Back Story
- 47yo Male
- 1976-2012 – Sustained 7 concussions playing contact sports, minor short term symptoms and fully recovered. Fit, active, and employed as adult. Satisfying family/social life. Higher intensity physical training 5-6 days per week outside or in gym. No drugs/alcohol since 2003, no medical issues or medications.
- 2012 – Post Concussion Syndrome – Fell and hit head skiing, diagnosed with concussion, symptoms did not resolve. No detectable damage on MRI.
Symptoms
- Fatigue, brain fog, intense and unpredictable nerve pain in head
- Cognitive and visual processing issues
- Sensitivity to light, loud noise, busy environments
- GI – constipation
- Multiple food, chemical, and environmental sensitivities
- Overall functionality reduced, still able to socialize, drive, complete tasks, problem solve, etc… sporadically and in short increments. Physical fitness mostly unaffected, continued to exercise, incorporated yoga/gyrotonic.
- Divorced
- Received disability benefits in 2019
- chronic sinus issues that started after concussion and worsened with vaccine.
- diagnosed w nasal mold colonization, nasal biofilms, and chronic staph aureus.
2021 – mRNA Vaccine Injury (2 shots Pfizer)
Symptoms:
- Total exercise intolerance, sympathetic activation, anxiety and confusion
- Exacerbation of pre-existing symptoms – severe fatigue, brain fog, food/chemical/medication/supplement sensitivities, constipation
- Neuropathy – pain, tingling, numbness in legs and feet.
- Minimal activity, short walks, occasional driving short distances, most time spent resting
Tests
- Microclotting confirmed by visual sample analysis
- Elevated Leukotiene 4 + typical symptoms suggests MCAS
- Reactivated EBV – elevated latent IFN-gamma, lytic IFN-gamma, lytic IL-2 (Infectolabs)
- Autoantibodies (Celltrends)
- Spike protein present in non-classical monocytes 5 months post-vax
- OATS – apergillus, clostridia, metabolic dysfunction
Research
We appear to have two happenstances cascading:
- Concussion
- COVID Shots – which build immunity by causing a reaction similar to COVID. This reaction includes some microbiome shifts.
Concussion
There is some literature here:
- Alterations to the gut microbiome after sport-related concussion and subconcussive impacts in a collegiate football players cohort [2022]
- Decrease in Eubacterium rectale [Agathobacter rectalis], and Anaerostipes hadrus
- Association of Blast Exposure in Military Breaching with Intestinal Permeability Blood Biomarkers Associated with Leaky Gut [2024]
