- Increasing research and innovation: Expanding studies into the relationship between the human microbiome and various health conditions have spurred industry growth.
Startup Landscape
The microbiome sector has seen a surge in startup activity, with numerous entrepreneurs recognizing the potential in this emerging field. While the market offers significant opportunities, it’s important to note that, as with all startup ventures, success is not guaranteed.
Investor Interest
Venture capitalists have shown keen interest in microbiome startups, recognizing the sector’s potential for breakthrough innovations and substantial returns. However, it’s crucial for entrepreneurs to develop robust business plans and demonstrate clear paths to commercialization to attract funding.
Prolog Summary
The human microbiome market presents a promising opportunity for startups, backed by strong market growth projections and investor interest. However, entrepreneurs should approach this space with a balanced perspective, understanding both the potential rewards and the inherent risks associated with startup ventures in an emerging scientific field.
What is Microbiome Prescription Place with Start-ups
Microbiome Prescription (MP) is dedicated to improving public health through accessible microbiome analysis and recommendations. The platform’s core mission is to empower individuals to enhance their well-being by providing free access to its comprehensive database and advanced algorithms.
Individual Access
For personal use, MP offers its services at no cost. This approach ensures that anyone can benefit from the platform’s insights into microbiome health, regardless of their financial situation.
Commercial Licensing
While MP prioritizes free access for individuals, it has established a licensing structure for commercial applications:
- Usage restrictions: Commercial entities are required to obtain a license before utilizing MP’s database and algorithms for business purposes.
- Licensing terms: The standard licensing agreement is straightforward, with a fee structure based on the volume of samples processed.
- Fee structure: Commercial users are charged 2% of the suggested retail price per sample analyzed using MP’s resources.
This balanced approach allows MP to maintain its commitment to public health while also ensuring sustainable development and ongoing improvement of its services. By implementing this licensing model, MP can continue to invest in research, expand its database, and refine its algorithms, ultimately benefiting both individual users and the broader scientific community.
“The laborer deserves his wages.” [ 1 Tim 5:18, Leviticus 19:13, etc. ].
What Does it take to do a Startup?
A successful microbiome startup typically requires three fundamental components, each playing a crucial role in the company’s operations and growth. Let’s explore these key elements:
1. Marketing: Driving Test Adoption
The first leg focuses on attracting customers and encouraging them to purchase microbiome tests. This involves:
- Developing a strong brand identity
- Creating compelling marketing campaigns
- Educating potential customers about the benefits of microbiome testing
- Utilizing various channels such as social media, content marketing, and partnerships
- Implementing effective customer acquisition strategies
2. Laboratory Services: Test Production and Processing
The second leg encompasses the technical aspects of producing and processing microbiome tests:
- Establishing or partnering with a certified laboratory
- Developing reliable and accurate testing methods
- Ensuring quality control and compliance with regulatory standards
- Managing logistics for sample collection and processing
- Scaling operations to meet growing demand
- Are the kits using the best preservatives?
- Are the labs doing best handling?
See Human Stool Preservation Impacts Taxonomic Profiles in 16S Metagenomics Studies [2022] for more details.
3. Test Interpretation: Providing Actionable Insights
The final leg involves analyzing the test results and offering valuable recommendations:
- Developing robust algorithms for data analysis
- Creating user-friendly reports with clear, actionable insights
- Offering personalized suggestions based on individual microbiome profiles
- Continuously updating the knowledge base with the latest research findings
- Providing ongoing support and guidance to customers
By effectively addressing these three core areas, a microbiome startup can establish a strong foundation for success. Each component is interdependent, requiring careful coordination and integration to deliver a seamless and valuable service to customers while driving business growth.

