This is a part of an ongoing series of posts that are intended for microbiome testing labs, or those interested in starting one. I am downstream from all of the microbiome labs and will gladly work with any of them — my main concern is making people better — not the financial bottom line.
This post looks at issues involved with selecting studies to use for giving suggestions to consumers of microbiome result. These are questions that I have looked at and have made my own choices (a.k.a. technically trade secrets).
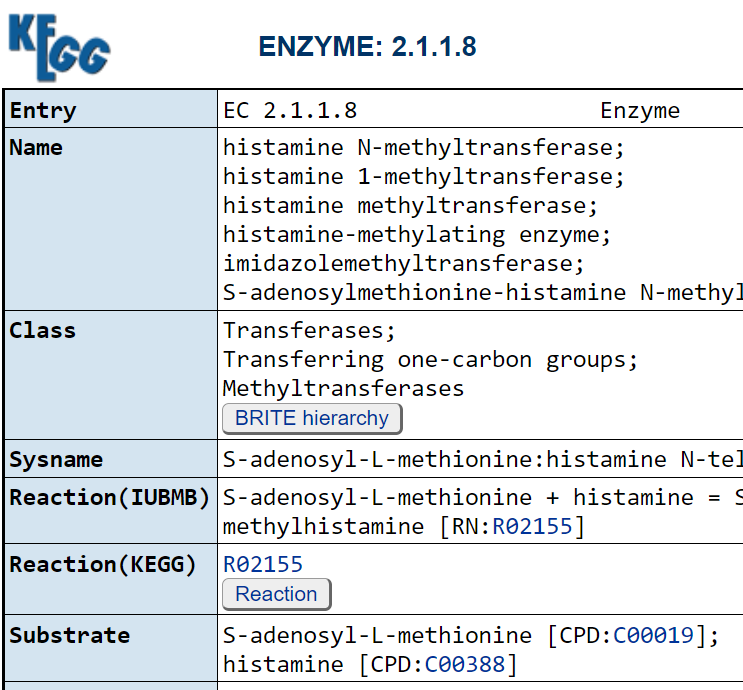
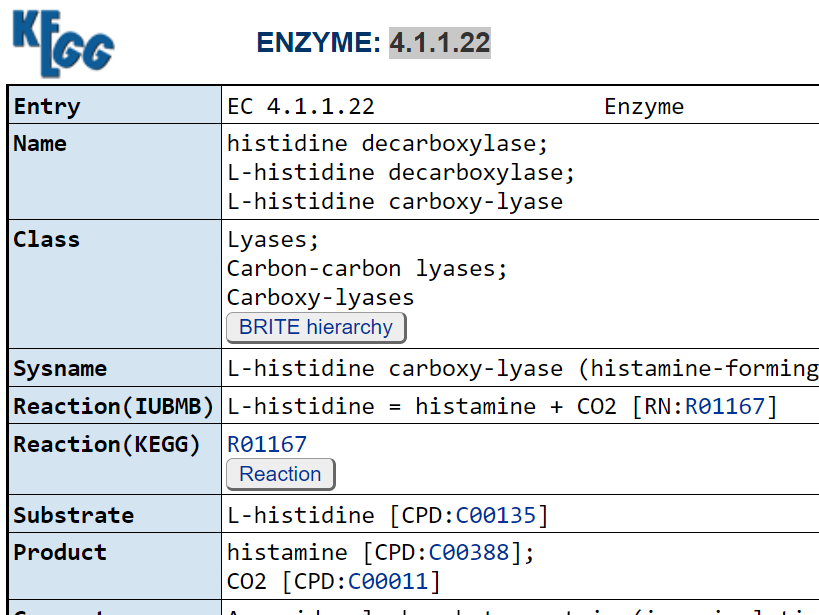
Method of microbiome detection used
There are three main types, listed below. Do you restrict to only one? Do you give a weight to different methods, for example the values suggested after each below?
- Cultured Sample – Weight 0.1
- 16s Sample – Weight 0.8
- Metagenomics – Weight 1.0
For a discussion of the last two, see Comparison between 16S rRNA and shotgun sequencing data for the taxonomic characterization of the gut microbiota [2021]
Life Form/non-form that the study was done on
We have a wide variety of “bacteria incubators” reported in studies, including
- Fish (Zebra fish especially)
- Animals – which ones? Horses, Dogs, Cats, Cows, Pigs etc
- Chemical Reactors simulating some living creature’s environment
- Humans
- Which ethnic groups
- Location that the study was done (a proxy for diet) — different results from Mexico and Japan!
- Age — children, adults and the elderly have different responses
- Medical conditions in the cohort
Do you do a binary include/exclude or do you apply a weight to each?
Quality of Study
The following are commonly used in evaluating studies:
- Read Beyond the Abstract – that means getting and reading the full study, including the appendix
- Determine Whether All Results Were Included
- Observational Study versus Randomized Controlled Trial
- Odds Ratios and Confidence Intervals
- Size of study
Do you give different weights based on the above? Some literature is below:
- Understanding and evaluating clinical trials
- A General Framework for the Evaluation of Clinical Trial Quality
- A Simple Method for Evaluating the Clinical Literature
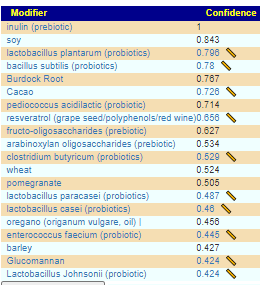
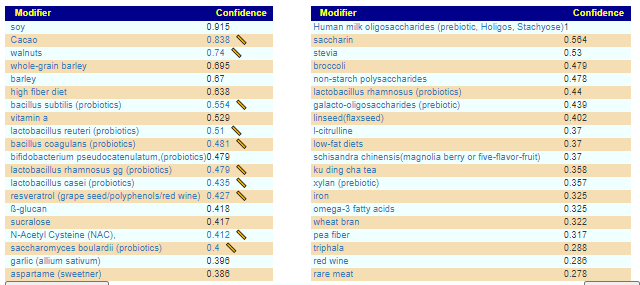
Interpreting Studies
Different studies report things differently. For example some may report the % change of a bacteria average, others may provide the actual distribution, others may just report that the control or the cohort average was higher with (P < 0.5). It is like trying to buy gas – one person is offering it by the gallon in US$, another in litres in Euro, a third “sufficient fuel to drive 200 miles in a 1958 Land Rover” for 3 oz of silver.
Method of Aggregation
Some studies use the Hartung–Knapp–Sidik–Jonkman random effects model [2021] to combine results. Other studies use DerSimonian-Laird method (cited by Cochrane) or The generic inverse variance outcome type in RevMan.
Bottom Line
I have my own magic in combining a multitude of studies and resolving the many many issues cited above. I encourage labs to do their own resolutions and then let people compare results (if they are in agreement, everyone should be happy). The real test is whether the suggestions work. So far, for my own experience and for a reasonable number of people that have provided feedback – they have. The suggestions may not be perfect, but my goal is to give suggestions that are more likely to help.






Recent Comments