- the plasma level of Zonulin was significantly increased after post blast exposure, indicating that blast may contribute to the impairment of the gut barrier in the paracellular pathway “
- Visceral hypersensitivity induced by mild traumatic brain injury via the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor: An animal model [2023]
- “Mild blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI) induces various gut symptoms resembling human irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) “
- Timing matters: Sex differences in inflammatory and behavioral outcomes following repetitive blast mild traumatic brain injury [2023]
- Repetitive blast exposure resulted in both similar (e.g., increased IL-6), and disparate (e.g., IL-10 increase only in females) patterns of acute serum and brain cytokine as well as gut microbiome changes in female and male mice. Chart is below
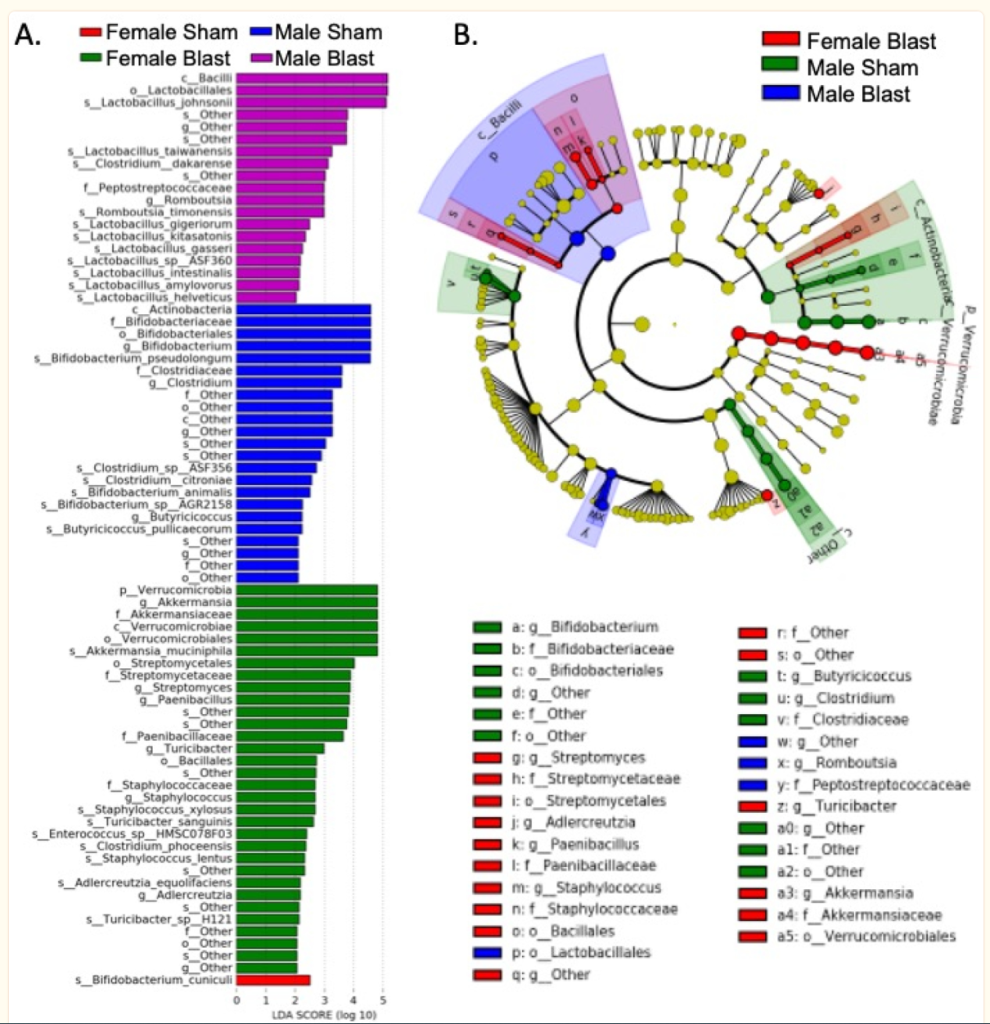
- Age matters: Microbiome depletion prior to repeat mild traumatic brain injury differentially alters microbial composition and function in adolescent and adult rats [2022]
- increased Clostridium innocuum and Erysipelatoclostridium
- reductions in Bacteroides and Clostridium Sensu Stricto
Reductions in Bacteroides have been associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) development and identified after stroke [87]. Bacteroides are imperative for the maintenance of intestinal barrier integrity, with supplementation being associated with increased tight junction proteins [88]. Reductions in Clostridium sensu stricto have been associated with reduced butyrate production and Alzheimer’s disease [89,90].
Age matters: Microbiome depletion prior to repeat mild traumatic brain injury differentially alters microbial composition and function in adolescent and adult rats [2022]
Treatment
- Involvement of Microbiome Gut-Brain Axis in Neuroprotective Effect of Quercetin in Mouse Model of Repeated Mild Traumatic Brain Injury [2023]
- “probiotic supplementation (Lactobacillus acidophilus or Clostridium butyricum) improved neurologic function.” [2022]
- ” Findings from this trial support the feasibility, acceptability, and safety of supplementation with an anti-inflammatory/immunoregulatory probiotic, Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938, among Veterans with PPC and PTSD symptoms.” [2020]
COVID Shots
Explicit studies are rare. What we do have is a variety of studies between high and low responder which enumerates the difference of bacteria. We do not clearly know which goes in any specific direction. We do know the bacteria that are likely to change.