Microbiome Prescription is an Interpretation Service supporting a wide variety of customization
Marketing And Administration
Marketing
- Identifying the target market
- It may be people with specific conditions (SIBO, IBS, Long COVID, Autism)
- Certain Legal Entities (there are places that restrict sales)
- Postal regulations for returning samples
- Identify Market Size
- Identify the viable cost point (i.e. how much to charge)
- Promoting the test to the target market
- Internet Ads
- Conferences
- Visiting medical providers
- Paper and Journal advertisements (i.e. Townsend Letter )
- Generating interest by blog posts and testimonials
Legal Considerations for Microbiome Startups
When establishing a microbiome testing business, it’s crucial to address various legal aspects to ensure compliance and mitigate risks. Here are key legal considerations:
1. Personal Health Information Protection
- Comply with relevant data protection laws in your target markets, such as:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union
- PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act) in Canada
- Implement robust data security measures and privacy policies
- Regularly audit and update compliance procedures
2. Jurisdictional Sales Restrictions
- Research and understand regulatory restrictions on direct-to-consumer genetic testing in different regions
- Be aware of specific limitations or bans in certain countries or states
- Develop a clear strategy for market entry that accounts for these restrictions
3. Sample Transportation Regulations
- Comply with international and domestic regulations for biological sample transport
- Adhere to guidelines set by organizations such as:
- IATA (International Air Transport Association)
- CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Ensure proper packaging, labeling, and documentation for all sample shipments
4. Marketing Claims and Content Review
- Conduct thorough legal reviews of all marketing materials, including:
- Website content
- Advertising campaigns
- Product packaging
- Customer communications
- Ensure all claims are scientifically substantiated and compliant with regulations such as:
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) guidelines in the US
- ASA (Advertising Standards Authority) rules in the UK
- Avoid making unsubstantiated health claims or promises
5. Informed Consent and Terms of Service
- Develop clear, comprehensive informed consent forms for customers
- Create transparent terms of service that outline:
- Data usage and storage policies
- Customer rights and responsibilities
- Limitations of liability
6. Intellectual Property Protection
- Secure patents for proprietary technologies or methodologies
- Protect trademarks for your brand and product names
- Implement confidentiality agreements with employees and partners
7. Regulatory Compliance
- Stay informed about evolving regulations in the genetic testing and microbiome analysis fields
- Engage with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and potentially influence policy development
8. Legal Counsel
- Retain experienced legal counsel specializing in healthcare, biotechnology, and data privacy
- Regularly review and update legal strategies as the business grows and expands into new markets
By carefully addressing these legal considerations, microbiome startups can build a strong foundation for compliance, protect their interests, and foster trust with customers and regulatory bodies alike.
Information Technology Infrastructure for Microbiome Startups
A robust IT infrastructure is crucial for the success of a microbiome testing business. Here’s an overview of the key IT components required:
1. Customer-Facing Ordering Platform
- User-friendly e-commerce website with:
- Secure account creation and management
- Clear product descriptions and pricing
- Streamlined checkout process
- Integration with payment gateways
- Mobile responsiveness for on-the-go ordering
- Features to include:
- Order tracking
- Reorder functionality
- Customer support chat or ticketing system
2. Results Presentation Portal
- Secure, HIPAA-compliant platform for displaying test results
- Interactive dashboards with:
- Visual representations of microbiome data
- Comparative analysis tools
- Personalized recommendations based on results
- Educational resources to help interpret results
- Option to download or share results with healthcare providers
3. Laboratory Data Management System
- Secure database for storing sample results
- Integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS)
- Data validation and quality control processes
- Automated data import from sequencing machines
- Backup and disaster recovery systems
4. Analysis Engine Integration
- API or microservices architecture to connect with analysis algorithms
- Scalable computing resources for processing large datasets
- Version control for analysis code and algorithms
- Automated pipeline for running analyses on new samples
- Logging and monitoring systems for tracking analysis jobs
5. Data Security and Compliance
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Access control and authentication systems
- Regular security audits and penetration testing
- Compliance with relevant data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
6. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System
- Integration with ordering and results platforms
- Tools for managing customer interactions and support tickets
- Analytics for tracking customer engagement and retention
7. Business Intelligence and Reporting
- Data warehousing solution for aggregating business metrics
- Reporting tools for generating insights on sales, customer behavior, and test results
- Predictive analytics for forecasting demand and identifying trends
8. DevOps and Infrastructure Management
- Continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
- Cloud-based infrastructure for scalability and reliability
- Monitoring and alerting systems for IT operations
- Disaster recovery and business continuity planning
By implementing a comprehensive IT infrastructure that addresses these key areas, microbiome startups can ensure efficient operations, secure data management, and a positive customer experience. Regular updates and maintenance of these systems will be crucial to stay competitive and compliant in this rapidly evolving field.