- Association between Gut Microbiota Composition and Long-Term Vaccine Immunogenicity following Three Doses of CoronaVac [2024]
- increase of Eubacterium rectale, Collinsella aerofaciens, Streptococcus salivarius
- Gut microbiota composition is associated with SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunogenicity and adverse events [2022]
- Increases Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Prevotella copri, Megamonas
- Stability of gut microbiome after COVID-19 vaccination in healthy and immuno-compromised individuals [2024]
- Increase Akkermansia muciniphila in some cases, but in general no change
The high response group were primarily characterized by a predominance of Enterococcus faecium, Prevotella bivia, Actinomyces massiliensis, Veillonella dispar, Veillonella_sp_T11011_6, Eubacterium_sp_CAG_38, Ruminococcus torques, Actinomyces odontolyticus, while Alistipes putredinis, Allisonella histaminiformans, Bacteroides clarus, Clostridium lavalense, Clostridium asparagiforme, Bacteroides eggerthii, Coprobacter fastidiosus, Sutterella parvirubra, and Blautia coccoides are more abundant in the low response group
Plasma and urine proteomics and gut microbiota analysis reveal potential factors affecting COVID-19 vaccination response [2024]
Analysis
We have two results to work from: Biomesight report and an OATS (Organic Acid) report.
Looking at Forecasted symptoms we have a high rate of pattern matches. This is hopeful because it implies we now have strongly suspected bacteria.
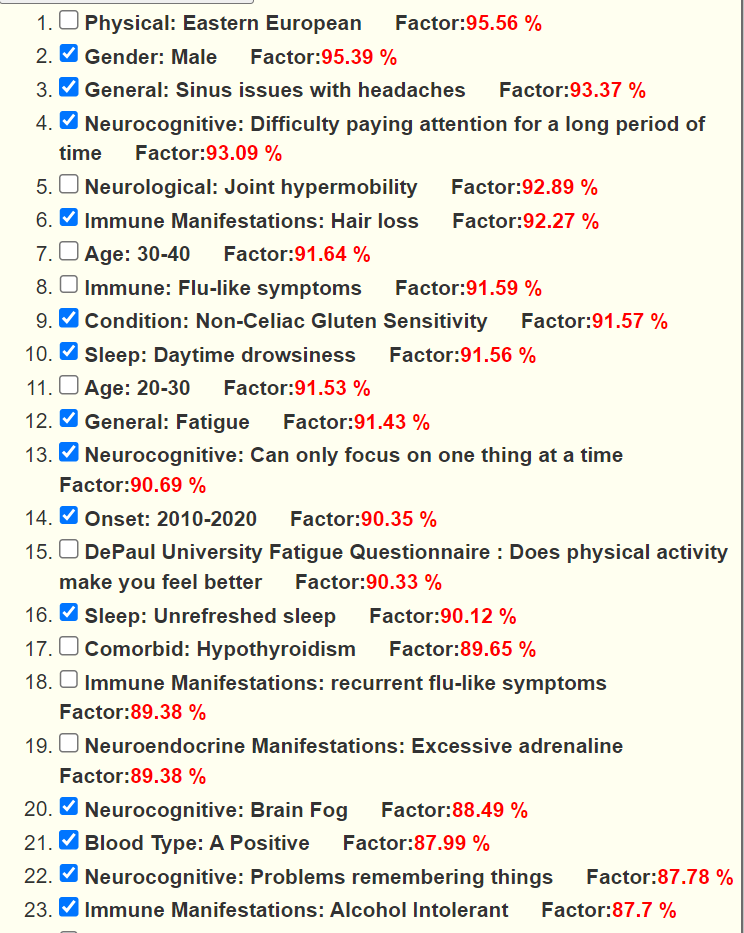
We also see a significant shift of bacteria that are atypically over represented.
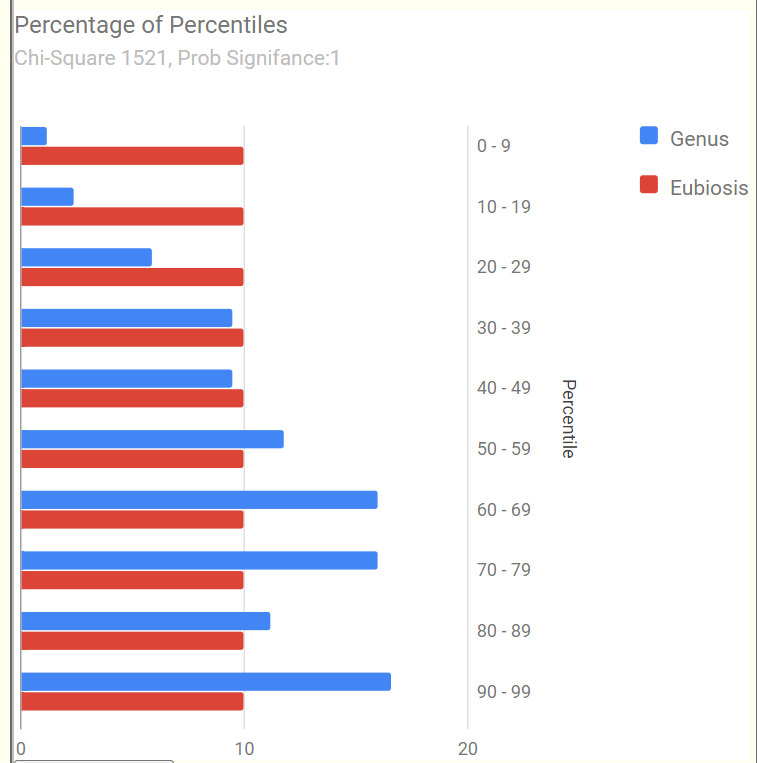
The reader noticed the dominance of some unusual bacteria (species and the genus they belong to). These amount to be 28.4% of the microbiome. These two bacteria usually average 3.5% of the microbiome.
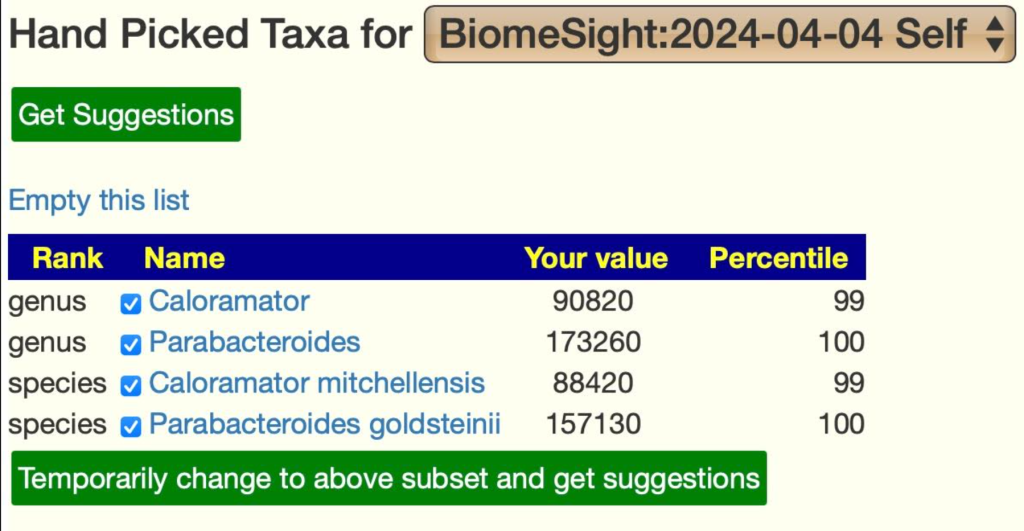
For Caloramator, the probiotics most documented to reduce are: lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus casei; fructo-oligosaccharides (prebiotic) (BUT inulin increases).
As a starting point, we will do [Just give me Suggestions include Symptoms]. Since we have some condition specific suggestions above, let us see where they rank.
- quercetin,resveratrol: 297; quercetin: 123
- clostridium butyricum (probiotics),Miya,Miyarisan: 187
- lactobacillus acidophilus (probiotics) : 67
- lactobacillus reuteri (probiotics): 96
This type of cross validation is nice to see — everything known to help TBI/concussion is in the recommended to take list. It builds confidence in the suggestions being generated.
The next thing is to see which of the bacteria shifts cited in the above literature. We go over the the Bacteria tree. We filter out those not usually reported by Biomesight and ended with just one (which illustrates the benefit of shot-gun tests).
- reductions in Bacteroides: was at 32%ile
Other incidental measures of note:
- Anti Inflammatory Ratio: 20% (so inflammation is likely)
Other Issues
Last, do we see Staphylococcus aureus in the sample? No.