Laboratory Services
When considering laboratory services for microbiome testing, several key factors should be evaluated to ensure high-quality results and customer satisfaction:
1. Sequencing Technology
16S vs. Shotgun Sequencing
- 16S Sequencing:
- Lower cost option
- Provides bacterial identification
- Limited resolution and functional insights
- Shotgun Sequencing:
- More expensive but offers greater detail
- Options include shallow or deep shotgun
- Provides broader microbial profiling and functional analysis
Professional consultation is recommended to determine the most appropriate method for specific research or clinical needs.
2. Laboratory Certifications
Certifications indicate better quality control and data accuracy. Look for accreditations such as:
- The College of American Pathologists (CAP)
- American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP)
- Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)
3. Data Reporting and Analysis
Evaluate the depth and quality of data provided:
- Bacterial percentage representation
- Reference ranges and their calculation methods
- Consideration of demographic factors:
- Age and gender
- Health conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
- Dietary habits (e.g., meat-eaters vs. vegetarians)
- Ethnic background
- Use of percentiles vs. ranges for result interpretation
4. Turnaround Time
Shorter processing times generally lead to higher customer satisfaction. Consider:
- Sample collection to results delivery timeline
- Reporting methods and accessibility of results
5. Additional Considerations
- Bioinformatics capabilities and data interpretation
- Customer support and result explanation services
- Integration with healthcare systems or research databases
- Cost-effectiveness and insurance compatibility
6. Applicability in Clinical Settings
Some pipelines may provide superior academic performance unfortunately they are rarely used in clinical studies of the microbiome. This makes things a pea to watermelon comparison. The methodology should be a close match to that used in clinical studies being applied. For background on this issue see The taxonomy nightmare before Christmas…
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a laboratory service that best meets your specific needs for microbiome testing, balancing quality, depth of analysis, and customer experience.
Interpretation Strategies for Microbiome Testing Results
The interpretation of microbiome test results is a critical component that can significantly impact the value proposition of your service. Here’s an overview of different approaches and their implications:
1. Professional Interpretation
- Pros:
- High-quality, personalized insights
- Ability to consider complex interactions
- Cons:
- Costly and time-consuming
- Difficult to scale with increasing test volumes
2. Automated Interpretation Systems
- Pros:
- Scalable to handle large volumes
- Consistent results across samples
- Cost-effective in the long run
- Cons:
- Requires significant initial investment (or using MicrobiomePrescription services)
- Needs ongoing maintenance and updates
3. Generic, Non-Sample Specific Suggestions
- Pros:
- Easy to implement
- Low cost
- Cons:
- Limited value to customers
- May lead to lower customer satisfaction and retention
4. AI-Assisted Ad-Hoc Interpretation
- Using tools like ChatGPT or internet research for bacteria-by-bacteria analysis
- Pros:
- Relatively quick to implement
- Can satisfy novice customers
- Cons:
- Ignores complex microbial interactions
- Potential for inconsistent or inaccurate information
- Unlikely to meet standards for medical advice
- No evidence trail on how suggestions are made
5. Microbiome Prescription Strategy
- Offering a customizable suggestion engine
- Pros:
- Cost-effective compared to in-house development
- Highly customizable to client preferences
- Maintained and updated by specialists
- Cons:
- Dependency on external service
- May require integration efforts
Cost Considerations
- Developing and maintaining an in-house system typically requires:
- At least one full-time employee with relevant expertise and education
- Ongoing investment in research and development
- Regular updates to keep pace with scientific advancements
Choosing the Right Approach
The best strategy depends on various factors:
- Target market expectations
- Available resources (financial and human)
- Long-term business goals
- Regulatory compliance requirements
For many startups, a hybrid approach might be optimal:
- Begin with a basic automated system or partnership with a service like Microbiome Prescription
- Gradually develop in-house expertise
- Offer tiered services with basic automated insights and premium professional interpretations
By carefully considering these options, microbiome startups can balance cost-effectiveness, scalability, and quality of insights to provide valuable interpretations to their customers.