Elevated Leukotriene E4 (LTE4) is an accepted indicator of Mast Cell Activation Syndromes, see Diagnosis, Classification and Management of Mast Cell Activation Syndromes (MCAS) in the Era of Personalized Medicine[2020]. I will look at LTE4 only and not the much bigger MCAS. LTE4 depends on 5-lipoxygenase (EC:1.13.11.34) [ Leukotrienes and inflammation [1990]]. This gives us some possible paths to explore:
- Natural anti-inflammatory products and leukotriene inhibitors as complementary therapy for bronchial asthma [2010]
- Boswellia serrata, Curcuma longa and Glycyrrhiza (AKA Boswellia, Tumeric, Licorice)
- These are also cited in Efficacy of Herbal Medicines on Lung Function in Asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[2023] with additional atypical herbs.
- Effect of plasma α‐tocopherol on leukotriene E4 excretion in genetic vitamin E deficiency – Kohlschütter – 1997
- LTE4 excretion proved inversely correlated to plasma α-tocopherol levels.
- Modulation of the endogenous leukotriene production by fish oil and vitamin E
Unfortunately, there are no reported bacteria associated with 5-lipoxygenase (EC:1.13.11.34) . What we find is:
- Targeting Mammalian 5-Lipoxygenase by Dietary Phenolics as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism: A Systematic Review (mdpi.com)
- “Some (poly)phenolics such as caffeic acid [found in Barley, Coffee], hydroxytyrosol [from Olive Oil}, resveratrol, curcumin, nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) [TOXIC ISSUES], and quercetin have been reported to reduce the formation of 5-LOX eicosanoids in vitro”
- From Suggestions:
- caffeic acid [found in Barley:266, Coffee:87],
- hydroxytyrosol [from Olive Oil: 207 / 173, olea europaea,olive leaf: 98],
- resveratrol:55,
- curcumin: 291,
- quercetin: 135
Again, we have cross-validations happening, i.e. the expert system suggestions and clinical studies are in agreement.
OATS Tests
Next we see what the OATS results produces. Only one was out of range where we have data
- (S)-Malate was to high
I should point out that something is very funky with the OATS report. Every value below is within their declared range but their graphics show it is out of range.
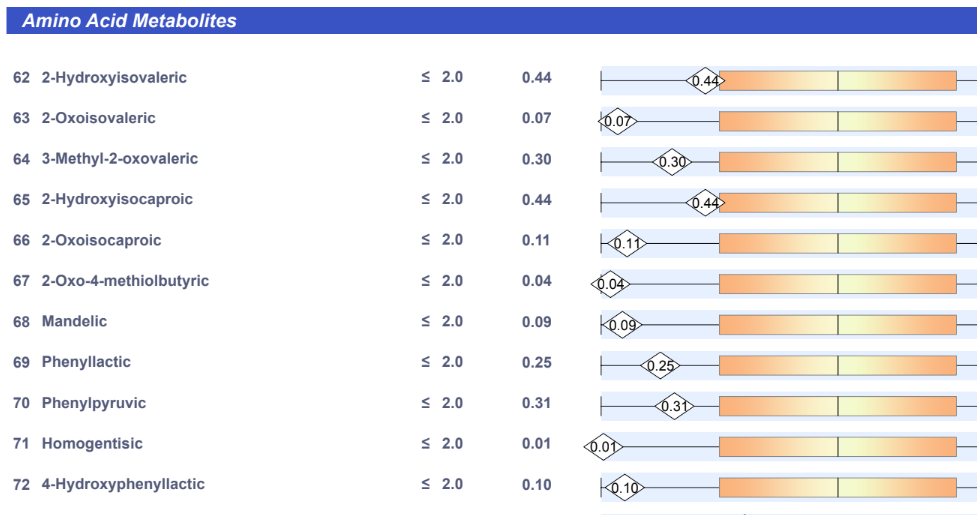

The result was 326 probiotics — specifically, probiotics that are known to consume Malate. We have no significant additions.
Action Plan
First item of note, above we have 100% cross validation on what the fuzzy logic expert system says should help with clinical studies of what helps given his particulars. This hints that other suggestions are far more likely to help than hurt.
The easy set of suggestions are quercetin, clostridium butyricum (probiotics),lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus reuteri (probiotics) because they are double recommended: both clinical studies and the microbiome. Since with this history, getting any prescription drugs is unlikely, the consensus suggestion leads me to consider the following (filtered for availability etc):
- Probiotics (no more than 2 at a time, and rotate to different ones every 2 weeks)
- lactobacillus casei
- bifidobacterium animalis lactis
- lactobacillus paracasei
- lactobacillus rhamnosus gg
- mutaflor escherichia coli nissle 1917 (if available)
- bifidobacterium longum
- lactobacillus brevis
- clostridium butyricum
- lactobacillus plantarum
- If possible, get single species OR mixtures containing ONLY the above.
- Supplements:
- Hesperidin (polyphenol)
- luteolin (flavonoid)
- quercetin
- Vitamin B-12
- Vitamin B1,thiamine hydrochloride
- selenium
- chicory (prebiotic)
- mastic gum (prebiotic)
- Bromelain
- N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC),
- Diet and Food
- high-fat diets / high-saturated fat diet
- whey
- garlic (allium sativum)
- thyme (thymol, thyme oil)
- rosmarinus officinalis,rosemary
- sorghum
- grapes
- Cacao
- whole-grain barley
- Take Far infrared Sauna if available
Ideally, the reader will use all of the details and avoid all of the negative values ones if possible

The high-fat diets / high-saturated fat diet suggestion takes a little figuring. I deduce that being high in fat from:
IMHO, This is the general problem with diet data — they contain vast baskets of substances: some good and some bad; with a wide variety of definitions. I prefer working substance by substance.
Retest
I would suggest a retest with Biomesight in 3 months (if the reader consents, I would be glad to do a follow up post). Remember these are not generic suggestions for anyone with a concussion but based on the individual’s microbiome with cross referencing to the literature to develop a clean consensus of what may help.
Questions and Answers
Q: What does with “Symptoms” mean?
- Using “With Symptoms” uses the bacteria associations found from donated samples (i.e. see Citizen Science Symptoms To Bacteria Studies (microbiomeprescription.com))
- Ideally, the user will do the time consuming process of checking the suggestions against the literature (which I did above for illustration).
- There is NO direct linkage using studies of symptoms to supplements by the engine. That is technically possible, but would require major funding to hire qualified people to enter the data.
- Experience have found that 85-95% of suggestions that has studies for a conditions are in agreement.
Q: Do you use studies on my conditions to pick bacteria?
- If there are sufficient studies, then yes. In your case there is not. Clinical studies on conditions often have contradictory results for a vast number of reasons: the lab and software used; the diet of the people in the studies; often low significance (often P < 0.05 is cited, with our lab specific analysis we typically use P < 0.001 as a criteria).
Q: The high Bilophila on my Biomesight got my attention. Is that something that MP.com does not identify specifically to address but rather it just corrects as part of the overall microbiome rebalancing?
- MP does a holistic analysis — so things that may reduce Bilophila but also shifts others bacteria in the wrong direction may be eliminated.
- “The typical MP matrix to solve is around 60 taxa (up to 430 in some cases) by 2092 possible modifiers – thus an array of some 12,000 to 800,000 elements to consider. The Monte Carlo method typically uses 5 runs resulting in 60,000 to 4,000,000 elements evaluated.” [blog]
Q: The prebiotic that shows up as #1 rec for me is Prefor Pro, but you have chicory. Is that due to availability?
- The retailed probiotic selection is based on the species in the probiotics ignoring additives and relative amounts (often not declared). If there are issues with these additives, then just move down the list.
Q: Do you think using the condition specific bacteria shifts is a better approach than the bacteria identified by the AI as “likely to be causing my symptoms”?
- Definitely, my observations from feedback is that targeting those bacteria do moderate or eliminate symptoms.
Postscript – and Reminder
I am not a licensed medical professional and there are strict laws where I live about “appearing to practice medicine”. I am safe when it is “academic models” and I keep to the language of science, especially statistics. I am not safe when the explanations have possible overtones of advising a patient instead of presenting data to be evaluated by a medical professional before implementing.
I cannot tell people what they should take or not take. I can inform people items that have better odds of improving their microbiome as a results on numeric calculations. I am a trained experienced statistician with appropriate degrees and professional memberships. All suggestions should be reviewed by your medical professional before starting.
The answers above describe my logic and thinking and is not intended to give advice to this person or any one. Always review with your knowledgeable medical professional.
Recent Comments