Customizations from Microbiome Prescription
The following are some examples of possible customization
- Restrict suggestions to vegetarian items only
- Restrict suggestions to supplements sold by site
- Restrict suggestions to probiotics sold by site
- Use a customer’s own algorithm and weight algorithm
- Use means and 2 standard deviations for ranges
- Use box-whiskers for ranges
- Use custom ranges
- Exclude some studies (for example, no studies done on mice)
- Do inferences on genus and family only or no inferences
No attribution to Microbiome Prescription is required. MP provides a database of facts
Importance of Cross-Validation in Microbiome Suggestion Systems
When implementing a customizable suggestion engine for microbiome test results, it is crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the recommendations. Cross-validation serves as a vital tool in this process, helping to verify the reasonableness and effectiveness of the suggestions provided.
Key Points:
- Necessity of Cross-Validation:
- Essential for validating the accuracy of AI-generated or automated suggestions
- Helps in identifying potential biases or errors in the suggestion algorithm
- Cross-Validation Process:
- Involves testing the suggestion system against known outcomes or expert-validated data sets
- Example: “Cross Validation of AI Suggestions for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease“
- Recommended Validation Thresholds:
- Minimum cross-validation accuracy: 80%
- Preferred cross-validation accuracy: 90% or higher
- Multiple Condition Testing:
- Cross-validation should be performed across various health conditions and scenarios
- Ensures robustness of the suggestion system across different use cases
- Benefits of Rigorous Validation:
- Enhances credibility of the microbiome testing service
- Increases confidence in the suggestions provided to customers
- Helps in continuous improvement of the suggestion algorithms
- Implementation Strategies:
- Regularly update and re-validate the system as new research emerges
- Consider partnering with academic institutions or research labs for independent validation
- Implement a feedback loop with healthcare professionals to refine suggestions
By adhering to strict cross-validation protocols, microbiome startups can ensure that their suggestion systems provide reliable, scientifically-backed recommendations. This approach not only enhances the value of the service but also contributes to building trust with customers and healthcare professionals alike.
Business Model
As a Master of Commerce, I must emphasize the importance of a realistic and well-structured business model. No wishful thinking please. Let’s reframe the content to focus on these crucial business considerations for a microbiome startup:
Key Business Model Considerations for Microbiome Startups
When developing your microbiome startup, it’s essential to address the following questions to ensure a viable and sustainable business model:
1. Target Market Definition
- Clearly define your primary target audience. Avoid the trap of targeting “anybody.”
- Consider specific groups such as:
- People with specific health conditions (e.g., Diabetes, Alzheimer’s, Autism)
- Age-specific markets (e.g., children only)
- Healthcare professionals (e.g., Naturopathic or Medical practitioners)
- Niche influencers (e.g., Body Hackers, Longevity enthusiasts)
- Assess the financial capacity of your target audience to inform pricing strategy
2. Market Potential and Growth Projections
- Estimate the maximum volume of business for your target market
- Project expected business volume for years 1-5
- Determine the timeline to profitability
3. Competitive Landscape
- Analyze existing competition in your target market
- Decide on geographical focus (regional, national, or global)
- Consider how pricing strategy may vary by country or region
4. Customer Retention and Repeat Business
- Estimate customer repeat rates
- Use data-driven insights, such as:
- 32% of customers doing a second test
- 20% proceeding to a third test
- 10% completing a fourth test
5. Cost Structure Analysis
- Calculate fixed costs, including:
- Laboratory expenses
- Analysis costs
- Shipping fees
- Customer support costs (per hundred tests)
- Determine variable costs that scale with business growth
6. Pricing Strategy
- Develop a pricing model that considers:
- Target market’s financial capacity
- Competitive landscape
- Cost structure
- Desired profit margins
7. Scalability and Operations
- Plan for operational scalability as the business grows
- Consider partnerships or outsourcing for key functions (e.g., laboratory services)
By thoroughly addressing these aspects, you can develop a robust and realistic business model for your microbiome startup. This approach will help you avoid overly optimistic projections and ensure that your business strategy is grounded in market realities and financial feasibility.
Recent Comments